NASA is set to launch two rockets into the atmosphere this October, and it’s sure to be an incredible sight! The two rockets, named Terrier-Improved Malemute and Black Brant IX, will be launched from the Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, and will be visible along the East Coast of the United States. The Terrier-Improved Malemute will fly for two and a half minutes, while the Black Brant IX will fly for six minutes, reaching an altitude of about 129 miles.

A recent study by researchers at the University of California, Davis, has revealed a new enzyme that could potentially boost the production of soybean oil by up to 20%. The enzyme, called a lipoxygenase, catalyzes the conversion of soybean oil to a biologically active form of omega-3 fatty acids, which could provide a wide range of benefits to the food and medical industries. The research team is now working on ways to increase the enzyme’s efficiency and potential uses for the converted oil, which could potentially revolutionize the soybean industry.

A new study has discovered that three supernovae explosions, which occurred between 2.3 and 8.7 million years ago, sent shockwaves all the way to Earth. Scientists analyzed the chemical composition of deep-sea sediments, and determined that the supernovae were located between 140 and 300 light-years away, making them close enough to have caused significant harm. This finding is the first evidence that supernovae explosions can cause serious damage even from such distances.

A new treatment to combat a hospital-acquired superbug has been discovered by researchers at the University of California. This potentially life-saving treatment, which has been tested on mice, has been identified as a combination of two existing antibiotics. In clinical trials, the combination of the antibiotics showed a dramatic reduction in the number of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria. MRSA is a dangerous superbug that is highly resistant to antibiotics, and is easily spread in hospitals.

In a revolutionary leap forward for space communications, a fleet of massive Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites is being launched into space. This move marks the beginning of a new era of global internet access, with the potential to bring people in remote regions of the globe into the modern age. The satellites will be able to provide high speed, low latency connections to broadband internet, which is currently not available in many rural and impoverished parts of the world.

Two centuries after the discovery of the first bacteria, scientists have discovered what they are calling an “evolutionary gateway” to the pneumonia-causing bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. This discovery marks a major breakthrough in understanding the evolution of this common and potentially deadly bacteria.
In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers from the UK, US, and Canada have identified a genetic mutation that has enabled S. pneumoniae to evolve from a harmless organism to one that can cause severe and sometimes fatal infections.
SpaceX is continuing its impressive streak of successful orbital launches. Earlier this week, the company launched its 69th orbital flight of the year, setting a new record for most orbital launches in a single year. The launch, which sent a Falcon 9 rocket into space carrying a Dragon spacecraft, marks a major milestone for SpaceX and its mission to revolutionize space travel. It also marks a significant step forward in the company’s long-term goal of enabling humans to explore and inhabit other worlds.

The Nobel Prize in Medicine is one of the most prestigious and coveted awards in the world, and the announcement of the winner is always highly anticipated. This year is no different as the Nobel Prize in Medicine is currently underway and is set to be unveiled soon. This year’s Prize is particularly special, as it marks the centenary of the Nobel Prize in Medicine, which was first awarded in 1923.

We’ve all been there: cramming for a big exam the night before. We try our best to stay up late, highlight bits of the text, and hope for the best. Unfortunately, recent research has shown that this strategy of highlighting bits of text is ineffective for learning and retaining information.
Dr. Monty McKeon from the University of Virginia conducted a study of college students and found that highlighting bits of text had no effect on how well the students remembered the information.

Recently, scientists have made a new discovery in the field of astrophysics. It was found that when two white dwarf stars collide, they can form a much denser object known as a dark star. Dark stars are made up of an even mix of matter and anti-matter, and when they collide, they annihilate each other and emit a burst of energy. This discovery could help to explain the mysterious bursts of cosmic energy that have been detected in space.

Forensic science has been revolutionized by the advent of new methods of firearm identification. For the first time, investigators are able to quickly and accurately identify firearms used in crimes and gather evidence from them. This breakthrough has led to a huge increase in the accuracy and speed of criminal investigations, leading to better outcomes for victims and their families. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the new forensic science method of firearm identification and how it can be used in criminal investigations.

A recent study from Australia has revealed the critical role social media can play in helping to understand the true scale of bushfire events. The study used data from over 1.3 million tweets to analyze the scale of bushfire events in Australia during the 2019/2020 season, and the results are quite remarkable. The research found that using tweets to measure the area of affected land was more accurate than traditional methods like satellite imagery.
Scientists have developed a new instrument for planet-hunting that can be mounted on a large telescope. The instrument, called a “planet imager,” is capable of detecting planets around nearby stars by taking direct images of them. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we look for planets outside our solar system.
The planet imager is the result of a joint effort between researchers from the University of Arizona, the Space Telescope Science Institute, and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan.

This week, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery that could have major implications for soil health. Through an analysis of soil samples, they have found that viruses can interact with bacteria in major ways, allowing for the exchange of genetic material and even the transfer of microbial genes. This means that viruses could be playing a role in shaping the composition of soil microbial communities, providing an important contribution to soil health.

A recent study conducted by a team of researchers from the University of Tokyo has revealed an unprecedented link between gamma ray bursts (GRBs) and supernovae (SNe). The team’s findings, which were recently published in Nature Astronomy, suggest that GRBs and SNe are actually produced by the same type of stellar explosion, a binary neutron star merger. This is exciting news for astronomers, as it could help us to better understand the formation and evolution of some of the most powerful events in the Universe.

A recent study has revealed groundbreaking discoveries in the field of cell biology. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have discovered that cell walls play a critical role in determining the mechanical properties of a cell, which in turn affects its ability to divide. This could have implications for the development and progression of diseases such as cancer, and could lead to new ways to treat and prevent them.
Space exploration has come a long way, and now scientists are set to unlock some of the secrets of asteroids. In a new project, a team of researchers have been able to get a better understanding of how asteroids form, and how they interact with the Sun. By studying the composition of asteroids and their orbits around the Sun, the team hopes to gain insight into the formation of the Solar System.

The universe is expanding at an ever-increasing rate, and a recent study has found that the collision of two neutron stars may be to blame. This exciting new discovery may provide insights into the mysterious nature of dark energy, which is thought to be responsible for this accelerated expansion. The study, conducted by researchers at the University of Cambridge, suggests that the collision of two neutron stars releases a powerful force which pushes the universe apart.
In recent years, experimental biologists have been exploring new approaches to understanding the structure and function of cells. A new study published in the journal Nature has revealed a promising new technique for investigating cell states in an effective and efficient manner. This method, known as “experimental cell state analysis,” uses genetically engineered fluorescent proteins to identify and measure the activity of individual cell states in real time. The proteins are attached to individual cell components, allowing researchers to track the activity of the cells.
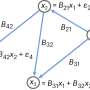
Cell biologists have long puzzled over the precise roles and interactions of different organelles within mammalian cells. In a recent breakthrough, researchers from the University of Florida have unlocked key insights into the inner workings of these intricate cellular environments. By leveraging advanced microscopy techniques, the team was able to observe and quantify the dynamic behaviors of organelles within living cells. This new understanding of the organelles’ dynamics could help inform drug design and medical treatments for a variety of diseases.
Scientists have recently conducted simulations that tell an atomic-scale story of how qubits interact. These simulations offer a deeper understanding of how qubits could be used to build powerful quantum computers. The simulations used the world’s fastest supercomputer, Summit, to study the interactions of millions of atoms and electrons in qubits. The study revealed that the behavior of an individual qubit is simple, but the behavior of multiple qubits interacting is extremely complex and not as easily predicted.
A new discovery by scientists at the University of California, Santa Barbara has revealed the possibility of creating ultra-strong colloidal crystals using DNA nanostructures. The team found that DNA nanostructures, when combined with colloidal particles, can create an incredibly strong and robust material with a range of potential applications. This breakthrough could pave the way for the development of more efficient and durable materials in the near future.
The research team was able to create 3D DNA nanostructures with colloidal particles using a technique called “DNA-mediated self-assembly”.

Recently, scientists have made an exciting breakthrough in understanding anion exchange systems. A team at the University of Science and Technology of China have discovered that the introduction of multi-cations to anion exchange systems can contribute to anion exchange.
This breakthrough is important for understanding how an anion exchange system works, and could potentially lead to new applications in areas such as energy storage, water purification, and drug delivery. The team’s findings suggest that the introduction of multi-cations may increase the capacity of anion exchange systems and make them more efficient.
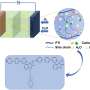
Today, an international team of researchers have unveiled the non-coding RNAs present in wheat grain, a breakthrough that could lead to greater crop yields and improved grain quality. Non-coding RNAs are a type of RNA molecule that does not code for proteins. They have been linked to a variety of important biological processes, including regulation of gene expression and metabolism. The team used a combination of computational and wet-lab approaches to identify and characterize these non-coding RNAs in wheat grain.
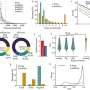
In a groundbreaking study, scientists have discovered a potentially new type of magnetotactic bacteria that could revolutionize astrobiology. This new bacteria, which has been dubbed “Renaissance”, has the potential to survive in extremely harsh environments, such as those found in space. This discovery could have a major impact on our understanding of life in space and its potential to exist on other planets. The findings of this research suggest that magnetotactic bacteria could be a key component of astrobiology, and could even be used to help explore extraterrestrial worlds.