
Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery about two spiral galaxies merging together: within the chaotic jumble of stars, gas, and dust, the galaxies are still preserving their spiral shape. This is the first time that such an orderly arrangement has been observed during a merger, challenging current theories about how merging galaxies form. The research team, led by Dr. Marc Freitag, used the Hubble Space Telescope to observe the galaxies in detail, and their findings provide an important insight into the process of galactic evolution.

A new study from researchers at Harvard has uncovered a link between cell biomechanics and wound healing. By using advanced imaging techniques, the researchers were able to track how cells move and interact in response to an injury. The team found that the cells responded differently depending on their stiffness: stiffer cells moved faster and interacted more intensely with the injury site, while softer cells moved more slowly and had less intense interactions.

As the world rapidly changes, so too does the employment landscape. A recent study has identified 10 key trends in employment that are likely to shape the future of work. Among the most interesting findings is the rise of employment opportunities related to microbiomes and forests.
Microbiomes are the communities of microorganisms living in and on our bodies and in our environment. The study found that jobs related to the study and management of these microbiomes are expected to increase, as more and more research is conducted into their role in human health and the environment.

Recently, a team of researchers have proposed a new way of exploring the surface of the moon. They intend to make it easier for astronauts to explore the moon by creating “easy trails” on its surface. The trails would be made by small robotic vehicles that would drive around the surface of the moon and create pathways that would be easy for astronauts to follow. These pathways would be built on the surface of the moon using lunar soil, allowing astronauts to travel to previously inaccessible places with ease.

Autophagy, the process by which cells break down and recycle their own components, has been found to play an essential role in the survival of cells that have lost their DNA. This finding was made in a study conducted by researchers at the University of York, and published in Nature Communications.
The team of researchers discovered that autophagy is able to rescue cells that have lost their DNA, allowing them to survive and even divide.

A recent breakthrough in research has provided insights into the respiratory system of the fruit fly. Scientists at the University of Montreal have identified a gene defect in fruit flies which affects the development of their respiratory system. This discovery could have implications for the treatment of respiratory diseases in humans. The research team found that the gene, called “Nano,” is responsible for the formation of a protein called TRPV1. This protein helps regulate the electrical signals in the fly’s respiratory system.
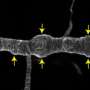
A new study by scientists from the University of California, Davis has revealed new genomic insights into the evolutionary history of plants. Through an analysis of thousands of genomes, the research team was able to trace the history of plants back to their ancient ancestors. The findings provide a better understanding of the evolution of plants that may inform future studies of plant biology. The team also identified new gene families in plants that may be key to their adaptation to changing environments.
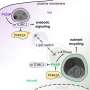
Today, scientists have discovered that lysosomes are much more than just the cell’s garbage cans. Using advanced imaging techniques, researchers have found that lysosomes are actually quick-change artists, adapting to different types of nutrients and providing essential nutrients to the cell.
Lysosomes are organelles found in most eukaryotic cells, and they have been thought of as the cell’s garbage cans for a long time. But now, researchers have found that lysosomes have much more complex roles in the cell than previously thought.
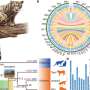
In a recent study, researchers have discovered that communication technology and infrastructure can have a significant impact on math skills. The study, which was conducted by the University of California, Davis, found that students who had access to computers and other digital learning resources showed higher levels of math achievement than those without access. Furthermore, the study found that students with access to digital communications tools like email and chat were better able to collaborate with their peers and receive feedback from their teachers, which helped them to better understand mathematical concepts.

NASA is taking a revolutionary step in space exploration technology with its new LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) system. The system works by using laser light to measure distances and can detect objects up to several kilometers away. This new technology will allow NASA to explore deeper into space than ever before, and it is expected to enable more accurate and efficient navigation for spacecraft. The LIDAR system also has potential applications in planetary exploration, where the system could be used to map the terrain of far-off planets and moons.

NASA is preparing to launch its first rocket, the Vulcan Centaur, in December 2023. This rocket is said to be the most powerful rocket ever built and will be capable of launching payloads up to 44 metric tons, more than twice the capability of the current most powerful rocket. This is an incredible achievement and will be a huge step forward in space exploration. The Vulcan Centaur will be used to explore the depths of space, launching satellites, space probes, and other payloads into orbit.

We’ve all heard about the negative environmental impact of disposable diapers, but a new innovation could be about to change all that. According to a recent report, a new technology is being developed that could enable diapers to be recycled in as little as 10 minutes. This could revolutionize the diaper industry, making it much more environmentally friendly and reducing the amount of waste produced. Plus, it would also make diaper changes much faster and easier for parents.

Europe’s Ariane 5 rocket is getting ready for its next mission, and it’s doing something a little unusual: rehearsing for its flight in the middle of the night. Last week, the rocket fired its main engine in a nighttime practice session, the first time such a test has been conducted for an Ariane 5 rocket. The rehearsal was a success, and it sets the stage for the launch of the rocket on October 20th.

It’s now 2023, and the world is taking a big step forward towards protecting whistleblowers. A new law has just been passed that rewards individuals who report wrongdoing in the workplace. This is a major breakthrough in protecting those who have the courage to speak up and shed light on unethical practices. The law is designed to protect whistleblowers from retaliation and offer them financial incentives for their efforts. This law is expected to have a positive effect on the workplace, encouraging more people to report unethical behavior.

“Scientists have made a breakthrough in the field of synthetic biology, developing a new method to custom-design the genome of a wild grass species. The new method could have implications for the development of greener, more efficient crops.
Led by researchers from The University of Queensland, the team used their new genome-editing approach to modify the genome of sheepgrass, a wild grass species that can be found in Australia. The process involved manipulating the plant’s genetic code to make it more resistant to drought, disease, and pests.

Scientists have developed the highest resolution single-photon superconducting camera to date. This camera is capable of imaging with a resolution of up to 2048 x 2048 pixels and can detect single photons with a temporal resolution of 125 ps. This new camera is a breakthrough in imaging technology and has the potential to revolutionize the field of imaging science. It is expected to be used in a variety of applications, from medical imaging to astronomical observations.

Scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery about what lies beneath the surface of Mars. After analyzing seismic data from two NASA spacecraft, they have determined that the core of the planet is composed of a molten layer. This molten layer is estimated to be around 180 km thick and is thought to be composed of a mixture of iron, sulfur, and nickel. This discovery has implications for the planet’s past and present, as it could suggest that Mars once had a magnetic field and is possibly still active today.

For the first time, researchers have successfully used a new technique to crunch the data of the mysterious Phoebus asteroid. This newly discovered asteroid, located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, was first detected in 2019. The data collected from this asteroid showed a unique chemical composition, prompting the researchers to investigate further.
Using the new observational technique, the researchers were able to identify the physical and chemical properties of the asteroid.

In a study published in Science Advances, scientists have uncovered a key player in photosynthesis - chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are tiny organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy. This process, known as photosynthesis, is essential for life on Earth. The research team found that the chloroplasts are able to sense light and respond to it, allowing them to move around and optimize the light they receive.

A new report released by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has revealed that, despite the efforts of conservationists, illegal wildlife trafficking is still a major threat to global biodiversity. The report found that China is the primary destination for illegally poached wildlife, with an estimated 50% of all illegally trafficked wildlife products ending up in China. The report also highlighted the need for greater international cooperation to prevent the illegal exploitation of wildlife, noting that China is the largest consumer of wildlife products in the world.

It’s official: West Greenland has experienced its hottest summer on record. According to a new report from the Danish Meteorological Institute, temperatures in the country were 2.2 degrees Celsius (3.96 degrees Fahrenheit) higher than normal throughout the summer. This is the highest temperature West Greenland has experienced since records began in 1900.
This past summer was a scorcher in West Greenland! According to a new report from the Danish Meteorological Institute, temperatures in the country were a whopping 2.

It’s a fascinating new development in the history of the Caribbean region: archeologists have discovered evidence of a pre-Hispanic immigrant population in the area that today is modern-day Cancun, Mexico. While the Maya have long been known to have lived in the region, this new evidence suggests that immigrants may have settled in Cancun as long ago as the 10th century. The evidence has been found in the form of artifacts such as ceramics and stone tools, as well as DNA analysis of human remains found in two burial sites in the region.

In recent years, there has been an alarming increase in the presence of heavy metals in shellfish harvested from coastal areas. Specifically, shellfish harvested from estuaries, tidal creeks, and open waters have been found to contain substantial levels of lead, cadmium, mercury, and arsenic. These heavy metals can be extremely hazardous to human health and can cause long-term health issues if ingested. As a result, traditional shellfish harvesting has become an increasingly dangerous activity.
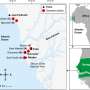
Scientists have recently discovered a groundbreaking new discovery about the core of Mars. After conducting a series of detailed simulations, they have concluded that the planet’s core is much smaller than previously thought. This suggests that the core of Mars is composed of liquid iron, rather than the solid iron previously believed. This new understanding of the planet’s core has implications for our knowledge of its evolution and could provide insight into how other planets in the solar system formed.

Today marks an incredible milestone for the UK space industry: the launch of a brand new space mission firm, UKSPACE. This firm will be focused on creating and launching world-class space missions, with a particular emphasis on exploration and discovery. This is the first such venture in the UK and will be the first of its kind in Europe. UKSPACE aims to create cutting-edge technology that will revolutionize the way we explore our universe.

