
A new study has found that some microbes have evolved to survive antibiotics, which could have serious implications for the future of human health. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, studied the genomes of hundreds of different microbes and discovered that some of them have adapted to survive in the presence of antibiotics. This means that even if an antibiotic is used, the microbe may still be able to survive, potentially leading to more antibiotic-resistant infections.

NASA is gearing up for one of its most ambitious missions yet: a revolutionary space telescope that will take us to the edge of the universe and beyond! The James Webb Space Telescope, set to launch in 2023, will be the most powerful telescope ever built. It will be able to observe a million galaxies, which is 10 times the number of galaxies ever observed before. This incredible feat will allow us to explore the most distant and ancient galaxies in the universe, giving us a clearer view of the very earliest stages of galaxy formation.

Chemists have made a major breakthrough in the field of synthetic biology! For the first time ever, scientists have used advanced imaging techniques to image the “building blocks” of synthetic molecules. This is a huge step forward in our understanding of how molecules are put together and will pave the way for more precise control over the design of new molecules. This could lead to advances in the development of new drugs, materials, and other products.
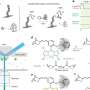
Recent advances in medical technology have opened up new possibilities for using DNA in medicine. In a recent study, researchers at the University of California, San Diego have explored the limits of DNA function in medicine. The study found that, while DNA has the potential to be used in diagnostics, gene therapy, and other medical applications, its use is limited by the fact that it is relatively difficult to manipulate at a molecular level.
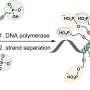
Innovations in gas technology are expanding the possibilities for what we can do with natural gas. A new study has recently revealed that the limits of gas technology may be much further than previously thought. Scientists at the University of Cambridge have developed a new model that shows that the potential of gas technology is far greater than what we previously believed, allowing us to create more efficient and effective uses of natural gas.
Recent research has found that mysterious swirls that can be found on the Moon’s surface are linked to its topography. The swirls, which appear as light and dark patches on the Moon’s surface, have long been a fascinating feature to astronomers and the public alike. Now, scientists have used data from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter to investigate their origin. The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, revealed that the swirls are related to the topography of the Moon, specifically its elevation, slope, and texture.
Recently, scientists have uncovered a new and exciting finding in the search for exoplanets that could be potentially habitable. They have discovered a new type of exoplanet, known as a subglacial classical habitable zone (SCHZ) exoplanet. These planets are similar to Earth in size and mass, and also have the potential to harbor liquid water on their surfaces. This is an exciting finding, as it opens up the possibility of finding more Earth-like planets in our galaxy.

Have you ever wondered how the universe works? Scientists have been trying to answer this question for ages, and now, there’s a new tool they are using to help them understand the complexities of the cosmos: slime mold. In a recent study, scientists used slime mold to simulate the movement of galaxies, and the results were remarkable. By studying the behavior of slime mold, scientists were able to gain insight into the underlying physics of the universe.

Earthlings have long speculated what the night sky would look like on the red planet. Now, researchers from the University of Arizona have determined that the visible range of light on Mars at night is much brighter than previously expected, suggesting that the night sky would be a beautiful and unique sight to behold. The research team used a combination of numerical models and data from the Curiosity rover to map the different wavelengths of light reflected throughout the Martian night.

NASA’s Juno mission to Jupiter is getting ready for its next big milestone: a daring dive through the planet’s dense atmosphere. On November 11, 2023, Juno will penetrate the planet’s low-density outer layers, and travel down to the heart of its powerful magnetic field. As the spacecraft plunges deeper into the atmosphere, it will measure the strength of Jupiter’s magnetic field, and take detailed measurements of its composition and structure. The mission will also provide us with the first direct measurements of Jupiter’s interior, allowing us to better understand the planet’s evolution and formation.

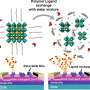
Today, a new authentication method for the identification of edible oils and fats has been developed. The method uses sitosterol, an abundant plant sterol, as a marker to detect and differentiate between different types of edible oils and fats. The method is based on the determination of the sitosterol content in edible oils and fats, and on the comparison of the results with the reference values obtained from a library of edible oils and fats.
Today, groundbreaking research has led to a major scientific breakthrough in the field of genetics. Scientists have successfully created a chimeric monkey embryo, which they hope one day could lead to the generation of live births. This achievement marks the first time this has been accomplished and could open the door to many potential applications, including the development of new treatments for human diseases. By combining cells from two distinct monkey embryos, scientists were able to create a single embryo that contains genetic material from both sources.

A new study conducted by the New York State Department of Agriculture indicates that the use of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides is increasing in the state. According to the study, the amount of these chemicals used in the state has more than doubled in the last decade. This is concerning for the health of residents, as these chemicals can have a number of negative impacts on human and environmental health. The study also found that the majority of these chemicals are used on crops such as corn, soybeans, and apples.

In the future, microbial cell factories are expected to provide a cost-effective way to produce drugs, biofuels, and other valuable products. Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a new simulation technique that can help speed up the process of designing and optimizing these microscopic workhorses.
The new method, known as the Metabolic Network Simulation (MNS), allows scientists to quickly and accurately simulate the metabolic pathways of microbial cell factories.
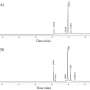
Astronomers have recently made a groundbreaking discovery: a Milky Way-like galaxy in the early universe. This is the first time that a galaxy this large has been observed so far back in time, and it provides new insight into how galaxies form and evolve. This discovery, which was made with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope, suggests that galaxies can form and grow at a much faster rate than previously thought.

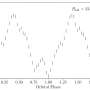
NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission has made an incredible discovery - a rare cataclysmic variable star, located about 400 light-years away. This type of star system, comprised of two stars orbiting close together, is extremely rare and can be used to study some of the most extreme stellar phenomena. The two stars in the newly discovered system, designated AT2018hso, are orbiting each other at a distance of about 500,000 miles every 78 minutes.
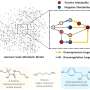
The era of space exploration is about to reach a new level of discovery. Thanks to the combined efforts of NASA’s upcoming James Webb Space Telescope and its predecessor, the Hubble Space Telescope, scientists will be able to explore the universe in an unprecedented way.
The James Webb Space Telescope, scheduled to launch in 2023, is designed to observe the universe in infrared light and provide an unprecedented view of the universe that is an order of magnitude deeper than what Hubble can achieve.

The UK government has recently announced that it is investing in artificial intelligence (AI) to help teachers use technology more effectively in the classroom. This investment will help teachers use AI to identify individual students’ strengths and weaknesses, so they can tailor teaching methods to each student’s needs. It will also help teachers create customised learning paths for students depending on their specific needs and capabilities. This investment marks an important step in the use of AI to improve teaching and learning in the classroom.

In this article, we explore the question of how particles interact with material in order to better understand and control the properties of materials. The answer lies in the particles themselves and the forces that act between them.
Particles interact with one another and with material through a variety of forces, including electrostatic, gravitation, and nuclear forces. By understanding how these forces act, scientists can learn to control the properties of materials, such as their strength, electrical conductivity, and optical properties.

Today, scientists have discovered a new phenomenon of surface diffusion of ions in two-dimensional channels. This phenomenon is observed when ions are confined to a two-dimensional channel, and the surface of the channel is exposed to a potential gradient. This surface diffusion causes the ions to move along the surface of the channel, rather than through the channel itself. This phenomenon could have important implications for the development of advanced nanoscale devices.
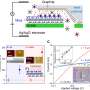
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have shed light on a poorly understood aspect of male fertility, providing insight into the mysterious functioning of sperm. Using a novel combination of imaging techniques and protein analysis, the team was able to observe and measure the physical properties of the sperm tail, and gain a better understanding of the force it produces. The findings, published in the journal Cell, could help inform future treatments for male infertility, and further clarify our knowledge of sperm physiology.
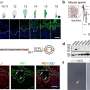
In a groundbreaking new study, a team of scientists have discovered that bacteria and viruses have a unique “arms race” of sorts that we’ve never seen before. The team studied a rare window of rapid evolution, which allowed them to witness the arms race between viruses and bacteria as it happens. This research provides us with an unprecedented view of how viruses and bacteria interact in real time and could be invaluable in developing new strategies to combat them.

The field of quantum computing is about to take a major leap forward, thanks to a new development from a team of scientists. They have demonstrated a way to leverage chiral phonons—a type of wave—to create a quantum effect. This could lead to faster, more efficient quantum computing than ever before.
The team’s research could be a huge breakthrough, as it could help make quantum computing more viable and accessible. By using chiral phonons, the team was able to create a quantum effect that could be used in a variety of quantum computing applications.

In a new study published in Nature, scientists have identified a way to use competition to enhance the performance of synthetic microbiomes. These microbiomes are made up of multiple, genetically-engineered bacteria that work together to produce a desired outcome. The scientists have found that by introducing competition between the bacterial species within the microbiome, they can increase the efficiency of the microbiome and the desired product output. With this discovery, scientists can now create more effective, dynamic, and efficient synthetic microbiomes.
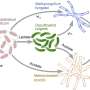
The past century of chemistry has been defined by the study of solid materials, but a new breakthrough in research could change that. Scientists have recently discovered a new way to manipulate liquid metals that could revolutionize chemistry as we know it. With this new technology, we can now study the properties of liquid metals more thoroughly, which could lead to a wide range of potential applications. This discovery is a major step forward in the field of chemistry and could open up a wide array of opportunities for further research.

