
Today, scientists revealed a discovery that could change the way we look at the Milky Way. A team of researchers has identified a new ring of phosphorous, located in the outskirts of the Milky Way. This phosphorous ring is thought to be the remnant of a major collision that took place between two galaxies billions of years ago. This discovery could help us understand more about the structure of the Milky Way and the formation of galaxies in general.

Recently, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery that could revolutionize our understanding of the universe. Researchers have determined that our universe is actually four-dimensional! While this new information may seem difficult to comprehend, the implications of this discovery are incredibly exciting.
The four-dimensional universe means that our universe is composed of four spatial dimensions, instead of the three that we were originally aware of. This means that our world is not limited to length, width, and depth, but also includes a fourth dimension, one that has never been explored before.

We are in awe of the universe’s vastness and its wonders. Today, we are thrilled to share news of a truly incredible discovery: the second most distant galaxy found to date! Discovered by the team of researchers led by Professor David Koo of the University of California, Santa Cruz, the galaxy has been nicknamed “James Webb” after the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope. This distant galaxy lies 13.4 billion light-years from Earth and is the brightest galaxy ever seen at such a great distance.

A team of physicists have recently developed a technique that could revolutionize our understanding of the vacuum of space. By tracking quantum fluctuations in the vacuum, the physicists can explore the properties of the vacuum itself. The technique, called “Quantum Vacuum Tracking”, could also provide insight into the mysteries of dark energy and dark matter. What makes this new technique so revolutionary is its ability to measure the quantum fluctuations that occur at the smallest scale, giving us a glimpse into the fundamental properties of the vacuum.
In a new study, researchers have taken a major step forward in understanding the speciation of arsenic in freshwater fish. The study, published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, looked at the bioaccumulation of arsenic in five different species of freshwater fish: rainbow trout, brown trout, walleye, largemouth bass, and yellow perch. The findings of the study could have far-reaching implications for improving the environmental safety of our freshwater fish.
For those looking to improve the efficiency of drug treatments, fluorine could be the answer. A recent study has shown that, when used as an additive, fluorine helps to “catch and attach” drug molecules to their targets, resulting in a greatly increased effectiveness. This means that the same dose of a drug could potentially have a much greater impact, leading to fewer doses being needed and ultimately better outcomes for patients.
NASA is set to return to the Moon by 2023, with the launch of the first woman and the next man on the lunar surface scheduled for 2024. This is part of the agency’s Artemis program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon by 2028. The mission is set to be a crucial step in NASA’s ambitious plans to send humans to Mars in the 2030s.

NASA’s Europa Clipper mission is set to launch in 2023 and will take us closer than ever to uncovering the secrets of Jupiter’s mysterious moon, Europa. The mission will be the first to conduct a detailed survey of the icy moon’s ocean and icy shell, and has the potential to discover evidence of life beneath Europa’s frozen crust. By flying through Europa’s plumes and making a series of close flybys of the moon’s surface, the Europa Clipper spacecraft will be able to map Europa’s surface in unprecedented detail.

A recent study has found that the coast of the Bay of Sweden is home to a variety of potentially unique and diverse marine ecosystems. The study, which was conducted by researchers from the University of Gothenburg, focused on assessing the diversity of species found in the bay and found that there were numerous species that were not previously known to inhabit the area. The findings suggest that the bay may have a wide range of undiscovered species that could potentially benefit from conservation efforts.
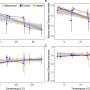
A newly identified species of phytoplankton has been discovered in Qinghai Lake, China. Cladophora qinghaiensis is an ecological phytoplankton species that plays an important role in maintaining Qinghai Lake’s unique ecosystem. This species was found to have a relatively larger cell size and a higher photosynthetic rate than other species in the lake, which makes it an important contributor to the lake’s overall productivity. The researchers also found that this species has an important role in the lake’s food web, as it is an essential source of food for many of the lake’s fish and other aquatic animals.
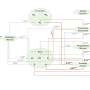
A recent paper published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters has provided the first detailed account of the Laniakea Supercluster, a massive collection of galaxies that includes our own Milky Way. Using data from the Hubble Space Telescope, the researchers were able to map out the structure of the supercluster, which is 500 million light-years across and contains tens of thousands of galaxies. The results of the study have also shed light on the “Hubble Tension”, a disagreement between two different measurements of the universe’s expansion rate.

A recent breakthrough in galactic astrophysics has revealed the existence of a large number of young star clusters in a previously unexplored region of the Milky Way. These clusters, dubbed “ultra-young clusters” are significantly younger than previously observed star clusters, with ages ranging from only 10 million years to less than a million years old. These ultra-young clusters are thought to have been formed by the merging of giant molecular clouds in the Milky Way, and could provide new insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies.
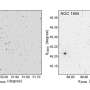
Scientists have recently identified a whopping 11 unique strains of African swine fever (ASF) virus in pigs. ASF is a highly contagious virus that affects pigs, and is one of the most serious swine diseases. The virus is found in Africa, Europe, and Asia, and the identification of the 11 strains may help us better understand the spread of the virus and its impact on farms. It is important to recognize the diversity of the virus to ensure that the best control strategies are used to keep pigs healthy.

New research from scientists at the University of California has uncovered a remarkable breakthrough in the field of protein research. Dubbed the “Goldilocks Effect,” this framework suggests that the ideal amount of protein for a given organism is like the Goldilocks story - not too little and not too much, but just the right amount. This research has implications for how we understand the optimal protein needs of species, and even has implications for human health.
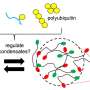
A recent study by scientists has shown the existence of an Aurora-like radio emission from the outer atmosphere of a star. This is the first time scientists have observed such a phenomenon outside of our own solar system. The emission was discovered when scientists used a radio telescope to observe a star system located some 100 light years away. The emission appears to originate from the outer atmosphere of the star, and is similar to the Aurora Borealis phenomenon seen on Earth.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have identified a key component in the potential for a natural cancer treatment. This discovery has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment and pave the way for new treatments that may be more effective and less invasive than existing treatments. The research, conducted by a team of scientists from the UK and US, used a technique called “targeted gene editing” to identify a gene that could be used in developing new treatments.

Research has uncovered a key mechanism of how changes in DNA can lead to cancer. Scientists from the University of Cambridge have identified 11 key clues that can be used to develop new treatments for the disease. The findings, published in Nature Communications, reveal that certain genetic mutations can cause cancer by disrupting the way the body’s cells respond to environmental signals. This disruption can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, which is the hallmark of cancer.
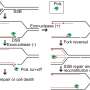
In a world-first, scientists have created an artificial “fatty acid factory” in a laboratory setting. The breakthrough could have profound implications for health, nutrition, and the production of bio-based products. The team of scientists from the University of Cambridge and the Université de Montréal in Canada used a combination of gene editing and synthetic biology techniques to create a living cell that can produce fatty acids from simple sugars. This is the first time this has ever been achieved, and the findings are a major step forward in the development of sustainable, renewable resources.

A recent study has discovered a potential new understanding of the process of cell division in green algae, which could provide insight into the way many other cell types divide. Scientists have identified a new process of division that occurs in green algae, which illuminates the way cells divide in other organisms. The findings could help to further our understanding of how cells divide, and how to control the process. This could potentially lead to new treatments for diseases, such as cancer, that rely on faulty cell division.
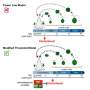
New research has uncovered a previously undiscovered special protein in marine bristle worms. This protein, known as “Lipocalin-2”, could have a variety of potential applications in the fields of medicine and biotechnology.
At first glance, it may not seem like there’s much to be excited about when it comes to marine bristle worms. But now, a team of researchers from Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology has discovered something remarkable: a special protein found in these creatures.
Today, astronomers announced a major breakthrough in their understanding of microlensing events, an astronomical phenomenon that occurs when a distant object passes in front of a bright background star, causing the light from the star to be magnified. Using data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, they were able to accurately measure the size and mass of the object causing the microlensing event. This knowledge will enable researchers to gain a better understanding of the nature of these objects and their role in the universe.

Scientists have discovered a new way to explore the cosmos: using transient space peering. By studying the light emitted from distant stars, they have developed a technique that could revolutionize our understanding of the universe. The results, published in Nature Astronomy, are a major breakthrough for astronomy and astrophysics.
It’s like a new way of peering into the universe! Scientists have discovered a ground-breaking technique that gives them the ability to study light from distant stars.

SpaceX is gearing up for a historic week of Starship flights, with launches planned for Monday, Wednesday, and Friday of this week. This marks the first time that SpaceX has attempted to launch three Starship prototypes in the same week. If all goes according to plan, this could be the first time that SpaceX has sent a Starship prototype into Earth’s orbit.
The first two flights planned for Monday and Wednesday are suborbital test flights, with the Starship prototypes reaching an altitude of around 10 kilometers.

Have you ever dreamed of taking a trip to Costa Rica? Now you have an extra incentive to make that dream a reality! Scientists have discovered that fly larvae from Costa Rica could be a sustainable alternative to traditional protein sources. The larvae are high in protein, low in fat and cholesterol, and have a long shelf life. This could be a game-changer for the global food industry, as these larvae could provide an affordable, sustainable alternative to traditional animal-based proteins.

A recent study has found a strong correlation between the number of siblings in a family and a child’s academic performance in school. This research, conducted by a team of scientists at the University of Michigan, concluded that children from larger families tend to perform better in school than those from smaller families. According to the study, this is likely due to the fact that siblings provide a unique environment in which children can learn and be challenged.

