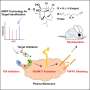
Scientists have discovered a novel way to block protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) enzymes. This discovery could open the door to potential treatments of diseases caused by misfolded proteins, such as cystic fibrosis and Alzheimer’s disease. The breakthrough was made by researchers at the University of Basel, who identified a molecule called vinigrol that is capable of inhibiting PDI enzymes. Vinigrol works by binding to the PDI active site, preventing it from carrying out its normal function.

A recent study has quantified the number of cells that form in zebrafish embryos over the course of development. By using high-resolution imaging, researchers were able to track the development of millions of cells in a single zebrafish embryo. The results of this study provide a comprehensive picture of how zebrafish embryos grow and develop. This research opens up new possibilities for understanding how embryos form and how different cell types contribute to the development of an organism.
Today, NOAA announced the launch of a new interactive tool that allows users to explore the beauty of coral reefs from the comfort of their own homes. The Coral Reef Explorer allows users to “dive” into 3D models of coral reefs from around the world and view their intricate and vibrant structures. This tool is a great way to explore some of the world’s most unique and fragile ecosystems in a safe and educational way.
Today marks a groundbreaking moment in space exploration: SpaceX has successfully launched their mega rocket, the Falcon 9, into orbit. After years of planning and development, the much-anticipated launch went off without a hitch, and the rocket is now orbiting the Earth. This is a major step towards SpaceX’s ambitious goal of reaching Mars, and a huge achievement for the company and for space exploration as a whole. It’s a momentous occasion for the future of space exploration, and something that will make history for years to come.

A recent breakthrough in gamma ray astronomy could revolutionize our understanding of the universe. Scientists have detected gamma rays with energies up to one trillion electronvolts, making them the brightest gamma rays ever observed. This is more than ten times higher than the highest gamma ray energies ever recorded before. These ultra-high energy gamma rays can be used to explore the extreme physics of the universe, such as the origin of cosmic rays and the structure of the universe at its largest scales.
We’ve all heard stories about cats and their hunting capabilities, but did you know that a new study has found that native fauna are more likely to be killed by housecats than non-native species? Researchers from the University of New South Wales and the University of Sydney have found that cats are more likely to hunt and kill native species, such as lizards, skinks, and rodents, than non-native species. The study, which was published in the journal Nature Communications, found that cats killed a whopping 97 percent of native species, compared to just 3 percent of non-native species.

The world of microscopic organisms is full of surprises. Recently, a rare marine amoeba species, known as Rhabdamoeba rosea, was rediscovered after almost two decades of being lost. The species was originally found in the late 1990s off the coast of California, but had not been detected since then. However, earlier this year, researchers from the University of California Santa Barbara (UCSB) were able to find the elusive species again. The amoeba is notable for its unusual shape and size, as well as its ability to thrive in extreme environments.

A recent study has revealed that young disabled people are facing discrimination and stigmatization in their everyday lives. The study, conducted by the University of Manchester, looked at the experiences of disabled young people between the ages of 18 and 25 over a period of three years.
The study found that these young people faced numerous forms of discrimination and stigmatization, such as physical and verbal abuse, exclusion from activities, and the withholding of support.

For years, scientists in California have been working hard to make advances in their fields, researching and developing new technologies and treatments that could have a major impact on the world. However, this progress has been recently stalled due to a new law that has been passed in the state. This law, known as Assembly Bill 5 (AB5), was designed to protect independent contractors in California but has had unintended consequences for thousands of scientists.

Scientists have recently discovered a way to tune the chirality of light, a phenomenon that occurs when light behaves differently depending on which direction it is travelling in. By manipulating the light’s polarization, researchers were able to change the chirality of the light, which could have implications for the development of new materials and technologies. This is exciting news for those in the scientific community, as this could lead to advances in areas such as quantum computing, optical communications, and more.
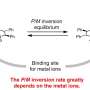
A recent study conducted by scientists at the University of California, San Francisco has revealed a molecular mechanism responsible for the asymmetric calcium-sensitive signaling pathway found in the brain. The findings, published in Nature Communications on November 13, 2023, have implications for understanding a variety of neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and epilepsy.
The research team used a combination of methods, including cryo-electron microscopy, to track the movement of calcium-sensitive proteins in the brain.
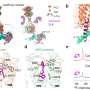
Forensic scientists have recently made a major breakthrough in the decades-old mystery of missing World War II soldiers. By utilizing a combination of DNA testing and historical research, they have identified the remains of nearly 200 American servicemen who went missing in action during the war. This is a significant development that will bring closure to the families of these men who have been searching for answers for decades. It will also provide a better understanding of the war and its effects on our nation.

A new study conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan has revealed the genetic basis of circadian rhythms and hibernation in mammals. By studying the genomes of two species of ground squirrels, the researchers discovered 11 genes that help regulate the animals’ hibernation and daily activity cycles. These genes are involved in processes such as metabolism, energy storage, and body temperature regulation. The findings could help scientists better understand how mammals regulate their body clocks and could potentially lead to new treatments for a variety of conditions related to sleep and circadian rhythms.

A new framework has been proposed that could revolutionize how we identify and classify microbial species. This framework, the Keystone Species Concept, is based on the idea that certain species are essential to the overall functioning of an ecosystem. This means that, by understanding and classifying these species, we can gain a better understanding of our environment and the role each organism plays within it. The framework suggests that instead of classifying species based on their physical characteristics, they should instead be classified by the role they play in the ecosystem.

Scientists have developed a new technique for imaging fluid mixing phenomena with remarkable resolution and accuracy. The new imaging method, developed by a team at the University of Cambridge, reveals the intricate details of how fluids interact and mix in unprecedented detail, offering a powerful tool for studying the physics behind this process. The method could have a wide range of applications, from understanding how pollutants are spread in the environment to improving industrial processes.

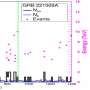
Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in our understanding of the 3D genome. Using a theoretical approach, researchers have discovered a way to identify the 3D genome’s role in determining a cell’s identity. This finding is an important step in unlocking the mysteries of the cell and could lead to new treatments for a variety of diseases.
By analyzing the 3D genome, researchers were able to identify patterns that showed how the 3D genome affects the identity of a cell.
Scientists have recently discovered a new way to create self-sorting coacervates, which are high-order protocell networks. This new method could potentially lead to the development of artificial cells and other cellular networks. The process involves isolating a single protocell from a mixture of other protocells and then using a mixture of proteins to create a complex network of protocells. The proteins act as a catalyst to cause the protocells to stick together and form a network.
Today, scientists announced a major breakthrough in the field of molecular simulation. For the first time, scientists have developed a machine that can accurately simulate how molecules interact in an external field. This breakthrough has major implications for many different areas of research, including drug design, materials science, and nanotechnology. With this new tool, scientists can now more accurately predict the behavior of molecules in a variety of real-world scenarios. This could lead to improved treatments for diseases, or even the discovery of entirely new materials.
In a major breakthrough in medical technology, researchers have developed a new nanoprobe for use in “vivo” (in the body) that can act as a real-time sentinel for lymph nodes. This new tool, developed by a team of scientists from the University of Michigan, is capable of detecting, detecting, and tracking the spread of cancer cells in the lymphatic system. This nanoprobe is designed to be injected into the lymph nodes, where it will seek out and identify cancer cells, alerting doctors to their presence.

A new study published in Science has unveiled a network of proteins that influence how cells interact with each other. This discovery could revolutionize our understanding of how cells develop and respond to their environment. The discovery of the social network proteins was made by a team of scientists at the University of California, Berkeley.
Researchers identified a set of proteins that work together to control how cells interact with each other.

STEM fields are traditionally seen as highly technical and analytical, but a new study by researchers from the University of Pennsylvania has found that the power of storytelling can be a major motivator in inspiring undergraduate students to pursue STEM. The research focused on a group of 66 undergraduate students and revealed that when presented with stories of successful STEM graduates, students were more likely to pursue STEM-related activities.
At the University of Pennsylvania, researchers recently conducted a study that revealed the power of storytelling in motivating undergraduates to pursue STEM-related activities.

A team of researchers from the University of Manchester have developed a new bio-inspired catalyst that could revolutionize the way we produce ethylene. Ethylene is an important industrial chemical used to produce a variety of products, including plastics and packaging materials. The new catalyst, which is composed of a cobalt-based metal-organic framework, is highly efficient and can be used in a variety of different reactions. This breakthrough could significantly reduce the cost of producing ethylene, making it a much more economical option for industry.

The classic game of chess is being revolutionized by a new breed of master chess players. Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms, combined with human expertise, are being used to create a new type of chess player that can think and move like a grandmaster. This new type of chess player is capable of using gambits, a series of moves that, when used correctly, can give the player an edge over an opponent.

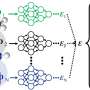
In a major breakthrough, scientists have developed new machine learning techniques that could revolutionize the way materials are analyzed using X-rays. This new technology could help engineers and technicians quickly and accurately identify the chemical composition of a material, a process that can currently take days or weeks to complete. The new method uses a combination of neural networks and X-ray diffraction to accurately identify the chemical composition of a sample without the need for manual sample preparation or complex analysis.

Today, scientists have made a breakthrough in the field of reactor physics, using advanced neural networks to revolutionize the way we predict the behavior of nuclear reactors. This new method is faster, more accurate, and more efficient than anything that has been used before. The neural networks are trained using data from simulations and experiments, and can then be used to make predictions about the behavior of the reactor. This new technology promises to make nuclear reactors more reliable and efficient, and could potentially be used to provide clean, safe energy for the future.

