
In an exciting new development, scientists are beginning to find evidence for a direct role of bacteria in modulating animal behavior. A new study published in Nature Microbiology has found that microbial populations in the gut can influence behavior in a variety of animals, including humans. This research is the first to demonstrate a link between gut bacteria and behavior in such a wide range of species. The study found that gut bacteria can affect the behavior of animals in areas such as communication, social behavior, and aggression.

Are you an astronaut or spaceflight enthusiast? If so, there’s good news for you! A new study has revealed that men who have been exposed to spaceflight are less likely to suffer from erectile dysfunction. The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston and NASA’s Johnson Space Center, looked at the medical records of over 400 current and former astronauts. The results showed that men who had been exposed to spaceflight were less likely to experience erectile dysfunction than those who had not.

A new development in the field of quantum mechanics could revolutionize the way we use extreme ultraviolet (EUV) sources. Researchers at the Institute of Physics in Vienna recently announced their findings on combining EUV sources with quantum mechanical properties. This could be a major breakthrough in the field of optics and optoelectronics. The scientists found that by using two EUV sources in a specific way, they could create a single beam of light with quantum mechanical properties.
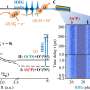
A remarkable new discovery has been made about a specific type of RNA oligomerization that occurs in the transmembrane environment. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have found that the oligomerization of a specific type of RNA is highly dependent on the pH of the environment in which it exists. This finding has the potential to unlock new insights into the complex roles of RNA in the transmembrane environment.
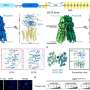
Today, researchers at the University of New South Wales have developed a revolutionary new technology called CRONT, or Controlled Robotic Optical Tweezers, that could revolutionize the biometric industry. CRONT uses optical tweezers, tiny beams of laser light that can manipulate molecules and particles, along with advanced artificial intelligence to detect and identify unique biological features like fingerprints or eye scans. This technology could be used to quickly and accurately identify individuals and verify their identities without any contact with the person being identified.
A recent study has found that math anxiety can lead to students feeling disengaged from their education. The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Toronto, found that math anxiety can lead to students feeling helplessness and lowered self-esteem. This feeling of helplessness can lead to a decrease in motivation, leading students to disengage from their education. The study also found that students with math anxiety were more likely to avoid math-related tasks and give up more easily when facing math problems.
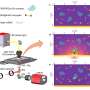
A new study by physicists has revealed how loops of DNA affect gene expression in chromosomes. The findings, published in Nature Physics, explain how loops in chromosomes control the activation of genes and could have implications for understanding the development of diseases such as cancer.
Physicists have been studying the shape of chromosomes for years, but this new study is the first to look at how the loops of DNA contained within them affect gene expression.
NASA is on the verge of making history with their Ingenuity Mars Helicopter. On April 11th, 2023, Ingenuity is set to become the first aircraft to conduct powered, controlled flight on Mars. This is a milestone in space exploration, and a testament to the incredible engineering and innovation of the team at NASA. The Mars Helicopter will be a key asset in helping NASA explore the Red Planet and collect data from a bird’s eye view.

With the alarming number of near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) that could potentially cause catastrophic damage to our planet, it is no wonder that scientists and policymakers are becoming increasingly concerned about how to protect us from an asteroid impact. In a recent article published in the journal Science, researchers from the University of Central Florida outlined a set of “technical and political considerations” that need to be taken into account when attempting to prevent asteroid impacts.

A new health initiative, Health-LinkedNZ, is being rolled out to primary schools around the country this November. Health-LinkedNZ is a program developed by the Ministry of Health to improve health outcomes for primary school-aged children. The program focuses on teaching children about healthy lifestyle choices, such as healthy eating, physical activity, and mental wellbeing. It also seeks to create an environment that encourages healthy behaviour, through activities such as health education, sports and recreation, and mental health support.

A new study published in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology has found that chlorine, a common disinfectant used in hospitals and other public places, is highly effective at eliminating bacteria that have become resistant to antibiotics. The research team tested the efficacy of chlorine against the superbug Staphylococcus aureus, which has developed resistance to antibiotics due to overuse. The results showed that chlorine was able to kill the bacteria within 10 minutes, and that the bacteria were unable to develop resistance to the disinfectant.

A team of scientists from the Georgia Institute of Technology have just made a groundbreaking discovery on the bacterium Pseudomonas. After extensive research, the team found that the bacterium is capable of producing a new type of biofuel. This new type of biofuel could potentially revolutionize the way we use energy, as it is both renewable and sustainable. The team’s findings are sure to have an impact on the future of green energy and could even lead to a decrease in our dependence on fossil fuels.
A new advance in energy storage technology has been made, thanks to a new carbon material that could revolutionize the way we store energy. Supercapacitors, which store energy through electrostatic charge, are a promising alternative to traditional batteries, offering higher energy densities and much faster charging times. This new material could make supercapacitors even more effective, allowing for even greater energy storage. It is made from carbon nanotubes, which are incredibly thin tubes of pure carbon that are incredibly strong.

In a world that is quickly becoming more digitalized, the wildlife centers of today are taking steps to keep up. A recent article from Phys.org details how the United States and other countries are looking to digitize their wildlife centers in order to better protect and conserve the world’s species. It looks as though digital technology may soon become one of the most common ways to monitor wildlife populations. By using sensors and tracking tags, researchers are able to track animal behavior more closely and accurately than ever before.

In a bold move, a group of business leaders have announced plans to forgo bonuses and instead divert the funds towards employee wages. This revolutionary approach to compensation has the potential to dramatically increase the purchasing power of employees, thereby boosting the economy. By shifting away from a bonus system, these business leaders are hoping to inspire other companies to follow suit and create a more equitable and efficient wage structure.

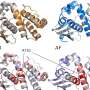
A recent breakthrough in protein folding technology promises to revolutionize the field of biochemistry. AlphaFold2, developed by DeepMind, is a computer algorithm capable of predicting the 3-dimensional structure of proteins with unprecedented accuracy. This technology is an incredible accomplishment that will significantly advance our understanding of how proteins interact with each other and the environment. This new approach to protein folding will allow us to identify new therapeutic targets, develop novel drugs, and create more efficient treatments for diseases.
In a shocking new discovery, scientists have found that a galaxy 11 million light years away is made up of a surprisingly large amount of metal. According to researchers from the University of Cambridge, the galaxy, known as NGC 1277, is made up of nearly three times the amount of metals usually found in a galaxy of its size. This finding could have major implications for our understanding of the early universe and the formation of galaxies.

Recently, a team of scientists from the University of California, Los Angeles, have discovered a new pathway in the stress response of cells. This pathway involves a novel interaction between RNA and protein, known as the ‘RNA-protein stress response (RPSR) pathway’. This pathway is activated when cells are exposed to stress and can help cells survive and adapt to their environment. The findings from this study could help in the development of treatments for diseases caused by stress, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
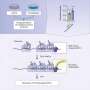
In a breakthrough study, researchers recently discovered a new defense mechanism in bacteria that allows them to resist antibiotics. Dubbed the “unicorn defense,” this unique mechanism involves a protein, which acts as an antibiotic-deflecting shield. This shield covers the bacterial cell, preventing antibiotics from entering and killing the bacteria. The unicorn defense is a major breakthrough in the fight against antibiotic resistance, which is one of the greatest global health challenges of our time.
Today marks a monumental moment in the field of Artificial Intelligence. A team of students from the University of Oxford have achieved a breakthrough in the development of Generative AI. This new AI system has the capability to both generate creative content and evaluate its quality, meaning it can both create and judge. This is a major leap forward in AI technology and has implications for the way AI can be used in the future.

A new study published in Nature Ecology & Evolution has uncovered the genomic secrets of the muskox, an ancient species of Arctic mammal that has been able to survive and thrive in one of the world’s harshest environments for hundreds of thousands of years. Researchers used the latest genomic technologies to analyze the genomes of muskoxen and found an array of genes and genetic pathways that have enabled the species to adapt to its extreme environment.

Today marks a revolutionary shift in the world of lasers with the announcement of a new dynamic Z-scanning ultrafast auto-focusing laser. This laser is capable of automatically focusing on a target in less than a second, making it the fastest laser auto-focusing system of its kind. The system is designed to be used for a range of applications, from medical imaging to industrial material processing. This breakthrough technology promises to revolutionize the way lasers are used in a variety of industries.

Scientists have recently discovered a new species of sea worm, and they are calling it the ‘posterior sea worm’. The posterior sea worm is a small, pinkish-red species of marine worm that was discovered in the South Atlantic Ocean near the Falkland Islands. The worm has a unique feature – a ‘posterior’ on its back, which is a protrusion that looks like a tail. This posterior is the first of its kind to be discovered on a marine worm and could provide insight into how worms evolved.
Today, an amazing advancement has been made in the field of nano-biosensors. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a technology that allows nano-biosensors to communicate with each other wirelessly and detect the presence of chemicals in a patient’s blood. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way we monitor our health and provide early warnings for diseases. The technology uses a combination of nanoscale devices and wireless networks to detect and transmit information about the presence of molecules such as glucose, proteins, and other biomarkers.
Scientists have recently discovered a universal common ancestor, a single-celled organism that is believed to be the origin of all life on Earth. This new discovery has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the history of life on our planet.
The universal common ancestor is believed to have lived between 3.5 and 3.8 billion years ago in a shallow marine environment. It is thought to be the common ancestor of all living organisms, from bacteria to humans.

