
Recently, scientists have been unraveling the icy secrets of Uranus, the seventh planet from the sun. In 2023, NASA is launching a spacecraft, the Uranus Orbiter and Probe, to explore this mysterious planet. This mission will provide us with a better understanding of how Uranus works as a planet and how it interacts with its environment. The spacecraft will observe the planet for a period of five years while studying its climate, atmosphere, and moons.

Do you ever feel like the modern world is just too much? We’re surrounded by clutter, chaos, and noise. But what if you could find a way to live a life of balance?
Introducing the concept of minimalist maximalism—a lifestyle that focuses on the simple things, but also embraces the joys of life.
The idea is to find the middle ground between the extremes of having too much and having too little.

Recent research has revealed that molecular diversity is driving the evolution of far-red photosynthesis. Far-red photosynthesis, or FRP, is a process in which plants use light in the far-red spectrum to photosynthesize. This process is most commonly seen in deep sea and desert plants, where the light available is too low to support regular photosynthesis.
Scientists have found that the FRP proteins used by plants to photosynthesize in far-red light are much more diverse than traditional photosynthesis proteins.
In a world of ever-evolving technology, scientists are always looking for new ways to improve fabrication techniques for micronano ultrafast devices. A recent breakthrough by scientists at the University of Michigan has made this goal a reality. By creating a new fabrication technique that is both fast and precise, they have increased the capability and speed of surface fabrication, allowing for the production of micronano ultrafast devices. This new technique is expected to revolutionize the manufacturing process for these kinds of devices, allowing for faster production and improved performance.
Ice is something most of us take for granted; it’s a part of our daily lives in the form of ice cubes, ice cream, and icy roads. But what if ice wasn’t so sticky and grainy? In a recent study, researchers have discovered a new phenomenon that could make ice smoother and less sticky. They’ve found that when salt is added to ice, it can form a more organized structure, making it less sticky and more like a solid.
The future of nuclear energy is here! We are now able to harness cutting-edge technology to create cleaner and more efficient nuclear energy. By using a combination of advanced materials and digital control systems, nuclear plants can now produce energy with fewer emissions and greater safety. This means that, in the future, we can look forward to a cleaner, healthier, and more efficient nuclear energy option.
Read Full Article Here
Scientists have recently made an incredible breakthrough in sustainable energy: they have discovered a way to use superconductors to create a new type of road! This road, called a superconducting road, is made up of a material that is able to absorb and store energy, making it much more efficient and environmentally friendly than traditional roads. With this new technology, electricity can be stored in the road and used to power nearby homes and businesses.

Today, a new theory of semantic realism has been proposed to help explain the concept of human survival. This theory suggests that the ability to understand the meaning of language and the ability to survive in a given environment are closely intertwined, and that the two are inseparable. According to this theory, we cannot truly understand and survive in an environment if we cannot understand the language of that environment. This means that we must be able to interpret the meaning of words and phrases in order to comprehend our environment and make informed decisions about our survival.

Today, scientists have created the first-ever woven material made of flexible crystals! This revolutionary new material is strong, lightweight, and capable of conducting electricity. It has the potential to revolutionize the world of technology and engineering. The new material is composed of ultrathin crystals, each only a few nanometers thick, and is woven together using a unique technique. The result is a flexible, stretchy material that is strong enough to be used for a wide range of applications.
NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) recently captured some remarkable images of the Red Planet’s surface. The orbiter, which has been circling Mars since 2006, managed to take remarkable pictures of Ares Vallis, one of the largest outflow channels on the Martian surface. Ares Vallis is a 2,000 km long and 400 km wide river-like formation that is thought to have been formed by catastrophic floods over 3 billion years ago. The images show the intricate and detailed features of the landscape, including the branching of the channel and the eroded, layered deposits of the sediment.

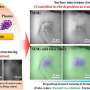
Recent research has revealed a new method that can be used to easily genetically modify bacteria. This method, developed by scientists at the University of California San Diego, allows for bacteria to be modified outside of the laboratory and in a much more efficient way than ever before. By using this method, scientists are able to rapidly create new organisms with valuable traits that can help us tackle a wide variety of problems.
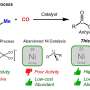
Today, scientists have unveiled a new nickel-based catalyst that could revolutionize the way we produce energy, with remarkable economic advantages. This newly discovered catalyst has the potential to drastically reduce the cost of energy production and could even lead to the widespread use of renewable energy sources. The catalyst works by allowing the conversion of electricity into hydrogen gas, which can then be burned to produce energy. This process is known as electrolysis and is much more affordable than traditional methods of energy production.
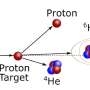
Today, physicists have made a groundbreaking discovery that could revolutionize our understanding of atomic physics. For the first time, physicists have observed a molecule-like nuclear ground state. This new discovery could potentially lead to a better understanding of the strong interaction, the fundamental force that binds the nucleus of atoms together. It could also open the door to new applications in nuclear energy, quantum computing, and beyond. This exciting breakthrough will undoubtedly spur more research in the field of atomic physics, and the possibilities are endless.
Recent research has revealed a revolutionary new way to reprogram tissue: mechanically wound tissue. Using a combination of mechanical and chemical methods, scientists have found a way to alter the tissue’s genetic code and cause it to take on new properties. This new technique could potentially be used to create treatments for various diseases, regenerate damaged tissue, and even create new organs.
This breakthrough marks a huge step forward in the field of tissue engineering and could pave the way for a variety of medical treatments and applications.
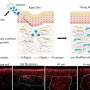
The future of safety is here! Scientists have developed a revolutionary way to make safety cleaner and safer. This new technology uses nanotechnology to create ultra-thin protective layers that are incredibly strong and resistant to damage. These protective layers can be applied to surfaces, making them resistant to scratches, abrasions, and even extreme temperatures. This revolutionary technology could revolutionize safety, making it easier and more efficient to keep us safe from everyday hazards.

Today, scientists at the University of California Irvine have made a major breakthrough in semiconductor production. They have developed a novel method for pressure-cooking raw birch material into semiconductors, a process that has typically been difficult to do due to the complex nature of the material. With this new technique, the team was able to achieve semiconductor properties in birch material that were not previously possible. This could have a major impact on the semiconductor industry, allowing for more efficient production of semiconductors and potentially reducing costs.

Slash and burn agriculture, also known as swidden agriculture, is an ancient farming technique used by societies across the world since the beginnings of human civilization. In recent years, however, this traditional land management system has come under attack for its negative impact on global forest biodiversity.
A new study published in the journal Science Advances has found that slash and burn agriculture is responsible for the destruction of nearly 17 million hectares of forests across the world.
This week marks the 66th year since the launch of the first spacecraft from the Space Coast of Florida. SpaceX, the private space exploration company, is proud to announce that their Falcon 9 rocket system has now launched over 100 successful missions from the historic launch pad. This is a remarkable achievement for the company and a testament to the hard work of all their employees. SpaceX has enabled our dreams of exploration and discovery to become a reality.

A team of scientists has recently proposed a new method for studying asteroid 3200 Phaethon, a mysterious object that orbits closer to the sun than any other known asteroid. By studying the composition of the asteroid, the team hopes to gain insight into the origin of Phaethon and its unique characteristics. The team proposes to use an innovative technique called “in-situ mass spectrometry,” which uses a robotic spacecraft to collect physical samples of the asteroid and analyze them in the lab.
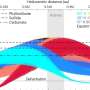
Scientists have long understood the importance of Earth’s magnetic field. This invisible force protects us from harmful radiation, helps guide migratory birds, and influences the way we use technology. Now, a new study has found that Earth’s magnetic field may play an even bigger role in sustaining life than previously thought. The research team has discovered that Earth’s magnetic field is constantly changing its poles, which could have a significant impact on the distribution of life on the planet.

Scientists have recently uncovered a groundbreaking discovery: the early ancestors of modern elephants, known as gomphotheres, had shorter trunks than today’s elephants. This discovery has sparked a lot of interest in the scientific community, as it suggests that the climate these animals lived in could have been different from the current environment. This shift in climate could have had an effect on the evolution of early elephants, leading them to develop shorter trunks in order to adapt to their environment.

A new study has found that global marine life will be profoundly affected by the end of the century due to rising sea temperatures. Researchers from the University of Technology Sydney have discovered that a sharp increase in ocean temperatures could drastically reduce the number of coral reefs, marine species, and other marine life. The findings show that ocean temperatures may rise by up to 3°C by 2100, with devastating effects on marine ecosystems.
In recent years, Indian farmers have been turning to bees to help boost their crop yields. A new study from researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras reveals that these honeybees are providing a powerful boost to the country’s agro-ecosystems. The researchers found that honeybees can increase crop yields by up to 20%, and their presence can reduce the impact of pests, weeds, and diseases on crops. The study highlights the importance of honeybees in supporting the health of India’s agricultural sector and in providing a vital source of food security for the country.
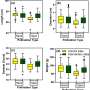
The Large Hadron Collider beauty experiment (LHCb) at CERN is unlocking the secrets of the birth of particles. The experiment is revealing new nuances to our understanding of how these particles form, and this has important implications for our knowledge of the fundamental building blocks of matter. The latest results from LHCb show that the production of certain particles, like the top quark, is more complex than previously thought. This means that the interactions between particles at the birth of the Universe may have been more varied than previously considered.
Today marks the opening of the new Museum of Roman Emperor Transbut, a revolutionary exhibition that seeks to bridge the gap between ancient Roman culture and modern-day life. The museum, located in Rome, Italy, features a range of interactive displays and artifacts that explore the life and legacy of Emperor Transbut. Visitors can explore the life and times of the Emperor through a range of interactive displays, including statues, coins, and an interactive map of the Roman Empire.

