The European Union has taken a major step forward in protecting nature and promoting sustainable agriculture. In a recent decision, the European Commission has announced that it will require all member states to cover at least 10% of their agricultural land with permanent grass cover by 2023. This move is expected to have a major impact on the biodiversity of the region, as well as the health of the soil and the environment.

Have you ever heard of llama nanobodies? Scientists have discovered that these tiny molecules are capable of neutralizing noroviruses, which are the leading cause of foodborne illness in the world. The results of this study provide hope for a much needed norovirus vaccine. The nanobodies are derived from llamas, which possess a unique immune system that allows them to create antibodies that are smaller than those of humans. These nanobodies can bind to norovirus and deactivate it, preventing it from causing infection.
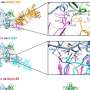
Today, a revolutionary new technology has been developed that could revolutionize the way we treat brain diseases. Scientists have developed a new type of microvehicle that can be injected into the bloodstream and travel to the mouse brain, delivering medication to specific areas of the brain without causing any damage or disruption to the brain’s normal function. This technology could potentially be used to treat a wide range of neurological disorders, including stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other brain diseases.
In a world-first, Japan is using cow dung to power a spacecraft destined to explore the Moon. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) announced the launch of its unmanned spacecraft, MOO-N, which is powered by methane gas produced from cow dung. This is the first time that cow dung has been used as fuel for a spacecraft. JAXA hopes to use this as a stepping stone towards the future utilization of the Moon’s resources.

DNA analysis of insects has revealed astonishingly high levels of biodiversity, with some species containing upwards of 100 distinct genetic variations. Scientists from the European Union have conducted a comprehensive survey of insect DNA, and their findings suggest that insect populations are far more genetically diverse than previously believed. This could have major implications for the conservation of insect species, as well as for our understanding of evolution. The study examined genetic samples from over 100,000 species of insects, and concluded that many species contain a wide range of genetic variation.

Recent developments in physics have enabled scientists to achieve a remarkable feat: entangling individual molecules. This breakthrough could have far-reaching implications for the advancement of quantum computing and other areas of research.
In a paper published in the journal Nature, a team of physicists from the University of California, Berkeley have demonstrated that molecules can be entangled at a distance of over a meter. This is the first time such an achievement has been made, and it could hasten the advent of powerful quantum computers.

Are we being watched? For centuries, astronomers have been searching the sky for signs of intelligent life from beyond our planet. Now, astronomers have begun to wonder if what they are seeing in the night sky are actually extraterrestrial probes sent to observe us.
In December 2023, scientists announced the discovery of a series of unidentified flying objects (UFOs) streaking across the night sky. While the exact nature of these objects is still unknown, some astronomers believe that they could be alien probes sent to observe our planet.

A team of researchers from Stanford University have announced the successful development of 3D DNA nanorobots that are capable of delivering molecular cargo to targeted cells. This breakthrough technology could be used to treat a variety of diseases and could even revolutionize the way medical professionals diagnose and treat illnesses. The nanorobots are composed of DNA origami, a technique where DNA strands are folded into various shapes. They can be programmed to carry and deliver molecules to precise locations inside cells.
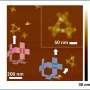
A new discovery has been made about the element germanium, a relatively rare element found in the Earth’s crust. Scientists have discovered that germanium can form three different crystal structures, or ‘allotropes’, when cooled to extremely low temperatures. This is the first time this has been observed for any element and could open up new potential applications for the element, such as in quantum computing. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research and the University of Stuttgart have spent the last two years studying the properties of germanium and their findings could revolutionize the way we use this element.
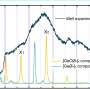
Today, scientists have developed a new type of particle that will revolutionize the way we use semiconductors - polaritons. Polaritons are quasiparticles, which are created by combining two particles - an electron and a photon - to form a unique type of particle. These particles travel along a “semiconductor highway” and have the potential to revolutionize the way in which semiconductors are used in electronic devices. By taking advantage of the properties of polaritons, such as their high speed and high efficiency, scientists can create faster and more efficient electronics.

The future of animal welfare is here! A new sensor implant has been developed to monitor the health and welfare of individual farmed animals. This revolutionary technology provides real-time data to farmers, allowing them to detect illness or distress in their animals quickly and efficiently. This innovative tool is expected to significantly reduce the number of sick or distressed animals on farms, improving animal welfare and giving farmers peace of mind.

In a new breakthrough study, scientists have discovered that algae have the ability to remember sudden exposure to sunlight. This new discovery could lead to the development of more efficient and sustainable biofuel sources. The study, conducted by researchers at the University of York, found that when exposed to a sudden burst of light after a period of darkness, algae can remember this event and use it to inform their future behaviour.
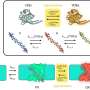
Scientists have recently uncovered evidence of a major shift in ancient life that occurred about 540 million years ago. This shift is known as the Cambrian Explosion, and it marks the transition from single-celled organisms to more complex life forms. To understand the cause of this shift, researchers have turned to molecular fossils, which are molecules that can be preserved in the fossil record for millions of years. By analyzing these molecules, scientists can learn about the environment and the organisms that lived during this time.
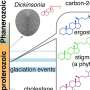
This blog post will focus on a new and exciting development in the field of physics: the discovery of an anomalous Floquet topological insulator. Researchers from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria) have identified a fractal photonic structure with properties that could lead to unprecedented control of light waves. This structure is a so-called Floquet topological insulator, and it works by periodically modulating the photonic crystal lattice. By doing so, it creates an optical bandgap that is capable of trapping and guiding light waves in a fractional pattern.
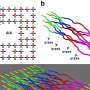
Recently, researchers in Brazil have developed a sensor that could revolutionize the way we detect antibiotic residues in food. This sensor is capable of detecting a wide range of antibiotics in food samples, and could be a huge help in reducing antibiotic overuse in the food industry. With the help of this new sensor, food producers can now more accurately test for antibiotic residues, allowing them to ensure the safety and quality of their products.

The use of animal tissues in cosmetics is a controversial topic. With increasing concern over the safety of animal-derived ingredients, scientists are now looking to develop alternatives that are safe, effective, and cruelty-free. In a recent study, researchers from the University of Barcelona have developed a method for testing the safety of animal tissues in cosmetics. The team developed a series of tests that assess the chemical and physical properties of animal tissues, as well as their potential contamination with hazardous components.
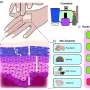
A new discovery in microfluidic devices has been made that could revolutionize the way we think about droplet formation! Scientists have found a new way to create droplets thousands of times smaller than previously possible. These minute droplets can be used in a variety of applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and even cooling systems. By adjusting the flow rate of the device, scientists are able to create droplets with a diameter of only 10 microns (one millionth of a meter).

In a recent breakthrough study, scientists have discovered a new and improved method for using magnesium oxide to increase the absorption rate of dietary supplements. The time-tested compound has been used for centuries to treat a variety of ailments, including constipation, weak bones, and low magnesium levels. But the new study is the first to uncover how magnesium oxide can help the body absorb essential minerals and vitamins more quickly.

In a breakthrough study published in the journal Nature Catalysis, an international research team has developed a new catalyst that can electronically control the functionalization of chiral molecules. This novel catalyst, based on an iron-based compound, has the potential to revolutionize the production of enantiomerically pure chiral molecules, which are essential components in the production of pharmaceuticals. The research team, led by Professor Kazuhiro Takanabe at the University of Tokyo, was able to fine-tune the structure of the catalyst to facilitate the efficient functionalization of chiral molecules.
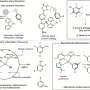
Microalgae have long been studied for their potential to produce biodiesel, but now researchers from the University of Massachusetts have found a way to use them for something else: storing lipids. The team has developed a 6MA code, a six-step process that can be used to engineer microalgae to store lipids. The code involves introducing genetic modifications that enhance the accumulation of lipids in the algae, as well as the ability to convert light energy into biomass.

For centuries, scientists have speculated about the origins of the heavier elements found on Earth. Today, new research offers an answer: ancient stars. According to a recent study out of the University of Basel in Switzerland, some of the oldest stars in the Milky Way likely played a major role in creating the heavy elements found on Earth.
This study, conducted by a team of astronomers, used data from the European Space Agency (ESA) Gaia satellite to map out the chemical composition of stars in the Milky Way.

Welcome to the future! Last week, scientists announced the development of a revolutionary new instrument that will be used to analyze asteroids in our solar system. The instrument, named the Psyche Gamma Ray Spectrometer (PGRS), is set to be launched in 2023 and will be used to study the chemical composition of the asteroid Psyche, helping scientists to better understand the origin and evolution of our solar system. The PGRS will measure gamma-ray emissions from the surface of the asteroid, helping scientists to determine its elemental composition and even search for evidence of life.

Biotechnology has taken a major step forward with a new research breakthrough that could lead to the coproduction of both exogenous arginine and biomass from astaxanthin. Researchers at the University of Tokyo have successfully achieved this feat, and the results of their study were recently published in the journal Metabolic Engineering. This breakthrough could have major implications for the food and pharmaceutical industries, as exogenous arginine is an essential amino acid that has numerous health benefits and is often used as an ingredient in dietary supplements.
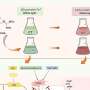
Today, scientists reported a major breakthrough in fluid dynamics: the extension of the Reynolds equation. This extended equation will be extremely beneficial to the field, as it is capable of predicting how lubricants will react at a microscopic level. The new equation is expected to offer unprecedented insight into the behavior of fluids, leading to the development of more efficient lubricants. The implications of this discovery are far-reaching, as the potential of lubricants could be utilized in a variety of industries, ranging from automotive to medical.
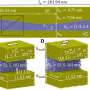
In a recent study, researchers have revealed that biofilms, which are complex communities of microorganisms, can host their own environment. These biofilms, which are mostly found in aquatic settings, can maintain its own environment distinct from the surrounding water, which can be beneficial for the microorganisms living within them. The study found that the biofilms contain their own nutrients and oxygen, which allow them to thrive without having to rely on the outside environment.