
The potential of ultrathin materials is seemingly limitless. From their potential applications in energy storage, electronics, and biomedicine, to their immense promise in nanoscale photonics and quantum computing, these materials have the potential to revolutionize our world. The potential of these materials is so great, that a team of researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have developed a new framework to ensure responsible stewardship of their development.

Have you ever thought about how rubber doesn’t conduct electricity? It’s true - rubber does not conduct electricity. This is why it’s used in a wide range of applications, from tires to electrical insulation. But why is that?
The answer lies in the molecular structure of rubber. Rubber is made up of molecules of long, flexible hydrocarbons. These molecules are arranged in a way that prevents the flow of electrons from one molecule to the next.

A recent breakthrough in rocket science has been made by a team of researchers at the University of Washington. The team has developed a new type of rocket engine that is 75% more efficient than existing models. This new engine will enable rockets to reach farther destinations in less time and with less fuel. The new engine is based on a concept called “critical acceleration,” which uses a combination of electric and chemical propulsion to achieve maximum thrust.

Are you ready for the future of poultry? Scientists have developed a revolutionary new way to raise turkey in the lab – the Petri Dish Poultry Tube Turkey! This breakthrough method of turkey production could revolutionize the way we raise turkeys, and even open up new possibilities for sustainable meat production. The process starts with a small sample of turkey embryo cells that are cultivated in a nutrient-rich liquid solution. The cells are then placed into a tube filled with a growth medium, where they are left to develop for several weeks.

In a groundbreaking new study, scientists have discovered a way to communicate with whales in a language never before seen on Earth. By using a combination of sound and light signals, they have managed to bridge the language barrier and establish a two-way communication with the whales. This breakthrough could potentially revolutionize the way we interact with other species and even open the door to communication with extraterrestrial life. Scientists are now in the process of developing a universal language that can be used to communicate with other species, both terrestrial and extraterrestrial.

A new research study has revealed that sex chromosomes are more responsible for human development than previously thought. Scientists used cutting-edge technology to analyze the genomes of more than 1,000 individuals and discovered that sex chromosomes (XX in women and XY in men) are responsible for a wide range of developmental processes, from brain structure to physical characteristics. This groundbreaking study has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of how humans develop and how sex-specific traits are determined.

A new law in the UK is set to make 12-year-olds legally accountable for their actions. This groundbreaking law, which is expected to be enacted in 2023, is aimed at giving young people the chance to learn right from wrong in a society that has long failed to provide such guidance. Under the new law, children aged 12 and over will be held responsible for their behaviour in court, allowing them to face the consequences of their actions and learn from their mistakes.

Universities across the United States are recognizing the importance of investing in their students by offering programs and services that are tailored to their needs. In a survey conducted by the American Council on Education, it was found that 12 universities have gone the extra mile to ensure their students are receiving the best possible education. These universities have implemented strategies such as providing increased access to academic advising, career counseling, and mental health services.

Alice Dynamics has revolutionized the way we study the behavior of particles. This groundbreaking research has opened the door to understanding the charm and beauty of particles that make up our universe. By using advanced particle accelerators, they have been able to observe and measure the interactions between particles like never before. This has led to the discovery of new particles, as well as deeper understanding of existing particles. The research of Alice Dynamics is revolutionary in its ability to observe and measure particles on an atomic level, allowing us to gain insight into the behavior of these fascinating particles.
Leaflet formation is a key process that enables the formation of cell membranes, and now, scientists have uncovered new molecular insights into the process. Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), researchers at the University of Washington have been able to observe, in real-time, how individual molecules interact to form a two-layered membrane.
This new research, published in Nature Communications, provides unprecedented insights into the sequential formation of leaflets that make up the cell membrane.
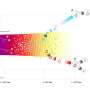
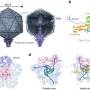
Scientists have recently discovered a new state of matter: a two-dimensional noble metal-based intermetallic compound. This discovery is leading to a better understanding of the properties and behavior of two-dimensional materials, which could have a huge impact on future developments in the field of nanotechnology.
For the first time, scientists have found a state of matter that combines the properties of two-dimensional materials and the noble metals. This new state of matter, called a two-dimensional noble metal-based intermetallic compound, has unique properties that could potentially be used in nanotechnology.
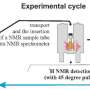
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed a new method for exploring hyperpolarization of hydrogen atoms. Hyperpolarization is a process in which the spins of hydrogen nuclei are aligned in order to generate an ultra-strong magnetic field. This process can be used to generate high-resolution images of hydrogen-based molecules and to increase the sensitivity of certain medical imaging techniques. The new method involves applying a microwave field to a sample of hydrogen gas, which produces an alignment of the spins and generates a magnetic field.
Optogenetics is revolutionizing the way scientists study and monitor the health of cells. A new breakthrough in this exciting field has been made by researchers at the University of California, who have developed an optogenetic acid sensor for cells. This sensor allows scientists to monitor the pH levels of cells in real-time with unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity. This technology could be used to better understand the environment within cells and even create treatments for diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s.
Scientists have recently developed a strategy for designing perovskites to be used in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), a key reaction for producing hydrogen gas. This strategy could revolutionize the production of hydrogen gas, a clean and renewable energy source.
The researchers have developed a design strategy for perovskite oxides that have the potential to outperform their traditional counterparts. The team used computational approaches to identify the most promising materials and identified a three-dimensional perovskite oxide with a significantly higher activity than current materials.
Scientists have made a major breakthrough in the field of chemistry: they have managed to capture an elusive transition state in a chemical reaction. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way we think about chemical reactions and could lead to more efficient and effective ways of synthesizing chemicals. Through the use of advanced imaging and spectroscopic techniques, the scientists were able to observe the transition state during a reaction between two molecules, providing new insight into the dynamics of chemical reactions.

Today, EasyDaMV3 - the world’s first AI-driven agricultural management system - was unveiled at a press conference in Beijing, China. This revolutionary new system promises to revolutionize the way farmers manage their crops, and could have a lasting impact on food production around the world. EasyDaMV3 uses a combination of Machine Learning algorithms, image recognition, and other advanced technologies to automate the entire agricultural cycle - from planting to harvesting. In addition, the system can provide real-time recommendations and advice to farmers, giving them access to the best practices and the most up-to-date information in order to maximize their yields.
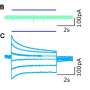
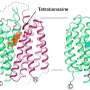
Today, scientists have revealed the molecular mechanisms of VMAT2 inhibition, an important step in understanding the actions of drugs used to treat neurological disorders. This research could lead to new treatments for Parkinson’s disease, depression, and schizophrenia, among other neurological disorders. The findings, published in Nature Communications, provide insight into how VMAT2 inhibitors work and how they could be used to help treat these conditions. VMAT2 is a protein found in the brain and other parts of the body that plays an important role in controlling the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
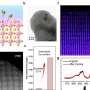
A little-known virus that infects cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae, has recently been discovered by researchers at the University of South Florida. It is the first virus of its kind to be observed in high resolution, and its discovery could be key in understanding how cyanobacteria infections spread and how to prevent them in the future. The virus, which has been named “Cyanophage FJW-1,” is a very small virus, measuring just 0.
The future of electronics is here! Scientists have recently developed a new technology that uses ultrafast lasers to accelerate electrons in ballistic graphene. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way we use electronics in our everyday lives. The ultrafast laser pulses can accelerate electrons in graphene up to a million volts, which is significantly faster than current methods. This could lead to faster and more efficient electronics that can operate on a much smaller scale.

As parents, we want what’s best for our children and are always looking for ways to help them develop healthy coping skills and lead a balanced life. A recent study suggests that only 12 minutes of mindfulness practice a day can have a positive impact on kids. The study, which was conducted by researchers at the University of California, Davis, found that children aged 8 to 16 who completed a 12-minute mindfulness practice each day experienced reductions in anxiety, stress, and negative emotions, while also reporting improved concentration and executive functioning.

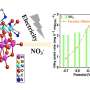
The water crisis is a global issue that needs to be solved quickly and efficiently. A new breakthrough from researchers at the University of California, Riverside could help. They have developed a catalyst that can efficiently convert nitrate pollution in water into nitrogen gas. This process is a significant step forward in the quest to reduce water contamination caused by nitrate pollution. The catalyst is made up of a nickel-based material, which is sustainable and cost-effective, and can be used to efficiently convert nitrate pollution in water into harmless nitrogen gas.
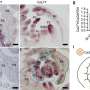
A new study by scientists at the University of California, Irvine has provided proof that marker-free DNA editing is a safe and efficient way to modify the genome of living organisms. The study, which was published in Nature Communications, found that marker-free editing was able to achieve a high editing efficiency with minimal off-target effects. This breakthrough could have far-reaching implications for medical treatments and gene therapy.
The marker-free editing technique, which is based on a modified CRISPR-Cas9 system, is much more precise and efficient than traditional marker-based editing methods.

Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have recently developed a new material that could revolutionize the production of clean energy through nuclear fusion. This material, which is made of a combination of rare-earth elements, is able to rapidly absorb and store hydrogen, the key fuel for nuclear fusion. This breakthrough could significantly decrease the cost of achieving fusion, making clean energy more accessible and sustainable in the future.

Astronomers have made a major breakthrough in understanding the population of binary stars. Using data gathered by the Hubble Space Telescope, they have discovered a new method of estimating the number of binary stars in the Milky Way. This new technique will help astronomers better understand the formation and evolution of stars and galaxies.
In a recent study, astronomers from the Space Telescope Science Institute revealed their new method of estimating the number of binary stars in the Milky Way.

In an incredible achievement, the Coast Salish people of the Pacific Northwest have recently discovered an ancient Indigenous site that is over 10,000 years old. This site, located in the Fraser Valley of British Columbia, is believed to be the oldest known archaeological site in Canada. The discovery of this site is a major breakthrough for the Coast Salish people, as it provides valuable insight into their culture and history. Not only does this site provide evidence of the Coast Salish people’s long-standing presence in the region, it also sheds light on their culture and activities in the distant past.

