The LHCb collaboration at CERN has recently announced the discovery of several exotic particles that could provide insight into the fundamental nature of matter. These particles are hypothesized to be a result of the strong force and could provide answers to long-standing mysteries such as the origin of mass. The particles, known as “mesons”, have been observed to decay into different types of particles that have never been seen before. This could provide new information on the structure of the strong force and could potentially lead to a better understanding of how particles interact.

Today, researchers from the University of Zurich have announced a new tissue and molecular imaging technique that could revolutionize biomedical research. This new technique, known as Multiplexed Ion-Coupled Imaging (MICI), is capable of imaging tissue samples at the single-cell level. It can detect multiple molecules simultaneously, allowing researchers to gain valuable insight into the inner workings of cells. With MICI, researchers can gain a better understanding of how molecules interact with each other and how they are affected by disease.

Today, scientists have announced a breakthrough in stem cell research. Through chemical techniques, they have been able to culture stem cells using animal-free and xeno-free methods. This means that stem cells derived from this process will be free of animal and non-human animal products, making them suitable for medical applications. This breakthrough is a significant step forward in the development of stem cell therapies, as it eliminates the risk of contamination from animal products and simplifies the production process.
Astronomers have recently discovered a new type of pulsar nebula, one that is incredibly luminous and about ten times brighter than any previously discovered. This new pulsar nebula, located in the constellation of Aquila, is estimated to be around 8,000 light-years away from us. This discovery is significant because it could provide astronomers with a better understanding of the physics of pulsar nebulae, which are known for their high luminosity and high-energy emission.

The European Space Agency (ESA) is pushing the limits of what we can do in space. In a recent announcement, they revealed that they have been stockpiling simulated regolith–the powdery material found on the surface of the moon and other planetary bodies. The ESA has been collecting this regolith so they can use it for future space experiments and activities. This simulated regolith will be the ultimate resource for astronauts and scientists who seek to explore the unknown.

Today, scientists are reporting the exciting news of a new discovery - a lost space object in our Solar System. This mysterious object is located in the Kuiper Belt, an area of icy bodies beyond Neptune. Scientists have named the object “Kuiper-X” and believe it to be an icy, dwarf planet-like body. It is estimated that Kuiper-X is about 400 kilometers in diameter, and is composed of a mixture of water ice and frozen methane.
NASA recently announced the launch of Chaser, a spacecraft designed to explore the mysterious outer regions of our solar system. This mission is part of their New Horizons program, and is expected to be the first of many spacecraft sent out to explore the area known as the Kuiper Belt. Chaser will be equipped with a suite of instruments to allow it to observe and collect data on the environment and composition of the area, as well as look for evidence of any potential habitability.

Japan is set to launch its first lunar lander to the Moon in December 2023. The mission, which is part of the country’s ambitious space exploration program, will deploy a robotic lander to the lunar surface from a satellite in lunar orbit. This mission will be an important milestone for Japan’s space exploration, as it will be the first time a Japanese mission has flown to the Moon.
Japan is set to take a giant leap in space exploration!

NASA has just announced that the OSIRIS-Rex asteroid sampling mission has been renamed to “The Bennu mission”. This exciting mission, originally planned to launch in 2016, will explore the asteroid Bennu and collect samples from its surface. OSIRIS-Rex, now referred to as The Bennu mission, will be the first US-led mission to bring an asteroid sample back to Earth. After a seven-year journey, the spacecraft is expected to arrive at the asteroid in 2023 and return to Earth in 2023 with a sample of its surface material.

In a breakthrough for sustainable agriculture, researchers have developed an electronic soil system to monitor and regulate crop growth. By utilizing a combination of sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, the system can accurately measure the nutrient and water levels in the soil, and then adjust the amount of fertilizer and water needed to optimize crop yields. This technology promises to revolutionize the way farmers approach crop production, as it can help them to maximize yields while minimizing environmental impact.

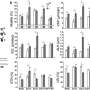
Recently, scientists have discovered an interesting phenomenon that can help explain why some males are more aggressive than others. It seems that the smell from male sweat can be an indicator of their level of aggression.
The research team found that when male sweat is exposed to female sweat, the female sweat can detect the presence of aggression-related hormones in the male sweat. This suggests that the female sweat acts as a sort of “aggression detector”, allowing females to assess the level of aggression in males.

The global pandemic of COVID-19 has changed the world in more ways than one. As we look ahead into 2023, it’s difficult to predict what the future holds. However, a new scenario from the World Health Organization (WHO) paints a picture of what the world could look like in 2023 if the right strategies are put into place.
According to the scenario, by 2023, the global response to COVID-19 will have been successful in reducing the impact of the virus.

Today, scientists have discovered something truly remarkable - fossilized soft tissues of a trilobite! Trilobites are an extinct species of marine arthropods from the Cambrian period, meaning they lived over 500 million years ago. The discovery of these fossilized soft tissues allows researchers to better understand the evolution of trilobites and their relationship to modern-day species. This discovery also helps to reveal how convergent evolution can result in similar anatomical structures in species that have evolved independently.

Today, scientists have discovered that the universe may be a hologram. This revolutionary discovery was made by astrophysicists at the University of Southampton who have been studying the curvature of space-time. Utilizing a mathematical model of the universe, they found that the entire cosmos could actually be an illusion and the universe is made up of two-dimensional information on the boundary of the universe. This means that three-dimensional objects, such as stars and galaxies, are actually projections of information stored on the boundary of the universe.

Today, bioengineers are at the intersection of organoids and AI, creating a new type of “Brainoware” that will revolutionize our understanding of the human brain. Brainoware is a combination of organoid technology - which uses stem cells and other materials to create miniature living models of human tissue - and artificial intelligence (AI) technology. By combining the two, scientists are able to create a system that can emulate how the brain works and make predictions about how it will respond to treatments or other environmental factors.
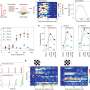
A research team has recently made an important breakthrough in the field of transistors, with the creation of a transistor that can be switched between two polarities using ferroelectricity. This new development could have far-reaching implications for the use of transistors in a wide range of applications.
The team, led by Professor Zhiyong Fan, of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, succeeded in creating transistors using a ferroelectric thin film that can be switched between two polarities using an electric field.
A recent study of ancient stars has revealed that the elements that make up our universe may have been created by protons that were present during the early stages of the universe. This study, conducted by a team of international scientists, has opened up a new way of understanding the formation of our universe. The researchers used a new technique known as “nucleosynthesis” to analyze the chemical composition of stars that were born shortly after the Big Bang.
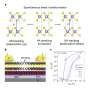
Today, scientists have developed an exciting new innovation that will keep you warm and cozy in the cold winter months: Sweater Aerogel! This revolutionary fabric is made from ultra-lightweight aerogel fibers that are embedded into a sweater-like material. The aerogel fibers are extremely efficient at trapping heat, making it a great choice for those who spend a lot of time outdoors in the cold. It’s also incredibly comfortable, with a soft, lightweight feel that won’t restrict your movement.

The world’s agronomists have long sought to understand the evolution of genetic diversity in millet, an important food crop for millions of people around the world. Now, researchers at the University of California, Davis have made a major breakthrough in understanding how genetic diversity has been maintained in millet over thousands of years.
The researchers analyzed the genomes of over 200 wild and domesticated varieties of millet, and found that the evolution of genetic diversity in millet is driven by a combination of natural selection and human-mediated selection.
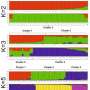
Scientists have made an incredible discovery - jellyfish can regenerate lost tentacles in a matter of days! A team of researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have been studying the regeneration of tentacles in the jellyfish species Periphylla periphylla. They found that after the jellyfish lost its tentacles, they could regenerate a fully-functional set of tentacles within three days! This is an amazing feat that could have implications for medical research and tissue regeneration.

Scientists using data from the Hubble Space Telescope have recently made a remarkable discovery - a galaxy that had been previously thought to be forbidden! The newly-discovered galaxy, which has been named “UDFy-38135539,” is located in the distant universe and is estimated to be around 13.2 billion light years away from Earth. It is currently the oldest and most distant galaxy to ever be found and it provides valuable insight into how the universe looked during its early stages.

In recent years, astronomers have made a major discovery about the structure of the universe: it’s made of filaments of matter, like a cosmic spider web. This discovery has revealed a great deal about how galaxies form and evolve, and now a new study has found that these filaments have an even bigger impact than previously thought. The study, published in the journal Nature, found that the filaments of matter have a surprisingly large influence on the growth and evolution of galaxies, even galaxies that seem to be far away from the filaments.

Have you ever wondered what it would be like to be a saboteur? Well, now you can get a taste of the excitement, as a new team of saboteurs have been recruited in England to outfox hunters in the countryside. The saboteurs are using a variety of methods to disrupt hunting activities, including using decoys to distract hounds, erecting signs to warn wildlife of hunters, and using GPS to track hunters’ movements.

Recently, the Idaho Fish and Game Commission has submitted a plan to the Idaho legislature that would allow a licensed trapper to be contracted to kill wolves. The proposal aims to reduce the wolf population in certain areas of the state in order to help big game populations recover. The plan was put together by the Commission after officials found that wolf predation was preventing the deer, elk, and moose populations from recovering.

The future of liquid storage is here! In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed technology that could revolutionize the way we store liquids in the long term. This technology is based on a simple egg-like structure called the “chicken”. The chicken is a membrane-enclosed container that separates liquids from the air. It’s made of biodegradable materials that are not only sustainable, but also cost efficient. This makes it an ideal solution for storing liquids for the long term.