NASA’s Mars 2020 Rover is set to explore a region of Mars never before seen by a rover. The region, called Jezero Crater, is a 28-mile-wide impact crater located in the northern hemisphere of Mars. This region is of particular interest to scientists, as it is believed to have once contained an ancient lake and river delta. Scientists believe that Jezero Crater could provide insight into the history of water on Mars, and may even contain evidence of past microbial life.

A new study has revealed groundbreaking findings regarding the evolution of insects. By studying fossilized insects, researchers were able to uncover the true origin of the insect group, which had previously been uncertain. The study, which was conducted by an international team of researchers, found that the insect group likely evolved from an extinct group of organisms called the euarthropods, which lived over 400 million years ago. This new discovery provides a wealth of information about the evolution of insects, and the findings could have major implications for our understanding of life on Earth.

Scientists have developed a new imaging technique that allows them to observe the smallest atoms in living cells in unprecedented detail. This breakthrough has provided new insights into how enzymes work, giving researchers a better understanding of how the building blocks of life are formed and function. This new technology has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the cellular environment and provide a powerful new tool for drug discovery.
NASA has just announced the results of a new simulation that is giving us a rare glimpse into the early stages of a young galaxy. The team, led by Dr. Rachel Friesen from the NASA Ames Research Center, used the Chandra X-ray Observatory to observe and simulate a star-forming dwarf galaxy located in the nearby universe. The results of their study provide a unique insight into how galaxies form and evolve over time.

Google has recently released a powerful Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool that is being hailed as a breakthrough in genetic engineering. The tool, called DeepVariant, is capable of quickly and accurately analyzing genetic data, and has the potential to revolutionize the way geneticists and researchers study and diagnose diseases. DeepVariant is based on machine learning algorithms, and is able to process massive amounts of data in a fraction of the time it would take a human researcher.

Recent research has uncovered a new way to make contact with individual graphene nanoribbons. This breakthrough could be a major step forward for the development of nanoelectronics and other applications of nanotechnology.
In a study published in Nature Nanotechnology, a team of researchers from the University of Groningen in the Netherlands and the University of Cambridge in the UK describe their method of making contact with individual graphene nanoribbons. Using a scanning tunneling microscope (STM), the team was able to measure the electrical properties of the ribbons and apply a voltage between the ribbons and a metal surface.
Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in the world of optics and photonics. They have found a way to create fiber lasers from composite 2D materials. This new type of laser is incredibly efficient and has the potential to revolutionize the way we look at light-based technologies. With the ability to tailor the laser’s properties and emission spectrum in a wide range of applications, these fiber lasers could be used in everything from medical imaging to manufacturing.
Today, scientists have successfully developed an AI-based camera system that can help detect the presence and coexistence of tigers in a remote area. This technology is a major breakthrough in understanding the wildlife and their natural habitats. Using this advanced camera system, the researchers have been able to monitor tiger movements in a remote area of India, and to map their range of activity. This groundbreaking research has not only revealed important information about the behaviour and habitat of tigers, but also provides an insight into how animals interact with their environment, and how we can protect them.

Coffee and tea lovers rejoice—your favorite drinks could soon be giving a boost to the shelf life of food products! Scientists have developed a new process that uses spent coffee or tea grounds to create an edible film that can help preserve food products with natural ingredients. The film is made up of a mix of carbohydrate polymers and spent coffee grounds or tea, and it was found to be effective at extending the shelf life of food products.

As the world continues to grapple with climate change, there is an increasing emphasis on finding ways to reduce the negative environmental impacts of agriculture. One way to do this is to incentivize farmers to adopt practices that are more sustainable. Recently, a program was launched that aims to do just that. The program, which is funded by the government, will provide incentives to farmers who switch to crops that are better for the environment and require fewer resources to produce.
Today, we have some exciting news to share: Scientists have developed a highly sensitive portable sensor for detecting formaldehyde in the air! This new device is capable of accurately measuring very low levels of formaldehyde with a single breath sample. This breakthrough technology could revolutionize the way we monitor our indoor air quality and help us protect ourselves from potential health risks associated with formaldehyde exposure. The sensor is small, lightweight, and easy to use, making it ideal for both professional and home use.

NASA is set to launch its most ambitious mission yet! In 2023, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft will launch a journey to an asteroid called Bennu. Its mission is to collect and return a sample of the asteroid, which will be the largest sample ever returned from space. The spacecraft will collect more than two ounces of material from the asteroid and bring it back to Earth for study. By learning more about Bennu, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of how asteroids, and possibly life, formed early in our solar system.

NASA is on the verge of an exciting new chapter in space exploration as they prepare to launch the first Artemis mission to the Moon. On September 23rd, 2021, two astronauts will take the first steps on the lunar surface for the first time in over 50 years.
The two astronauts, Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley, will be launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.

A major breakthrough in the fight against diabetes has been made. Scientists have developed a new drug that can reverse the effects of the disease in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. The drug has been tested on mice and human cells and has been found to be highly effective in restoring normal glucose metabolism, which is essential for controlling diabetes. This is a major step forward in the treatment of diabetes and could potentially bring relief to millions of people living with the disease.

In the Galapagos Islands, the paradise of birds, a new strain of avian flu has been discovered. This strain, known as the Galapagos avian flu, is believed to be a cross between the already existing avian flu virus and a new strain. Scientists are worried that if this virus spreads, it could have devastating effects on the bird populations in the Galapagos Islands, as well as other areas around the world.

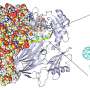
Self-cleaning membranes could revolutionize desalination technologies, making them more efficient and cost-effective. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a new membrane to desalinate water that does not require cleaning or backwashing. The new membrane is made of two layers of materials: a top layer of hydrogel and a bottom layer of graphene oxide. The hydrogel layer is designed to repel dirt and particles, while the graphene oxide layer is designed to absorb the salt particles from the water.
Have you ever heard of microcombs? Microcombs are devices that convert light into microwaves with unprecedented efficiency. A team of scientists from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) has recently developed a new method to use these microcombs for efficient light-to-microwave conversion. This new method could have a variety of applications, such as in wireless telecommunications, medical imaging, and quantum computing.
The new method developed by the UCLA team uses a technique called dual-polarization dual-comb spectroscopy.

Scientists have recently developed a biodegradable optical fiber that could revolutionize the way we use electricity. This new fiber can modulate electricity, which means it can increase or decrease the flow of electricity in certain areas. This type of technology could be used to provide electricity in remote or hard to reach areas, such as disaster zones or rural areas. The fiber is made of a biodegradable material, making it ideal for applications where it may need to be disposed of quickly or in environmentally sensitive areas.

The plastic waste crisis has become an alarming global trend, but a new study offers hope for a cleaner future. Scientists have discovered a way to convert polyethylene plastic into a useful chemical compound without the need for harsh solvents or high temperatures. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way we handle plastic waste, allowing us to turn it into something useful instead of simply throwing it away. This could be a major step forward in the fight against plastic pollution.

Are you tired of your swim cap making you look like a dork? Well, you’re in luck! A new technology has been developed that will allow you to ditch your swim cap and let your hair go green! A new “chlorine-free” swimming pool has been developed that will keep your hair healthy and free of chlorine. The new pool is filled with a special liquid that contains natural enzymes and minerals that help to keep the water clean and free of chlorine.

Astronomers have recently made a groundbreaking discovery: black holes may be spinning faster than previously thought! This new finding challenges our current understanding of the supermassive black holes at the centre of quasars.
Using a new technique to estimate the spin rate of these black holes, researchers have found that some of them may be spinning at nearly the speed of light. This is a significant discovery, as previously believed, the spin rate of black holes would be limited by the amount of matter and energy surrounding them.

A recent study has revealed a pathogen that is threatening the survival of a rare parrot species. The endangered ‘Kakapo’ parrot is native to New Zealand and is currently facing a major threat from a virus known as avipoxvirus. The virus causes severe disease in the parrots, leading to lesions, thinning of feathers, and ultimately, death. In order to protect the species from extinction, the researchers suggest that immediate steps should be taken to better understand the virus and to find ways to manage and control the spread of the disease.

In a recent breakthrough study, scientists have discovered the potential beneficial role of an enzyme called Chameau in the human body. This enzyme is found in certain areas of the human body and is believed to help regulate the production of hormones, as well as aiding in the digestion of food. This important discovery could lead to further exploration of the role Chameau plays in maintaining the body’s health. The team of researchers are hopeful that this new understanding of Chameau’s role in the body may lead to potential treatments for a variety of diseases and disorders.
In a breakthrough study published today, researchers have identified the genes that are responsible for the development of heart muscle disorders in humans. By studying the genomes of over 200 people with heart muscle disorders, the researchers were able to pinpoint the genes that most likely cause these diseases. These findings could lead to improved treatments and preventive measures for those affected by these types of diseases. Furthermore, the research team hopes to use this information to develop new therapies that will target the underlying genetic causes of the heart muscle disorders.

The dingo, a free-ranging wild dog of Australia, has been found to have a surprisingly high number of mutations, making it genetically distinct from its inbred domestic counterparts. A new study, published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, has revealed that dingoes have more than twice the number of mutations as domestic dogs.
The authors of the study, from the Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology at the University of Tartu, Estonia, investigated the genetic diversity of the dingo by analyzing the genomes of over 800 dogs from around the world, including wild canids, dingoes, and domestic dogs.