Recent research from scientists at the University of Minnesota has revealed a new method for driving electrocatalytic reactions using voltage rather than metallic catalysts. This breakthrough opens up the possibility of using nonmetallic catalysts to drive electrochemical reactions, which could lead to more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly processes. The team developed a method for driving electrocatalytic reactions using voltage in aqueous buffer solution. Their method involves applying a voltage to the reaction solution, which then drives the reaction at the electrode surface without the need for a metal catalyst.

A recent discovery of a new method for the efficient sieving of fuel molecules has the potential to revolutionize the renewable energy industry. Scientists at the University of Manchester have developed a new technique that uses graphene oxide to sieve fuel molecules. Graphene oxide is a material that is derived from graphene, an atomically thin layer of carbon atoms arranged in two-dimensional honeycomb lattices. Graphene oxide has a unique network of oxygen-containing groups that allow it to act as a highly efficient molecular sieve.
Glass is a remarkable material that has been used for centuries in a variety of applications. It has many unique properties and has been studied extensively for its special characteristics. Now, researchers at the University of Toronto have discovered something new about glassy liquids—they are fundamentally different from their solid counterparts. The U of T team has been studying the behavior of glassy liquids in extreme conditions, and their findings shed new light on the mysterious nature of these materials.

Recent research out of the University of Toronto has uncovered the composition and regulatory mechanism of the nucleolar protein. This breakthrough discovery has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of how cells control their gene expression. By elucidating the molecular components of the nucleolar protein, scientists can now track its activities and identify how it influences gene expression. This could lead to potential treatments for a variety of diseases, including cancer, and provide new insights into the development of therapeutic drugs.

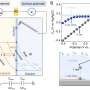
Today, a new study reveals that the cosmic star formation rate was much higher during the early universe than previously thought. Results from the study, conducted by an international team of researchers, show that the cosmic star formation rate peaked 10 billion years ago—about three billion years earlier than previously believed. The findings provide valuable insight into the early evolution of galaxies and the universe as a whole.
The team of researchers used data from the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories to observe over 10,000 galaxies in the distant universe.

As the world continues to make strides in the fight against new and existing illnesses, scientists and pharmaceutical companies are turning to machine learning to help speed up and improve the drug discovery process.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh have developed a method of using machine learning algorithms to identify the most efficient way to reduce the number of steps required in the drug discovery process. This method, called fold reduction, works by analyzing the structure of a particular drug molecule and identifying which steps in the drug design process are unnecessary.
Scientists have developed a new technique to filter carbon nanotubes from a solution, which could lead to a new paradigm in dialysis. By using a nanofiltration membrane that is able to selectively remove carbon nanotubes from a solution, researchers have created the first filter capable of removing nanotubes from aqueous solutions. This new technique could be used to help clean up contaminated water and to help diagnose and treat diseases. The breakthrough could also open up new possibilities for manufacturing and engineering applications.

A new type of diffractive optics has been developed that could revolutionize the way we view virtual reality. By combining liquid crystal and diffractive optics, scientists have created achromatic diffractive liquid crystal optics (ADLCO) that could open up new possibilities in virtual reality, from better image quality to more efficient light utilization. ADLCO works by controlling the light passing through liquid crystal layers, directing it to the desired location. This allows for more efficient light utilization and improved image quality, as the light is more accurately focused on the user’s eyes.
Today, a new video released by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) provides an incredible glimpse of the world beneath the waves. The video captured by NOAA’s remotely operated underwater vehicle, which was sent to explore the depths of the Pacific ocean off the coast of Washington State, showcases a pod of Pacific white-sided dolphins, a serene group of Pacific harbor seals, and a humpback whale shooting water spouts from its blowholes.

Research from the University of Southern California has developed a new nanoparticle-based vaccine candidate for protection against tick-borne diseases. This groundbreaking new vaccine candidate is set to revolutionize the way we protect ourselves against tick-borne illnesses. The nanoparticle vaccine candidate is made up of a combination of small pieces of proteins from several tick-borne diseases, which are then delivered to the body via a nanoparticle. This novel approach to vaccination could help to protect us from a range of different diseases, including Lyme Disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and other illnesses caused by ticks.

Recently, scientists have been exploring the potential of using entangled particles to create wormholes in general relativity. The idea is that if two particles are entangled, they can be used to create a bridge between two points in space-time, which could potentially be used to travel through time and space. While the research is still in its early stages, researchers are hopeful that this could offer a novel way of probing the mysteries of the universe.
Recently, archeologists were shocked to discover vandalism of an ancient pictograph in Bon Echo Provincial Park, Ontario. The pictograph, estimated to be more than 4,000 years old, was defaced with a spray-painted cross and the phrase “Jesus Saves”. The pictograph is painted onto a large boulder that is part of an ancient rock shelter, and is believed to date back to the Late Archaic period. This vandalism has been met with shock and dismay from the archeologists who study the site, as well as community members and Indigenous groups who are connected to the area.

A major research breakthrough has just been announced! Scientists have for the first time successfully observed the earliest stages of human embryonic development in detail. Using a unique technology called “time-lapse imaging,” researchers at the University of Cambridge were able to capture the earliest stages of embryonic development, from fertilized egg to blastocyst stage, in an unprecedented level of detail. This breakthrough will provide invaluable insight into the development of the human embryo and could lead to improved treatments for infertility and other reproductive disorders.

Scientists have recently discovered a new pathway to explore the quantum Hall effect, a phenomenon in which materials can conduct electricity with zero resistance. This pathway involves a type of material known as a topological material, which exhibits unique properties that allow for the exploration of the quantum Hall effect. Topological materials have the potential to revolutionize the field of electronics and could lead to the development of highly efficient energy-saving technologies.

NASA recently announced that they have launched a new mission to study the atmospheric environment of space. The mission, called the Space Environment Testbeds (SET), is designed to collect data about the environment of Earth’s upper atmosphere. This data will help to better understand the physics of our atmosphere, and how it interacts with our planet and the universe around us. With this new mission, NASA hopes to gain a better understanding of how the atmosphere affects satellite and spacecraft operations.

Scientists have been studying the possibility of making contact with extraterrestrial life for decades. Today, a new study published in the journal Astrobiology shows that humanity may be closer to making contact with extraterrestrial life than ever before. The study was conducted by a team of researchers from the University of Edinburgh, and it looks at the potential of using technology to detect and communicate with alien civilizations. According to the research, the current rate of technological development suggests that humanity has a good chance of establishing contact with extraterrestrial life in the next couple of decades.

NASA’s newest rover, the Autonomous Perseverance, is ready to take on the challenge of exploring Mars. Set to launch in July of 2023, Perseverance will be the first rover to be fully autonomous, meaning it will be able to make decisions on its own without human input. Perseverance is equipped with a suite of science instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and a drill. It will be able to explore the surface of Mars, search for signs of ancient microbial life, and collect rock and soil samples for return to Earth.

A recent study has uncovered a significant breakthrough in our understanding of embryo cancer metastasis. Scientists at the University of California, San Francisco, have discovered a cell-level mechanism that allows cancer cells to spread from an embryo to other parts of the body. This research has uncovered a crucial link between cancer metastasis in embryos and the process of cell migration.
This discovery could provide the basis for a better understanding of cancer metastasis in embryos and how it can be prevented or treated.
In September 2023, generative AI will be in the majority of college classrooms across the country. This groundbreaking technology has been designed to help educators and students alike, by providing personalized learning experiences. Generative AI can identify and tailor material to each student’s interests and learning style, as well as providing real-time feedback on their performance and progress. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we learn and teach, by providing a much more personalized experience to every student.

Scientists have discovered a new way to form structurally stable supramolecular complexes using azobenzene molecules, a type of organic molecule that can be used to manipulate light. This discovery has the potential to revolutionize the development of optical materials, leading to the production of more efficient and cost-effective optical systems.
In a recent study, researchers were able to create a supramolecular complex with a high degree of structural stability using the small azobenzene molecules.
A team of researchers from the University of Cambridge have developed a new solar-powered electrode made from diamond materials, which could revolutionize the way scientists study spectroscopy. This groundbreaking technology could help scientists understand more about chemical and biological processes, as well as other physical phenomena. The diamond-based electrode is made from a thin layer of synthetic diamond material that is coated with an electrochemically active material. This coating allows the electrode to absorb light from the sun and convert it into electrical energy, which can then be used to power spectroscopic experiments.

A recent study has revealed the fascinating discovery of a parasitic worm that is able to convince its hosts to eat its own flesh. This is the first example of such behavior in any known parasitic species. The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Calgary, found that the parasite, known as Cordiceps pustulata, is able to manipulate its hosts into consuming its own body parts, even though it can be fatal to the host.

Astronomers are excited to announce a new breakthrough using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). For the first time, they have detected the earliest stages of a supernova explosion, giving them the opportunity to study the birth and death of stars. This is an important milestone in understanding how stars come to be and how they die. The team of astronomers used the JWST to observe the supernova in the galaxy NGC 4258, which is located about 23.
Experts recommend that teacher well-being be a priority in schools, and now there is research to back it up. A recent study found that when teachers felt supported in their work, it had a positive impact on the quality of education they provided. The study also found that when teachers felt appreciated and valued, they were more likely to stay in their jobs. This is important because teacher retention is key to having a successful school.

NASA is getting ready for a new space telescope called SPHEREx. This telescope will be able to take an unprecedented look into the universe, gathering data on galaxies, stars, and everything in between. SPHEREx will have the ability to measure the composition of galaxies and stars, giving us insight into how the universe has evolved over time. SPHEREx will also be used to search for clues about dark energy and dark matter, two mysterious substances that make up most of the universe.

