Today, scientists have made an incredible discovery in the fight against dengue fever: mosquitoes have a strategy to avoid transmitting the virus. Researchers from the University of Liverpool have found that mosquitoes have an innate ability to recognize the presence of dengue virus in the bloodstream and actively avoid transmitting it. This incredible finding could have important implications for controlling the spread of dengue fever and other diseases spread by mosquitoes.

Astronomers have recently made an incredible discovery: the abundance of Milky Way-like galaxies in the universe is much higher than previously thought. By examining the properties of galaxies across billions of light years, they have been able to determine that these galaxies actually make up the majority of galaxies in the universe. This means that our own Milky Way galaxy is not as rare as we once thought, and that there are many other galaxies out there that are similar to it.

Today marks a bittersweet moment for the Puget Sound orca community. Tokitae, the beloved 74-year-old matriarch of the Southern Resident Killer Whales, has passed away. Her death was announced by the Whale Museum in Friday Harbor, Washington, where Tokitae was remembered for her strength, wisdom, and courage.
Her ashes will be spread in the waters of the Salish Sea, her home for many years. This will be a special moment for the community, many of whom have been following and loving Tokitae since she was first seen in the 1970s.

It’s almost that time of year again! On Wednesday, September 23rd, the fall equinox will occur in the Northern Hemisphere marking the official start of autumn. During this time, day and night will be almost equal in length, with the sun rising due east and setting due west. This is a special moment of balance in our yearly cycle that celebrates the transition from summer to fall. As the days start to grow shorter and the weather begins to cool, now is a great time to take a moment to appreciate the changing of the seasons and the beauty of nature.

Do you ever feel guilty after throwing away the paper cup and plastic lid from your daily morning coffee? Well, feel no more! Scientists have discovered a new way to make use of your coffee grounds, and it could help in the fight against plastic pollution.
Researchers have developed a process to turn spent coffee grounds into an alternative to plastic. This new material is strong, water-resistant, and biodegradable, making it perfect for use in food packaging and other everyday items.

A new study published in the journal Nature Astronomy has revealed that stars in the Milky Way may be connected to their descendants billions of years later. Using data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia satellite, researchers from the University of Edinburgh were able to trace the paths of stars and connect them to their descendants in the present day. This groundbreaking research is providing new insights into the evolution of the Milky Way galaxy, including how stars form and move over time.

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced their first mission to explore the moon’s sulfur-rich environment. With the launch of Chandrayaan-2, the ISRO will be the first to explore the moon’s surface and subsurface for sulfur. This could provide new insight into the moon’s geology and the potential for future science and exploration. The mission, set to launch in 2023, will be the first to investigate the sulfur-rich environment, which could open the door to new lunar science.

The Parker Solar Probe is about to embark on an historic mission that will take it closer to the sun than any other spacecraft before it. On September 2, 2023, the spacecraft will be launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida on a seven year mission to explore the sun’s atmosphere and the origins of the solar wind. The spacecraft will fly within 6.2 million kilometres of the sun’s surface—closer than any other spacecraft has ever gone—and will experience temperatures of over 1,300°C and a solar radiation intensity more than 500 times greater than on Earth.

Today, scientists from all over the world have made an exciting discovery: the days on Mars are now the same length as the days on Earth! This is due to the recent successful landing of a solar-powered station on the Red Planet. The station was able to measure the exact length of a day on Mars and, much to the surprise of the scientific community, it was found to be 24 hours and 37 minutes.

Recent research has uncovered a new way of exploring the relationship between thermalization and quantum dynamics. This research, conducted by a team of scientists at QuTech in the Netherlands, has revealed a new approach to understanding the thermal behavior of quantum systems, and potentially even controlling it. The team’s findings could be a major step forward in developing quantum technologies with improved control and accuracy.
The team’s findings suggest that controlling the thermalization of quantum systems is more than just a matter of changing the temperature of the environment.

Astronomers have discovered a vast population of newborn galaxies in the distant universe thanks to the power of the James Webb Space Telescope. The results, published today in The Astrophysical Journal, reveal a population of galaxies that were previously undetected with current telescopes. The discovery provides a unique window into the earliest stages of galaxy formation.
Today, astronomers have announced a remarkable discovery with the help of the James Webb Space Telescope - a vast population of newborn galaxies in the distant universe!

In a new study, scientists have proposed a new way of looking at black holes that could explain some of their mysteries. By analyzing the properties of Kerr black holes, the researchers have proposed that these black holes can actually amplify the amount of energy they emit. This could help explain why black holes appear to be so bright and active in space. The findings could also lead to a better understanding of how black holes interact with their environment.

NASA is about to take a very special journey. In September 2023, their spacecraft, OSIRIS-REx, will bring back the first ever samples of material from an asteroid back to Earth! This groundbreaking mission will be the first of its kind, and it’s sure to bring us a wealth of new knowledge about our Solar System and the origins of our Universe. OSIRIS-REx will travel to the asteroid Bennu, which is located hundreds of millions of miles away from Earth, and collect a sample of the asteroid’s surface material.

A new method for purifying contaminated glyphosate has been developed by Brazilian researchers. The breakthrough could help reduce the environmental risks posed by glyphosate, a commonly used herbicide and weed killer. The method involves using a combination of natural materials to filter out glyphosate and other contaminants from water sources. The researchers believe their method could be used to help protect rivers, lakes, and other water bodies from glyphosate contamination. The findings of the study have been published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology.

Palm oil is a type of vegetable oil derived from the fruit of oil palms and widely used in many products like chocolate bars, snack foods, and cosmetics. Unfortunately, the production of palm oil is linked to severe deforestation, which has caused many species of plants and animals to suffer immeasurably.
Today, we’re seeing the devastating effects of deforestation caused by palm oil production. According to recent studies, global deforestation rates have increased by more than 50% since the 1990s due to the expansion of palm oil plantations.

Recently, scientists have discovered an exoplanet orbiting the star Gliese 887, just 11 light-years away. This exoplanet is unique among known exoplanets because it is a solid ball of rock, with no atmosphere and no water. This makes it the closest known rocky planet to Earth. The planet is about 1.3 times the size of Earth and has a mass of 7.2 times that of Earth. It is tidally locked, meaning one side always faces the star, and the far side is in permanent darkness.

Space exploration and colonization has long been a dream of humankind. We have been intrigued by the idea of living in a world beyond our own, where the boundaries of possibility are infinite. In recent years, space exploration and colonization has become a more tangible goal, with companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin leading the charge. The idea of space exploration and colonization is both exciting and daunting, and there are many questions that still need to be answered.

A groundbreaking new study has revealed that mere chemical exposure can cause long-term changes in behaviour. Researchers from the University of Southern California (USC) and the University of North Carolina (UNC) looked at the effects of chemicals on mice. The team found that even low levels of exposure can cause changes in behaviour that last for up to a year.
This study is a game-changer for the field of toxicology, as it demonstrates for the first time that chemicals can have long-term behavioural consequences.

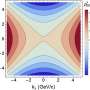
Recently, physicists have discovered a new type of particle, called a vector meson. This new particle could give us the answers to some of the fundamental mysteries of our universe. By studying the properties of the vector meson, we could gain insight into the nature of dark matter, the origin of mass, and the behavior of quarks and gluons. The vector meson could also help us understand how the universe works at its most basic level.
Today, scientists from the University of California, San Diego, have made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of post-translational modification. They have discovered that histidine can be methylated, a process which modifies the structure and function of proteins. This finding could have implications for a variety of diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. By understanding more about how histidine methylation works, researchers may be able to develop new treatments and therapies for these diseases.
A new study has revealed that Africa, the ancestral homeland of all humans, is home to a unique and deep genetic diversity. Using data from the 1000 Genomes Project, an international effort to create a reference map of human genetic variation, scientists were able to construct a timeline of human genetic history. The research team, led by the University of Pavia, was able to trace the genetic history of Africa back to its earliest human inhabitants, who lived in the region over 200,000 years ago.

The future of computing is here — cloud-based quantum computing is set to revolutionize the way we think about data processing. A new study, published in Nature Communications, has found that cloud-based quantum computing is capable of providing a “quantum advantage” over traditional computing. This means that quantum computing can solve certain problems much more quickly and efficiently than traditional computers. The study also found that cloud-based quantum computing is more secure and reliable than traditional computing.

Today, researchers have created a new way to encrypt and secure smartphones, using 3D printing and dual light-emitting materials. This breakthrough technology combines the best of 3D printing and light-emitting materials to create an encryption key that is virtually impossible to hack. The key is created through a unique 3D printing process, using dual light-emitting materials to create a pattern of light and dark areas that are visible only when viewed from specific angles.

In a recent breakthrough, German scientists have developed an innovative method for generating homozygous mutant populations in barley. This method, which uses high throughput phenotyping, has the potential to revolutionize the way genetic studies are conducted in the field of plant biology. By providing an efficient and cost-effective way to generate homozygous mutants, researchers are able to identify and study novel traits that are not possible with traditional methods. This new technique could open up a whole new range of possibilities for research in the field of plant biology.

Gold nanoclusters have been found to be an effective material for electrochemical hydrogen production. Scientists recently discovered that gold nanoclusters could be used to produce hydrogen in a more efficient and cost-effective manner than existing materials. The researchers used a combination of theoretical and experimental approaches to study the properties of the gold nanoclusters, and their findings could lead to a new generation of materials for electrochemical hydrogen production. The gold nanoclusters showed a high catalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction, allowing them to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen more quickly and efficiently.

