
Today, chemists have developed a new machine that has the potential to revolutionize the field of anticancer drug discovery. The machine, called a molecular potential machine (MPM), is capable of rapidly simulating the behavior of small, organic molecules, such as those used in chemotherapy drugs. This is a significant breakthrough, as it increases the speed and accuracy in which potential drugs can be developed. With this technology, researchers can quickly identify molecules that are most likely to interact with cancer cells and create a drug that will target them.

Scientists have recently developed a new technology that could revolutionize the world of catalytic technology. The technology, called electromagnetic field assisted thermal catalysis (EMFAT), is capable of greatly improving the efficiency of catalytic reactions, which are essential in many industrial processes. This new technology has the potential to reduce the energy costs associated with catalytic reactions, as well as reduce the environmental impact of these processes. EMFAT works by applying an alternating electrical signal to the catalytic surface.
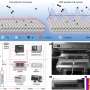
In a revolutionary breakthrough, scientists have developed a method to manipulate glass using femtosecond laser pulses. This method allows them to alter the optical and mechanical properties of the glass without melting it. The new development could pave the way for a variety of new applications in industry, medicine, and research.
This latest development is a major step forward in the manipulation of glass materials. By using femtosecond laser pulses, scientists can alter the physical and optical properties of glass without melting it.

In a new study published in the journal Nanomaterials, researchers from the University of California San Diego have revealed the potential of mineral nanoparticles as nanozyme mimics. Nanozymes are artificial enzyme-like molecules that can catalyze chemical reactions in the body without the need for enzymes. The study found that mineral nanoparticles, such as iron oxide and titanium dioxide, can act as nanozyme mimics, which could potentially be used to treat various diseases.
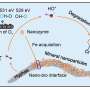
In the future, medical imaging could become less invasive and more accurate thanks to a new technology developed by scientists. The technology, called optoacoustics, combines MRI, ultrasound, and optical imaging into one device, making it possible to capture images of soft tissues inside the body with unparalleled detail. The device is also able to detect the presence of disease in the body before it becomes visible on traditional imaging methods. With this new technology, doctors will be able to more accurately diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions, from cancer to heart disease.
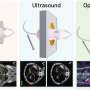
Recent research has revealed an exciting new technique for boosting second harmonic generation in materials. By stacking two layers of strain on top of each other, scientists were able to dramatically enhance second harmonic generation in a sample of lithium niobate. This finding could be used to develop new kinds of optical devices for data transmission, signal processing, and sensing. By applying two layers of strain, scientists were able to produce an effect that was more than twice as strong as what could be achieved with just one layer.
Astronomers have made a major breakthrough in understanding how supermassive black holes form and evolve over time. An international team of astronomers, led by researchers at the University of Cambridge, have found evidence that these giant black holes can form in two different ways. By studying the structure of supermassive black holes in the early universe, the team was able to distinguish between two evolutionary paths that the black holes can take.

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) recently observed a quiescent galaxy that is massive and compact, unlike any other galaxy ever seen before. This discovery has led to a new understanding of how galaxies like this form and evolve.
The galaxy, named MQGC-1, was observed by the JWST for the first time, and it is located about 12.7 billion light-years away in the constellation of Draco. The galaxy is estimated to be about 6.

The infamous ‘eagle killer’ bacterium, Streptococcus pyogenes, has been found to produce toxins that are potentially more harmful to human health than previously thought. Researchers from the University of Zurich have discovered that the bacterium produces two distinct toxins—one of which is capable of destroying bacterial cell walls, while the other has the potential to damage human tissues. This finding could pave the way for new treatments against the bacterium, which is responsible for numerous infections, including strep throat and skin infections.

Scientists have recently developed a new way to make use of glass by-products from windshield and window manufacturing. This new method involves using these glass by-products to create protective coatings for wood. This breakthrough technology not only allows us to repurpose these materials, but also provides a layer of protection for wood that makes it more durable and longer-lasting. The coating is applied using a process similar to painting, and the glass by-products are melted down and mixed with a resin to form a protective layer.

Recently, researchers from the University of Vienna have discovered the memory-induced Magnus effect, an unexpected curveball in the physics of sports. The Magnus effect is a phenomenon where a spinning ball curves away from its expected path due to the interaction between the air and the spin of the ball. Until now, this effect was known to only occur when the ball was moving. But the Vienna team has discovered that this effect can also occur when the ball is stationary, and the memory of its previous spin affects the air around it.
The world of nanotechnology is constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible, and a recent breakthrough from researchers at the University of Pittsburgh is no exception. By introducing thiol ligands to a metal nanocluster, they were able to create a material with an unprecedented degree of optical clarity. This breakthrough could have major implications for the fields of optics and photonics, as the material is capable of transmitting light with a bandwidth of up to several hundred nanometers.
Today, scientists from the Institute of Molecular Biology have announced a major breakthrough in the field of oil production. They have discovered a species of yeast that can be used to form oil that can be used in a variety of industrial, commercial, and personal applications. This new species of yeast, known as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is capable of forming oil at a much higher rate than other yeasts that have been studied in the past.

Nanotechnology is revolutionizing the medical field, and a new discovery at the University of California, Davis has the potential to make a major impact on treating bacterial infections. Scientists have developed a safe nanocarrier that can deliver antibiotics directly to bacterial cells, without killing healthy cells in the body. This nanocarrier acts like a Trojan horse, delivering the antibiotics directly to the bacterial cells without harming other cells. This could help reduce the amount of antibiotics needed to fight infections, which could prevent antibiotic resistance and reduce the risk of side effects from antibiotic treatments.

Today, an exciting breakthrough in cancer research has been announced! A team of scientists have developed a unique method for studying cancer cells in the lab. By using a combination of genetic engineering, artificial intelligence, and 3D printing, they are able to create models of cancer cells that mimic the behavior of real cancer cells in the body. This new method offers researchers a better way to study cancer and could lead to new treatments and cures for the disease.
“A new method of automatically measuring the growth rate of broiler chickens has been developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge. The new system could help farmers to more accurately predict the growth rate of their chickens, as well as provide a more humane way of measuring it.
The new method uses infrared sensors to measure body temperature, which can then be used to calculate the growth rate of the birds.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered that life may be possible on Mars, and other planets beyond our solar system. Researchers have used Artificial Intelligence (AI) to develop a new technology that can detect and analyze the atmosphere of distant planets, making it easier to detect signs of life. By combining data from telescopes with AI algorithms, researchers are able to study the atmospheres of other planets and identify any potential signs of life.

Scientists have recently announced an incredible breakthrough in space exploration. After years of research and development, a spacecraft that was launched in 2023 has successfully collected and brought to Earth a sample from an asteroid! This is an exciting moment in space exploration as it marks the first time ever that a sample from a celestial body outside of the Earth has been retrieved. This is a major step forward for our understanding of the universe and will no doubt lead to further scientific discoveries.

A recent study conducted by a team of scientists has discovered a potential breakthrough in the fight against cancer. After decades of research, the team has developed a theory that nanoparticles can be used to treat tumors. The study found that when certain nanoparticles are injected into the body, they can specifically target and attach to malignant tumors, allowing for localized drug delivery to the tumor. This could prove to be a much more effective way to fight cancer than traditional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation.
Are student satisfaction surveys an effective tool to measure the success of a college or university? It’s a hotly contested question, but a new methodology has been developed to try to settle the debate. The new methodology, developed by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, uses a combination of quantitative and qualitative data to measure student satisfaction in a more comprehensive way. Rather than relying solely on survey responses, the researchers focus on student engagement and interaction with faculty, staff, and the institution as a whole.

Exploring life at 125F: Scientists have made a major discovery about the limits of life on Earth. Researchers have found that the bacteria Thermococcus gammatolerans can survive and thrive at temperatures as high as 125F (51.7C). This is the highest temperature ever recorded for a living organism and offers insight into the potential for life in some of the most extreme environments on Earth. This study offers hope for finding life in places like hydrothermal vents and other extreme heat environments, and could potentially lead to the discovery of new species of bacteria that could have applications in biotechnology.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered a new way to construct nanomaterials that could revolutionize the way we think about manufacturing. Through a technique called “bottom-up” assembly, scientists can now create nanomaterials with precise control of their physical and chemical properties. The technique involves building up molecules from the bottom up, rather than the traditional top-down approach, which involves breaking down large molecules to smaller parts. This new approach enables scientists to precisely control the size, shape, and composition of nanomaterials, making them more efficient and effective for applications such as energy storage, photonics, catalysis, and biomedicine.

The Hubble Space Telescope has recently made a remarkable discovery near the constellation Draco: a peculiar pair of galaxies known as Arp 142. The galaxies, known as NGC 2936 and NGC 2937, are located approximately 140 million light-years from Earth and have been gravitationally distorted by their close proximity to each other, a phenomenon known as ‘tidal interaction.’ The two galaxies have been pulled and stretched into their current shapes, sparking a brilliant display of star formation around their edges.

Scientists have recently discovered a new type of fungi in space! This remarkable finding was made using a series of experiments conducted in the International Space Station (ISS) which analyzed how gravity affects the growth of fungi. Through their research, the scientists determined that fungi can survive and even thrive in a low-gravity environment, suggesting that they may be able to survive and even potentially colonize other planets in our solar system.

The long-awaited James Webb Space Telescope is set to launch in early 2023, and it promises to revolutionize astronomy and space exploration. With its powerful spectrometer, the telescope will be able to analyze the spectrum of light from distant stars and galaxies, giving us an unprecedented glimpse into the universe. Astronomers will be able to measure temperatures, compositions, and velocities of stars and galaxies, as well as detect signatures of planets and even molecules in dust clouds.

