Today, scientists announced a major breakthrough in space exploration - the discovery of a radio emission coming from the far side of the moon! This groundbreaking discovery was made with the help of the Chang’e 4 spacecraft, which landed on the far side of the moon last January. According to the study, the radio emission was detected in the frequency range of 100-800 MHz, indicating the presence of a plasma environment.

A new study has discovered a way to take a close-up look at some of the most intricate and tiny biological nanomachines ever seen. Using a novel combination of sophisticated imaging techniques, researchers from the University of California, San Diego and the University of California, San Francisco have been able to look deep inside a cell’s peroxisomes - tiny organelles responsible for a variety of metabolic processes.
This is an exciting breakthrough that could revolutionize our understanding of the inner workings of biological nanomachines.

A recent study conducted by astronomers from the European Space Agency has revealed a startling discovery: our galaxy is teeming with planets that could be similar to Earth. Using data collected by the Gaia mission, the team identified over 300 exoplanets that could have Earth-like characteristics such as rocky surfaces, temperatures suitable for liquid water, and potential for life. This is an incredible breakthrough in the search for habitable planets in our Milky Way.

In a recent breakthrough, researchers from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln have discovered a way to reduce the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers using genetically associated diazotrophs. Diazotrophs are bacteria that can fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, allowing for the growth of nitrogen-rich crops. By introducing these bacteria into the plant’s genetic material, they can convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by plants. This could potentially reduce the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, which are often harmful to the environment and costly to produce.
Recent advances in genomics have revealed new insights into the biology of pest moths. By sequencing the genomes of two pest moths, the cotton bollworm and the tomato leafminer, researchers were able to identify key genes that may be responsible for the moths’ ability to damage crops. This information can be used to develop new strategies to control and manage these pests. In addition, the genomes revealed the presence of several genes that can be manipulated to create more effective pest management tactics, such as releasing pest-resistant crop varieties.
Today marks a major milestone in the construction of the Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT)! The first of seven primary mirror segments, which will make up the GMT’s 24.5 meter-diameter primary mirror, has been completed after three years of hard work. This segment is the largest of its kind ever created, consisting of 81 individual hexagonal pieces. Each hexagonal piece is made from a combination of borosilicate glass and ceramics to ensure its durability and accuracy.

A new study conducted by researchers from the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) has found a link between iron deficiency and cell growth. The findings, published in the journal Nature Metabolism, suggest that cells deprived of iron can’t grow as quickly as they normally would, making them more vulnerable to disease. This could lead to novel treatments for diseases caused by faulty cell growth, such as cancer.
Researchers studied human cultured cells that lacked a protein called transferrin receptor 1, which helps cells absorb iron from the body.
As space exploration advances, some scientists are researching ways to make planets more habitable for humans. A recent study has suggested that the use of megastructures, such as orbiting space habitats and large-scale terraforming projects, may be the key to creating livable worlds in other solar systems. This could open up new possibilities for human exploration and colonization of distant planets, allowing us to venture further into the unknown than ever before.

Thermal Magic is an ambitious new thermometry camera that is revolutionizing the way we measure temperature. This innovative camera is capable of quickly and accurately measuring the temperatures of objects without the need for contact. It boasts a wide range of features, including a 6.2-megapixel resolution, a wide temperature range from -40 to +300 degrees Celsius, and a rapid response time of only 50 milliseconds. Thermal Magic offers unprecedented accuracy and flexibility in thermometry, allowing users to measure temperatures of moving objects, measure multiple targets simultaneously, and create thermal images quickly and easily.

The Australian government has just announced the launch of a new national skills passport, which will help connect workers with employers and provide greater transparency in the labour market. The passport will provide an easy way for workers to present their skills and qualifications to employers, and employers will be able to see the skills of potential employees quickly and easily. This will help to ensure that employers are hiring the right people for the right jobs, and ensure that workers are getting paid what they are worth.

NASA has just released the first image of the darkest moon in known history! Captured by the telescope onboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, the photo reveals a never-before-seen side of Earth’s only natural satellite. Scientists have long known that the moon has dark patches, but this is the darkest one yet. The patch is so dark that it’s almost the same color as the surrounding terrain. Scientists believe this patch could hold clues to the moon’s composition, as well as how it was formed billions of years ago.

NASA is gearing up for an unprecedented mission to explore interstellar space beyond our solar system. We will send an interstellar probe to explore the mysteries of the universe and to uncover secrets that have been hidden for years. This new probe will be the first of its kind and has the potential to reveal insights into the physics of interstellar space, the origin and evolution of our universe, and even the possibility of extraterrestrial life.

NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has successfully landed in Houston, Texas, after a 6-year journey! This marks the first-ever return of a sample of an asteroid to Earth, and the first sample from a primitive, carbon-rich body that could yield clues to the solar system’s earliest days. The sample-return capsule is carrying more than 2.1 ounces of material from the asteroid Bennu, which was collected during a series of touch-and-go maneuvers last October.

Vitamin B12 is essential for human health, but it can be hard to get enough of it in our diets. Now, researchers have made a breakthrough in creating a sustainable way to get a daily dose of B12: pea-derived B12. This innovative new source of the essential vitamin has been found to be as effective as traditional sources. The researchers have developed a method of extracting B12 from peas and then concentrating it into a daily supplement.

The world is facing a major crisis in the declining numbers of endangered wildlife species. The devastating effects of climate change, human activity, and habitat destruction are taking an alarming toll on our species. To help combat this, new laws are being proposed to provide better protection for endangered species.
The new proposed law, titled the Endangered Wildlife Protection and Conservation Act, is an ambitious attempt to address the issue of dwindling wildlife populations.

Scientists have discovered a new way to capture carbon dioxide using minimal nanozymes. These tiny catalysts, which are made up of just a few atoms, are able to reduce carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide with an efficiency that surpasses traditional catalysts. This new method has the potential to revolutionize the way we capture and store carbon dioxide, one of the major contributors to climate change. With the development of these minimal nanozymes, more efficient and cost-effective carbon dioxide capture technologies may be on the horizon.

NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory is rewinding the story of one of the greatest known supernovae of all time, SN 1006. Located in the constellation of Lupus, what remains of SN 1006 is one of the brightest and most complex supernova remnants ever seen. A new Chandra image of the glowing remains of this stellar explosion reveals a bright core with a series of filaments radiating outward. These filaments are formed from the shockwave that was created when the star exploded and is still expanding outward at millions of miles per hour.
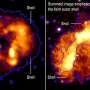
A team of researchers at the University of Birmingham have recently discovered a new form of refractory high-entropy nitride (NbMoTaWHfN) that has a higher melting point than any other known refractory material. This breakthrough has potential implications for the development of equipment that operates under extreme temperatures, such as aerospace and nuclear industry components. The new material was achieved by a technique known as spark plasma sintering, which involved applying a combination of pressure and electricity to a mixture of elements to create a dense and homogenous material.

Today, scientists announced a major breakthrough in nuclear energy: the development of an exascale supercomputer that can run simulations of nuclear reactors. This new technology could revolutionize how we use nuclear energy, allowing us to better understand the behavior of nuclear reactors and make them safer and more efficient. With this new technology, simulations of nuclear reactors can now be done in a fraction of the time that it would have taken before, and with much more accuracy.
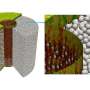
Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in imaging an elusive particle known as a skyrmion. Using a unique form of neutron tomography, they were able to observe the skyrmion in a single crystal of iron-platinum. This is the first time that a skyrmion has been imaged in such a way, and the results could help to better understand the behavior of these particles.
Skyrmions are tiny particles that are made out of magnetic and electric fields and are theorized to play an important role in the fields of quantum computing and spintronics.
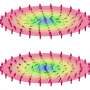
The future of biosensor technology is here, and it’s more exciting than ever. Scientists have developed a new type of bacterial biosensor that can detect and analyze a wide variety of analytes, from toxins to heavy metals. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we monitor and detect contaminants in our environment. By using bacteria as biosensors, scientists hope to provide faster, more accurate readings than traditional methods, and to better protect our environment and population from hazardous chemicals.
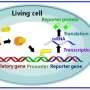
A recent study has uncovered a critical process in the development of cancer cells, which could potentially lead to new treatments and therapies for the disease. The research team at the University of California, San Diego has discovered that chromosomal instability – a phenomenon in which large numbers of chromosomes become rearranged or deleted in cancer cells – can cause the cells to become more aggressive and resistant to treatment. This instability leads to changes in the cells’ DNA, which can result in the production of proteins that allow cancer cells to survive and proliferate.
In a new paper published in Nature, researchers from the University of California, Santa Cruz, have identified a crucial role of a little-known chemical process in the evolution of life on Earth. Dubbed “silent architects”, the process is based on “non-enzymatic” chemical reactions, which occur outside of the cellular environment and have been largely overlooked. In this paper, the team has uncovered how these silent architects have been instrumental in the development of some of the most important molecules that form the basis of life, such as proteins and nucleic acids.

The future of wildlife conservation is here! Researchers have developed a groundbreaking approach that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to track the behavior of animals in the wild. This new technology is capable of recognizing individual animals, understanding their behavior, and predicting their movements. With this unprecedented level of insight, biologists and conservationists can now better understand how animals interact with their environment and how their presence impacts ecosystems. The potential for this technology to make a real difference in wildlife conservation is immense, and we can’t wait to see the results!

We’re living in a world of increasing technological advancement, and this has produced some exciting new developments in the field of holography. A recent breakthrough in holographic hybridization techniques has now enabled the creation of holograms with unprecedented depth of field. This new technique combines the traditional holographic projection method with advanced 3D imaging technologies, allowing for a more realistic and accurate representation of the object being projected. The result is a hologram with a greater sense of depth, allowing viewers to observe the object from different angles, as if it were actually there.