A groundbreaking discovery has been made by a team of researchers that could revolutionize the carrot industry! The researchers have identified two recessive genes that, when combined, can produce an orange carrot. The discovery could lead to a more diverse range of carrot varieties, many of which may be more resistant to disease. It could also pave the way for more flavorful and nutritious carrots for consumers. This is an exciting development for the carrot industry and has the potential to revolutionize how we grow and enjoy carrots!

In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have successfully identified a gene which can be used to produce embryonic stem cells. These stem cells can be grown into any type of tissue or organ in the body, providing a huge potential for medical treatments and therapies. This discovery could revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine, and open the door to a wide range of treatments for chronic diseases. Scientists are already planning to use this gene to create personalized treatments for cancer, diabetes, and other life-threatening illnesses.

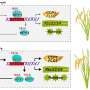
A new study has just revealed a fascinating discovery about a gene called HPY1 that could be the source of increased grain yield in certain crops. Through their research, the team of scientists was able to identify a trait called a “gain of function” allele associated with the gene that is responsible for higher yields. This allele causes the gene to produce a specific protein that works to improve the efficiency of photosynthesis within the plant.
Astronomers have recently witnessed an incredible phenomenon - the growth of baby galaxies! Using the powerful James Webb Space Telescope, researchers have been able to observe the birth of new galaxies as never before. By studying the formation of these galaxies, astronomers can better understand how galaxies form and evolve over time. This knowledge could help us to better understand the universe and our place in it.
Read Full Article Here

The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has just taken a giant step forward in subatomic particle physics. Scientists at CERN have successfully collided lead ions at the highest energy levels ever achieved. This will allow researchers to explore the properties of quark-gluon plasma, the state of matter thought to have existed in the first moments after the Big Bang. This new capability could also lead to the discovery of new particles and insights into the structure of matter.

Scientists have just unveiled a revolutionary new X-ray microscope that is set to revolutionize the way we view the world around us. This new microscope, called the XFEL, is the first of its kind that can capture images of nanoscale objects in unprecedented detail. By using extremely short pulses of X-rays, the XFEL is able to capture images of objects that are too small to be seen with conventional microscopes. This new technology is expected to provide a wealth of new insights into the deep structure of matter, and could help to answer some of the most pressing questions in science.
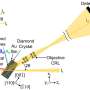
Recent breakthroughs in multi-sensor fusion methods are revolutionizing the way we interact with machines and devices, allowing them to rapidly and accurately detect and interpret the data they receive. By combining multiple sensors, such as cameras, microphones, and radar, these methods can better recognize objects, sounds, and movements in any environment. This technology can be used in robots, drones, and autonomous vehicles, providing them with the ability to quickly and accurately perceive their surroundings and make decisions accordingly.
Scientists have recently developed a revolutionary photodetector device which produces ultra-broadband detection of light. This device, based on a bilayer structure of graphene and a topological insulator, is the first of its kind to take advantage of both graphene’s high speed and the topological insulator’s high responsivity. This combination of properties makes it the perfect tool for applications such as optical communication, imaging, and sensing. The device is able to detect light from the near infrared to the visible spectrum, across a range of frequencies, with amazing accuracy.

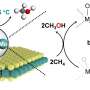
Scientists have recently discovered a way to convert methane gas to oxygen at room temperature. This process could provide a much-needed solution to the global energy crisis, since methane gas is an abundant and renewable resource. The process takes the methane gas and combines it with a copper and nitrogen based catalyst to produce oxygen and solid carbon. This could be used to produce oxygen for industrial uses, as well as provide a source of clean energy.
A groundbreaking scientific advancement has just recently been made in the field of cell engineering. Scientists have developed a new technique that allows them to reprogram cells to behave like stem cells, giving them the potential to regenerate and repair damaged tissue. This advancement has the potential to revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine, allowing for tissue and organs to be repaired or replaced in a much more efficient manner. This breakthrough will be a huge step forward in our understanding of cell biology and genetics, and could potentially be the key to curing many previously untreatable diseases.
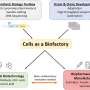
As the world of science continues to advance, so does the use of technologies that can help us better understand our cells and use them to become our own biofactories. A recent study conducted by scientists at the University of California, San Diego, has revealed a new technique that uses nanoscale technology to manipulate individual cells, allowing them to become mini biofactories. This technology could revolutionize the way we develop therapeutic treatments, allowing us to create targeted therapies that could have a positive impact on a range of diseases.
Astronomers have recently discovered an extraordinary mid-infrared outburst coming from a distant, young star. This outburst, likely caused by an eruptive event, is one of the brightest ever seen in the Milky Way.
The star, located in the constellation Cygnus, is approximately 6,500 light-years away and has been classified as a young stellar object. This type of star is still in its formation stages and can vary greatly in brightness. However, the recent mid-infrared outburst was so bright that it was visible from Earth.
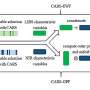
Scientists have just unveiled a revolutionary new tool in the fight against antimicrobial resistance: the BSI-AST Chip. This new chip uses genetic sequencing to rapidly identify and classify bacteria, even those that are resistant to antibiotics. This technology will allow us to make better and more informed decisions about how to treat infections, based on the specific type of bacteria present. This means that infections can be targeted more effectively with the right antibiotics, and that the spread of antimicrobial resistance can be slowed.

Today, Chinese astronauts have completed the incredible feat of setting up a base on the moon’s lava plain. This marks the first time in history that humans have been able to construct a permanent dwelling on the moon. The base, which is made up of three parts, is designed to accommodate two astronauts for a long-term stay. The astronauts will be able to carry out research and experiments in the fields of astronomy, lunar geology, and space medicine.

The future of space exploration is looking brighter than ever! A team of researchers from the University of Toronto have been developing a new type of CubeSat, a tiny spacecraft, which is able to fly in formation without any fuel. This is a revolutionary new technology known as “Vega” which could be used to explore space without the need of any propellant. By using the power of the sun, these CubeSats can stay in formation, allowing for a more efficient use of resources.

In a new study published in Nature Astronomy, scientists have uncovered evidence that could help us better understand the evolution of oxygen in the universe. The researchers found that a merger between a white dwarf star and a low-mass companion star could be responsible for the oxygen found in some white dwarfs. This merger would effectively create a new star composed of neon and oxygen, which would make it a very different type of star than what we typically observe.

A new study released this month shows that areas of New York City are facing a growing disparity in income levels. The study, conducted by the New York City Department of Planning, found that median household income in Manhattan’s Financial District has increased by 97% since 2000, while median household income in the Bronx has decreased by 5%. This growing gap in income levels highlights the need for policies that promote economic equity and social mobility in New York City.

A remarkable discovery has been made: antimatter is embracing Earth, falling downward! Scientists have recently discovered that a stream of antimatter particles is falling downward towards Earth from the outer reaches of our solar system. This discovery could potentially revolutionize the way we think about our universe and the laws of physics that govern it. The particles are very low in energy, so they do not pose a threat to us or our environment.

In a fascinating new study, researchers have revisited the mass of the Milky Way and determined it to be significantly smaller than previously thought. This new finding has major implications for our understanding of the evolution of our galaxy and the cosmology of the universe. The study, conducted by a team of international astronomers, has been published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
This groundbreaking research challenges our understanding of the Milky Way’s mass, which has been estimated to be around 1.

In a major breakthrough for regenerative medicine, scientists have discovered a new way to use cell transplants to regenerate cells and tissues in the body. The breakthrough, which was recently published in the journal Nature, is the result of a collaboration between researchers from the University of Cambridge, the University of Oxford, and the University of Manchester.
The team of scientists used a revolutionary technique known as “cell transplantation” to regenerate cells and tissues in the body.
NASA has announced a groundbreaking new mission: sending astronauts to live in space for an entire year! This mission will be the longest human spaceflight mission ever attempted and will involve four astronauts living and working in space for 365 days. The mission is set to launch in 2023, and it is sure to be an incredible journey that will teach us a lot about the effects of long-term spaceflight on the human body.

Recent research has revealed that RNA may have a larger role to play in the origin of life than previously thought. Scientists from the University of Washington have been studying the role of RNA in the development of life and have discovered that RNA can be used to create structures that form the basis for life. These structures, called “membrane-less organelles,” are collections of proteins and other molecules that are believed to be necessary for life to exist.
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have discovered a quorum sensing circuit in the mosquito gut that is essential for the mosquito to survive with its commensal bacteria. By understanding the quorum sensing circuit, researchers are one step closer to understanding how the mosquito can be protected from disease-causing bacteria. The findings, published in Nature Communications, could pave the way for novel approaches to controlling mosquito-borne diseases.
Do you ever wonder how mosquitoes are able to survive with their commensal bacteria?

A team of astronomers have recently discovered a new radio galaxy, known as M87, and the discovery has shed new light on the mysteries of black holes. What makes this radio galaxy unique is that it is located near the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. By studying the radio galaxy, the astronomers were able to obtain valuable information about the behavior of a black hole. For instance, they were able to discover that M87 is the closest radio galaxy to an observed supermassive black hole.

In a breakthrough for nanotechnology, researchers have developed a way to integrate particles into graphene. The discovery could lead to a new class of graphene-based materials with enhanced properties.
Particles embedded in graphene could create new materials with enhanced properties, such as electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. Researchers at the University of Würzburg in Germany have developed a new method for integrating particles into graphene. The technique involves using a laser to create tiny holes in the graphene, then adding the desired particles.