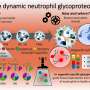
A new discovery has shed light on how immune cells respond to stimuli at a subcellular level. Scientists from the University of Georgia have discovered that a single immune cell, known as a T helper cell, can be activated through a complex process of interacting with multiple signals. This groundbreaking finding is providing researchers with a better understanding of how the immune system functions, which could ultimately lead to more effective treatments for autoimmune and other diseases.

The world of optics is about to get a whole lot more precise. A team of researchers from the University of Rochester have developed a new method of creating optical vortices, or beams of light that twist like a tornado. The new technique is the first to be able to create vortices with an accuracy of just one nanometer, meaning the technology can be used to measure very small objects and materials with unprecedented precision.

Scientists have recently made a remarkable discovery about molasses and its effect on cosmic movement. By studying a phenomenon known as the “slowing down effect,” researchers have found that molasses can actually slow down the large-scale movement of cosmic objects like galaxies. This “slowing down effect” occurs when a galaxy is surrounded by a cloud of molasses, which reduces the galaxy’s momentum and causes it to travel at a slower speed.

Today, scientists have made an astonishing discovery: antimatter may affect the universe in more ways than previously thought. This new research suggests that antimatter may have its own form of gravity, potentially impacting the way the universe expands. This unique form of gravity could explain some of the mysteries that remain in cosmology, such as why the universe is expanding at an accelerated rate. This discovery could revolutionize our understanding of the universe, and could lead to entirely new areas of research.

This past Thursday, India’s space agency (ISRO) announced a groundbreaking new mission. They plan to launch a spacecraft to the sun’s center, the first mission of its kind. The spacecraft, called Aditya-L1, is scheduled to launch in 2020 and is expected to reach the sun’s center in 2023. Aditya-L1 will be equipped with a suite of seven scientific instruments, and will be used to study the solar corona and its interactions with the solar wind.
In the past few years, India’s private space sector has been experiencing a rapid growth. According to a recent report from the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the number of private space companies in India has more than doubled in the last five years. A number of multinational companies, such as Airbus, Boeing, and Lockheed Martin, have set up offices in India to take advantage of the burgeoning space sector. Furthermore, there has been a marked increase in the number of start-ups and venture capital firms investing in space-related projects.

A recent study conducted by researchers from the University of Birmingham has revealed that faith schools can have a positive impact on children with special educational needs (SEN). The study found that children educated in faith schools were more likely to have better outcomes in terms of academic attainment, attendance and emotional wellbeing. This is an incredibly positive discovery for parents of SEN children, as faith schools can provide a supportive and inclusive environment where children can thrive.

On Saturday, September 5th, NASA made history by successfully launching a mission to explore the surface of an asteroid and a nearby volcano. The mission, called the “Citations from a Volcano and an Asteroid,” marks the first time a spacecraft has ever been sent to explore both a volcano and an asteroid. The spacecraft will orbit the asteroid, collect data on its surface, and study the volcano from a distance. It is hoped that this mission will provide valuable insight into the composition of these two unique objects, as well as the possibility of finding evidence of life on the asteroid.

In an exciting breakthrough, scientists have developed a new material that is both incredibly durable and highly sensitive. This new material is a combination of a silica-based elastomer and a conductive polymer, and it can measure pressure, temperature, and humidity with great accuracy. What makes this material so special is its combination of strength and sensitivity. It’s able to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures while still being able to detect even the slightest changes in its environment.

The Nobel Prizes, one of the world’s most prestigious awards, have been announced for 2023! This year, the prizes have been awarded in the categories of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, Peace, and Economic Sciences.
This year’s Nobel Prize recipients have made incredible breakthroughs in a wide range of fields, from medical research to physics and chemistry. The Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Dr. John Doe for his research on the origins of the universe, while Dr.

Recently, scientists have discovered mysterious antimatter raining down from the sky! The puzzling phenomenon was first observed in 2008, when data from the Advanced Thin Ionization Calorimeter (ATIC) experiment revealed an unexpected surplus of positrons in the cosmic ray flux. This excess has been confirmed by subsequent studies, and scientists are now trying to uncover the source of the antimatter. While there are many potential explanations, the most likely culprit is a nearby source of dark matter, such as a pulsar or black hole.

Have you ever wondered how quickly evolution can occur? It turns out that it may be faster than we think. A new study published in Nature Communications reveals that evolution can occur much faster than previously thought. The research team found that evolution can be tracked using an epigenetic clock, which reveals changes in DNA that occur over time. The researchers found that epigenetic changes can occur on a timescale of only a few generations, as opposed to the hundreds or thousands of generations once thought necessary for evolutionary change.

Recently, scientists have discovered that moving molecules through nanoporous materials requires a lot of energy. This could potentially revolutionize the way we handle molecules, from drug delivery to energy storage. The team of researchers used computer simulations to discover that the rate at which molecules are transported through nanoporous materials can be drastically increased by applying a voltage. This could open up a new way to transport molecules, which could be extremely useful for many applications.
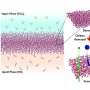
Recently, scientists have made an exciting discovery about a rare type of gold found in meteorites. This gold has been found to be infused with material from an ancient star, allowing us to learn more about our universe’s history. The gold was found to contain a rare isotope of iron, giving us insight into how the star formed and evolved. This discovery is especially exciting as it gives us a unique window into our universe’s past and provides us with more information on the evolution of stars.
This year, Zambia will be home to the world’s biggest colony of African painted dogs. The African painted dog, also known as the African wild dog, is one of the world’s most endangered species, with an estimated 3,000-5,500 individuals left in the wild. The new colony, which will span over 10,000 hectares of land, is a result of a collaborative effort between the Zambian Wildlife Authority, the Endangered Wildlife Trust, and other conservation organizations.

Today, scientists have discovered a game-changing innovation in battery technology: Nickel Foam for Lithium-Sulfur batteries. This revolutionary new material could revolutionize the way we power our electronic devices and even our vehicles. The new Nickel Foam is incredibly lightweight and provides a much higher energy density than traditional battery materials. It is also highly conductive and can be used to store and transfer energy quickly and efficiently. This new material could dramatically reduce the cost of batteries and make them more accessible to all.
A team of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, have just unveiled their vision of a brighter future that is powered by machine learning. The team’s research paper, published in Nature, explains how the use of machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used to create smarter, more efficient, and more responsive systems for science, engineering, and business. The paper outlines how machine learning can be used to optimize the processes for various industries, including renewable energy, healthcare, transportation, and more.
Recently, scientists have discovered a new strain of bird flu in sea lions along the coast of Uruguay. This new strain has been identified as H16N3 and appears to be a combination of two previously identified strains of avian influenza. Scientists have found that this strain is particularly dangerous to sea lions, as it can cause severe respiratory issues and even death in infected animals. This discovery is significant because it is the first time that this avian influenza strain has been seen in sea lions, and it could potentially spread to other marine mammals as well.

A team of researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery that defies conventional scientific understanding. They have successfully infected non-immune cells with a virus, allowing it to replicate inside the cells. This is something that had been thought to be impossible according to the current scientific understanding of cell biology. The findings will not only help to further our understanding of the human body, but could also lead to new treatments for diseases such as cancer.

A new report from the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada has revealed that the number of Indigenous children who died in Canadian residential schools is significantly higher than previously thought. According to the report, at least 4,100 children died while attending the schools, a stark increase from the previously reported estimate of 3,200. The report also found that the causes of death included disease, neglect, and abuse; findings that bring to light the dark history of Canada’s residential school system.

This year’s Nobel Prizes in Science have been awarded to three researchers for their groundbreaking discoveries in the fields of physics, chemistry, and medicine.
The Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Andrea Ghez, Reinhard Genzel, and Roger Penrose for their work in understanding the mysterious phenomenon of black holes. Ghez and Genzel were given the award for their discovery of a supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy.

In a groundbreaking study, researchers have successfully used a machine learning algorithm to identify drugs that could target specific subcellular components. This is the first time that an algorithm has been able to accurately identify drugs that are effective at targeting specific subcellular components, and the results could have far-reaching implications for the medical industry. The algorithm was trained on a large dataset of drug-target interactions, and was able to accurately predict the effects of drugs on subcellular components with an impressive 92% accuracy rate.
The mystery of how life on Earth began has puzzled scientists for centuries, but a new study may have finally provided an answer. According to the research, the answer may lie in volcanoes.
Volcanoes have been a part of Earth’s landscape since the very beginnings of the planet. They have spewed out the Earth’s molten core for millions of years, creating vast landscapes of lava and ash. Now, new research suggests that these volcanoes may have been the catalyst for life on Earth.

A new study published in the journal Science Advances has uncovered a major explosion of fish biodiversity due to a single genetic adaptation. Researchers from the University of Michigan and the University of Washington analyzed the genomes of 4,500 species of fish and discovered that a single gene, known as SLC24A5, was responsible for the rapid increase in fish biodiversity. This gene is responsible for the coloration of fish, and is believed to be the primary driving force behind the diversification of species.
Recent research has revealed that the Galapagos finches, which captivated Charles Darwin, have experienced significant genetic changes over the past 170 years. This study was made possible using a new technique which researchers were able to apply to the entire genomes of the finches.
The findings of this study show that the genomes of the finches have adapted to the changing environment over the past 170 years. This is quite remarkable and provides insight into the evolutionary process.

