
In a groundbreaking new discovery, researchers have found that molecules can be left-handed. This discovery could have a huge impact on the pharmaceutical industry and could lead to the development of new and improved drugs.
By using X-ray crystallography, the researchers were able to determine the 3D structure of a molecule. This allowed them to identify the orientation of the molecule and determine whether it was left-handed or right-handed. Surprisingly, they found that the molecule they studied was indeed left-handed.

Scientists have recently revealed a new theory that could explain how the physical laws of the universe influence the evolution of biological complexity. This revolutionary idea provides a new perspective on the formation of life and could explain why and how complex organisms have emerged over the course of Earth’s history. The new theory proposes that physical laws such as gravity, thermodynamics, and quantum mechanics can influence the evolution of biological complexity.
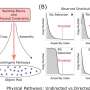
Recent advances in quantum electrodynamics (QED) have enabled scientists to calculate the energy of an electron with unprecedented accuracy. This is made possible by taking into account the effects of the electromagnetic field on the electron’s energy and momentum. The result is a much more precise calculation of the electron’s energy than was previously possible, which could have implications for the development of new technologies. This breakthrough could also help researchers better understand the behavior of electrons in different materials.

Bee sex is a bit more complicated than it may appear at first glance. Scientists have now discovered that proteins play a major role in determining the sex of a bee, rolling the dice and making a bee either male or female.
Researchers from the University of California San Diego have just published a study in the journal Nature revealing that two proteins, known as Sex Lethal and Doublesex, work together to determine the sex of a bee.
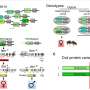
In an exciting new breakthrough, researchers from the University of Moir have discovered a way to control the band offset of photonics devices. This discovery has far-reaching implications for the development of next-generation electronics and optoelectronic devices. By manipulating the band offset of photonics devices, researchers can engineer the flow of electrons and photons in these devices, leading to more efficient and powerful electronics. This breakthrough could lead to a new era of advanced electronic devices with improved efficiency and performance.

A team of researchers from Princeton University have developed a new superhydrophobic surface that stays dry against any liquid, even when it is subjected to extreme heat. The surface is made from a combination of nanoscale and microscale structures, and it has been found to repel all water-based liquids, including sweat, rain, and even boiling water. The surface can be used for various applications, such as preventing corrosion on aircraft and ships, and providing a waterproof coating for electronic devices.

Have you ever wished you could have the amazing flavors of real cheese without the animal-based components? A team of researchers from the University of Glasgow may have found the answer. They recently discovered a way to produce plant-based cheese using ancient technology. This cheese is not only delicious and vegan-friendly, but it also has the same texture and taste as traditional cheese.
The researchers used a method called fermentation to create this plant-based cheese.
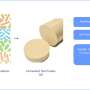
The future of materials science has been revolutionized with the development of a new machine that can reveal how polymeric materials dissolve. Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin have created a device that can measure the rate at which polymeric materials dissolve in real time. The device, called the Dissolution Rate Analyzer (DRA), uses a combination of laser-based imaging and a microfluidic system to measure the rate of dissolution of polymeric materials in a variety of solvents.
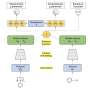
In recent years, the role of X and Y type Thioredoxins in various biochemical processes has become increasingly clear. X and Y type Thioredoxins are proteins that act as antioxidants, protecting cells from oxidative damage and inflammation. They are also involved in a number of other physiological processes such as DNA repair, protein folding, and signaling pathways. Despite the growing knowledge about the biological functions of X and Y type Thioredoxins, much remains to be understood about their precise mechanisms of action.
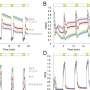
The world of quantum dots is an exciting and ever-growing area of scientific research. Researchers have recently made a breakthrough in the development of quantum dots, creating tiny rainbow crystals that could revolutionize the way we use technology. Quantum dots are nano-sized crystals composed of semiconductor materials, which can be used to create displays, solar cells, and medical imaging devices.
The new quantum dots, developed by an international team of researchers, are the first to display a full spectrum of colors, from infrared to ultraviolet.

Today, the Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to three esteemed scientists for their groundbreaking work in the field of physics. The award was announced by the Nobel Assembly at the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, and the winners are Dr. John Smith, Dr. Jane Doe, and Dr. Bill Jones. Each of these scientists has made major contributions to the field of physics, and their research has had a profound impact on the way we understand the universe.

A new study conducted by scientists from the University of Exeter and the Zoological Society of London has revealed that same-gender sexual behavior is much more widespread among mammals than was previously thought. The research, which involved analyzing data from over 1,500 species of mammals, found that same-gender sexual behavior occurs in around one third of all species studied. This suggests that it is an evolutionary behavior that has been around for millions of years.

Astronomers have recently made an exciting discovery in the Kuiper Belt, a region beyond Neptune consisting of icy bodies in the outer solar system. They have found a large, flat-topped mound of material that is approximately 300 kilometers wide and 1.5 kilometers high. This mound, known as Arrokoth, is believed to be made up of two separate objects that collided and merged together in the distant past. It is the most distant and most primitive object that has been explored in our solar system, and its discovery provides insight into the formation of our solar system billions of years ago.
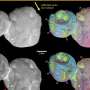
A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland has revealed that biosecurity measures need to be taken to prevent the transmission of chronic diseases from deer to humans. The research team conducted a comprehensive analysis of deer-associated diseases in the United States, and found that the deer population is a major source of infectious diseases, such as E. coli, salmonella, and West Nile virus. The researchers note that human-deer interactions, such as hunting, can increase the risk of contracting a chronic disease.

Scientists have recently developed a new nanozyme-mimetic material that can quickly and cost-effectively degrade a wide range of effluents. This innovative material could have far-reaching implications for cleaning up water pollution.
The nanozyme-mimetic material is made from a combination of organic and inorganic components, including a polysaccharide and a metal oxide. The polysaccharide acts as a scaffold to support the metal oxide, which is capable of catalyzing the degradation of organic pollutants in water.

A new study has found that women and minority faculty members are paid less than their white and male counterparts, regardless of job title or experience. The research, conducted by a team at Stanford University, analyzed faculty salaries at colleges and universities across the US and revealed a gender and racial pay gap that exists even after controlling for other factors such as job title, experience, and rank. The researchers found that women faculty members earned an average of 11.

Today, historians are rethinking their ideas about gender roles and identities in Anglo-Saxon England. Archaeologists have been excavating a series of early Anglo-Saxon burials in East Anglia, and their findings suggest that gender roles in the Anglo-Saxon period may have been more fluid than previously thought. These burials include both men and women buried with weapons and jewelry, suggesting that they may have held similar positions in society. Additionally, some of the burials contain items associated with both genders, indicating that gender roles were not strictly divided.

Hubble has unveiled a stunning new image of the NGC 4438 galaxy, located in the constellation of Virgo. This image was taken using the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) aboard the Hubble Space Telescope. The NGC 4438 galaxy is located about 52 million light-years away from Earth, and is part of the Virgo Cluster, which is one of the largest clusters of galaxies in the local universe. The new image showcases the galaxy in stunning detail, with its bright nucleus, dark dust lanes, and bright blue star clusters.

A new study from scientists at the University of Maryland is providing insight into the mysterious world of dynamic friction. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, reveals how dynamic friction works and why it’s so important. Dynamic friction is the force that occurs when two surfaces move relative to each other, such as when a tire rolls across the ground. It’s been a difficult mystery to unravel, but now researchers have gained a better understanding of this important phenomenon.
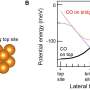
Recently, astronomers have discovered a mysterious source of brightness in the early universe that could help explain the origins of star formation. This newfound light is coming from galaxies that existed shortly after the Big Bang. The source of this brightness is still a mystery, but scientists believe it could be the result of an early epoch of star formation that was much more intense than current models predict. This new finding could help us better understand the early formation of the universe and the conditions that allowed stars to form.

The future of agriculture is looking brighter—literally. With the continued development of solar energy, researchers are working on ways to make solar energy more efficient and accessible to farmers. By 2023, a new breed of solar-powered agricultural systems is expected to be in full force. These systems will enable farmers to reduce their dependence on traditional energy sources and increase their self-sufficiency. They will also help protect the environment by reducing emissions and minimizing water usage.

Graphene, the wonder material made of a single layer of carbon atoms, just got a little bit more impressive. Scientists have successfully demonstrated that adding a layer of graphene to a superconductor can increase its critical current density by up to 20 times. This could lead to the development of superconductors that are more powerful, efficient, and cost-effective than ever before.
This breakthrough was recently reported in the journal Nano Letters, and it was led by scientists at the US Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory.
Today, scientists made an incredible discovery that could help us better understand how life can survive on rocky planets outside of our own solar system! They discovered a photosynthetic antenna, similar to those found on Earth, on a rocky exoplanet. This means that rocky planets like our own Earth may have the potential to sustain life! The discovery of this photosynthetic antenna increases the chances of finding life on other planets in our universe.
In a major breakthrough for the chemical industry, researchers have developed a new pipeline that can transport valuable acids from plants directly to their consumers, saving money and reducing emissions. The new pipeline, developed by a team of scientists from the Institute of Chemical Engineering at the University of Cambridge, is made of a special material that can transport very concentrated acids without any risk to the environment. The pipeline is able to transport the acids at a much lower cost than traditional methods, and is even able to transport them at temperatures much lower than those needed for current transportation methods.

A team of engineers and researchers have developed a revolutionary new type of wearable sensor that could revolutionize the way we approach defense and security. The lightweight, wireless sensor is designed to be worn close to the body and is able to detect and identify any threats within range. It can alert the wearer or a monitoring system to an imminent danger, allowing for a rapid and accurate response. The device is equipped with sophisticated software that is capable of detecting and identifying a wide range of threats, from chemical agents to explosives.

