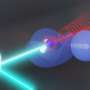
Scientists have just made an incredible discovery—they have discovered a way to capture the dissociation of protons in ultrafast detail! Using an ultrafast electron camera, scientists were able to capture the process in which two protons break apart in a matter of femtoseconds. This discovery is significant because it is the first time that the process of proton dissociation has been captured in such detail. The researchers hope that this new technology will pave the way for further discoveries and advancements in the field of physics.

A remarkable discovery has been made in the field of ancient leaf miner research. Scientists have unearthed fossils of leaf miners that date back an astonishing one million years! These leaf miners, which are small insects that feed on plants, lived during the Late Pleistocene era, a period of time lasting from 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago. This is the first time that fossilized leaf miners of such antiquity have been discovered, and the implications of this discovery are far-reaching.

The world of photonics has just been revolutionized by a new discovery made by scientists in the field: exciton scissoring of perfluoroarenes! This new technique is capable of triggering photomultiplication to its full potential. This discovery promises to open up a world of applications in the near future, ranging from ultra-fast communications to quantum computing. Exciton scissoring of perfluoroarenes is a new technique that uses the light from an LED to generate a cascade of electrons, which can then be used to power a device.
A team of astrophysicists has made a major breakthrough in understanding supernovas, one of the most powerful explosions in the universe. The team has found that a supernova’s power comes from its core, which is filled with energy generated by the fusion of heavy elements. The team’s research could have implications for the study of the evolution of galaxies and the origin of heavy elements. This discovery could also provide valuable insights into the nature of dark energy, a mysterious force believed to make up the majority of the universe.

For the first time ever, scientists have developed a semi-device independent randomness-free quantum key distribution protocol that allows two parties to securely communicate without any prior trust. This new technology can be used to protect valuable data and ensure secure communication between two parties. The new protocol, described in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, is based on a quantum entanglement technique known as the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen effect. The protocol is the first of its kind to enable secure communication with two parties without the need for trust or prior knowledge of each other’s security parameters.

Astronomers have recently determined that pulsars, long-known objects in the night sky, may also be associated with dark matter. In a new study published in the journal Nature, researchers from the University of Manchester have found evidence that pulsars may be connected to the mysterious substance that makes up most of the universe. The findings suggest that pulsars, which are highly magnetized spinning neutron stars, could be a major source of dark matter.

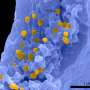
Paleontologists have recently discovered molecular evidence of ginger pigment in the fossilized bones of an ancient human ancestor. This finding, published in the journal Nature, is the oldest known evidence of red hair and suggests that humans may have already had this unique trait approximately 1.2 million years ago. This discovery adds to the growing body of evidence that suggests the human species has been evolving in unique ways for much longer than previously thought.
In the world of space exploration, the name ‘Vega’ is becoming increasingly well-known. Vega is a small cubesat, or miniature satellite, that is designed to provide navigation assistance to Earth-bound spacecraft. Its mission is to provide better, more precise satnav signals for spacecraft that are in low Earth orbit, which can be difficult to acquire from the ground. This tiny satellite is making waves in the space exploration community, as its accuracy and reliability are proving to be invaluable.

In the wake of the pandemic, TikTok farmers have stepped up to meet the challenges of this turbulent time. They are using the platform to educate their followers about the importance of sustainable farming practices and the need to be mindful of climate change. Through creative and engaging videos, TikTok farmers are cultivating empathy among viewers and inspiring action on climate-related issues. Whether it’s composting and gardening tips, discussions about the importance of regenerative farming, or simply sharing stories of their own struggles and successes, TikTok farmers are helping to cultivate a culture of climate-consciousness and sustainability.

A new study has found that a simple and inexpensive method of early cancer diagnosis could save hundreds of thousands of lives every year. This method is called the ‘liquid biopsy’, and it involves testing a patient’s blood for cancerous cells. The method is revolutionary because it can detect cancer much earlier than it would be found through traditional methods, such as a CT scan.
The study, which was published in the journal Nature Medicine, found that the liquid biopsy was able to detect cancer in 94% of cases studied.

Today marks a major milestone in the development of quantum computing. Scientists have successfully developed a 10-qubit platform based on a single atom, a breakthrough that could lead to more powerful quantum computers with greater computational power. The new platform is the first of its kind to be able to control ten qubits at once, allowing for more complex calculations than ever before. This could have a major impact on the development of quantum computing, paving the way for a new era of powerful, faster computers.
Today, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery that could revolutionize the way we combat future infectious disease and cancer. Researchers at Harvard Medical School have identified a new class of molecules that could be used to create targeted therapies to combat a wide range of viruses and tumors. The team has developed a specialized screening technique that can detect and identify molecules that can selectively interact with specific viruses and cancer cells.
A new microscope method promises to bring us a sharper focus on the hidden world of plankton. Scientists from the University of British Columbia have developed a revolutionary way to image plankton in unprecedented detail. Using a technique called “super-resolution microscopy”, they are able to capture images of plankton at a resolution of just 1 micron - that’s around a thousand times sharper than the resolution of a conventional optical microscope.

Today, artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the field of microscopy. Scientists are now using AI to develop self-driving microscopes that can analyze images with unprecedented speed and accuracy. These AI-driven microscopes can be programmed to identify and analyze features in the image, such as the shape and size of cells or the presence of bacteria. This technology is enabling scientists to quickly and accurately identify features that would otherwise be too difficult or time-consuming to detect.

A team of scientists has developed a new microplastics kit that uses artificial intelligence (AI) technology to identify and quantify the amount of microplastics present in water samples. The kit, which is currently being tested in various locations around the world, allows for the rapid and accurate analysis of water samples by analyzing images of the microplastics in the sample. The team believes the kit has the potential to revolutionize the way microplastics are monitored, making it easier and more cost-effective for researchers to detect and measure the presence of microplastics in our environment.
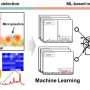
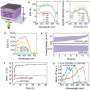
Chemists have developed a new sensor system that can detect potassium and sodium ions in real time, with potential applications in biomedical and environmental research. The sensor utilizes a novel combination of organic and inorganic materials, and offers highly sensitive and selective detection of these vital ions. The findings, published in the journal Nature Chemistry, could have far-reaching implications for studies of human health and the environment.
Scientists have long sought to develop a sensor that can monitor potassium and sodium ions in real time, but without success due to the materials used in traditional sensors.
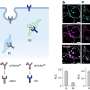
Chemists have recently developed a promising new approach to preventing bacterial infections, using iron as an antibacterial agent. With this innovative technique, bacteria can be killed quickly and effectively, without the need for harsh antibiotics. This could revolutionize how we fight bacterial infections and save countless lives.
The new technique utilizes iron oxide particles, which are very small and can easily penetrate a bacterium’s cell wall. Once they reach the inside of the cell, the particles react with the bacteria’s proteins and enzymes, destroying them and killing the bacterium.
Today, researchers have made a thrilling discovery in Australia: a previously unknown species of possum! This extraordinary creature, believed to have lived in Australia around 20 million years ago, has been dubbed the “feather-tailed possum.” The fossilized remains of the animal were found in a cave in Western Australia and are the most complete of any ancient possum discovered in the region. The feather-tailed possum is remarkable not only for its size (it was about the size of a guinea pig) but also for the fact that it is the earliest known ancestor of modern possums found in Australia.

A new quantum ruler developed by scientists at the University of Bristol could revolutionize our understanding of the exotic physics of quantum materials. The device’s ability to measure extremely small distances could help shed light on the behavior of particles in quantum materials, unlocking potential insights into previously unexplored realms of physics. This opens the door to new possibilities in computing, communication, and more.
Researchers have developed a “quantum ruler” that promises to revolutionize our understanding of the exotic physics of quantum materials.

Recently, scientists have proposed a new theory of gravity that could help explain the mysterious phenomenon known as “dark gravity.” This theory suggests that gravity can be distorted by the presence of other masses, such as stars or galaxies, resulting in a phenomenon known as gravitational distortion. This could explain why some areas of the Universe appear to be “dark” or devoid of matter. This could also provide insight into how galaxies and stars form and evolve over time.

The future of medicine is rapidly evolving and soon, artificial life forms may be playing an important role in the healthcare industry. Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics have opened up the possibility of creating artificially intelligent life forms that can be used to diagnose and treat diseases. These artificially intelligent life forms could be used to detect and diagnose diseases at an early stage, as well as to provide personalized treatments based on a patient’s genetic make-up.

In the future, nanotechnology could be used to make medical treatments safer and more effective with fewer side effects. A team of researchers from the University of Toronto has developed a new method for controlling the release of drugs from nanomaterials, which could be used to reduce the side effects of treatments. The new technique, described in a paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, uses the forces of electric fields to control the release of drugs from nanomaterials.

NASA is about to embark on a mission to explore a unique asteroid in our solar system: Psyche 16. This mission has been long-awaited, as Psyche 16 is a unique metal-rich asteroid that could potentially provide insight into the formation of our universe. The Psyche 16 mission will launch in the summer of 2023, and will explore the asteroid’s composition and structure. Scientists hope that this mission will provide key insights into our solar system’s history, and how planets form and evolve.

It has long been a dream for the future: an energy system powered solely by renewable sources. But a new development in photo-electrochemistry may make this dream a reality. Scientists have recently developed a new technology that can convert solar energy into storable chemical energy, using a combination of photovoltaic cells, electrochemical cells and catalysts. This technology could revolutionize the way we generate and store energy, allowing us to build a clean, renewable energy system.
Studies by researchers at the University of Adelaide have revealed an incredible new discovery: mammals have a unique ability to survive mass extinctions. It seems that mammals have an evolutionary strategy that allows them to not only survive but also to thrive in the face of cataclysmic events. This strategy involves rapid diversification and expansion of their population, enabling them to colonize new habitats and environments and outlast other species. In the face of mass extinction events, the ability of mammals to rapidly adapt and diversify has enabled them to survive and eventually prevail.

