
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission has made history, becoming the first spacecraft to successfully collect a sample from an asteroid. On October 20, 2023, the spacecraft collected more than 2.1 ounces of material from the asteroid Bennu, marking a major milestone in space exploration. The material collected will now be stored and analyzed, a process known as sample curation. Sample curation is an important part of the OSIRIS-REx mission, and will help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of our Solar System.

The future of healthcare is on the brink of a revolution in the form of bacterial products. Scientists have recently discovered a way to genetically modify bacteria so that they can produce a variety of drugs, vaccines, and other medical treatments. This revolutionary breakthrough promises to revolutionize healthcare by providing an unprecedented level of quality and affordability.
A key feature of this new technology is the ability of these bacteria to “opt” for a certain price to quality ratio.

In a major breakthrough for space exploration, scientists have announced plans for the first ever Vega flight, which will launch a fleet of satellites into space. This will mark a new era in exploration, as the satellites will be equipped with advanced technologies that will be used to study the universe, as well as to take images and collect data about Earth and our solar system. The Vega mission is expected to launch in 2023, and will be the first of its kind, as it will utilize a unique combination of propulsion, guidance, and control systems to maneuver the satellites in space.

Today, scientists around the world are beginning to explore the possibilities of phase-changing high-density ultra-hot ice. This new form of matter could potentially be used to store and transport energy more efficiently than ever before. In laboratory experiments, this material has been shown to maintain its properties at temperatures up to 10,000 degrees Celsius. In addition to its remarkable heat resistance, this type of ice can also be compressed to an ultra-high density of up to 1 million times the density of water.

Scientists have just made a breakthrough in the cloning of a gene that is responsible for the production of the herbicide glufosinate. Glufosinate is a key component in the fight against weeds, and this new cloning technology could open the door to more efficient and effective weed control methods. This breakthrough could allow farmers to use fewer chemicals and increase yields, while protecting the environment. Scientists are hopeful that this technology could revolutionize the way we combat weeds in the future.
SpaceX has announced an ambitious plan to expand their operations along the Space Coast of Florida. The plan includes launching the first space-based internet system, building a research and development center, and constructing an advanced rocket manufacturing facility. This expansion is expected to bring hundreds of jobs to the area and will provide a major boost to the local economy. With this new venture, SpaceX is positioning itself to become a major player in the space exploration industry.

Atlas, the world’s first fully electric cargo spacecraft, is set to make its debut launch from Cape Canaveral in October 2023. Developed by Amazon, this prototype spacecraft is equipped with advanced technology that will enable it to transport cargo to and from Earth. The spacecraft is powered by a new type of electric thruster that uses a combination of Xenon gas and electric fields to propel it through space. The thruster is designed to provide maximum efficiency and reliability, allowing Atlas to travel farther and faster than ever before.

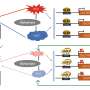
Ultra mild and functional group tolerant methods for producing arynes have been developed by scientists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Arynes are intermediate organic compounds which can be used to synthesize a wide variety of organic molecules, including pharmaceuticals. The team of researchers, led by Professor Paul Hergenrother, has managed to develop an ultra mild and functional group tolerant method for producing arynes, which is much milder than conventional methods.
The humble three-finger snake may be one of the most poisonous animals on the planet, but new research reveals its evolutionary history may be even more fascinating than first thought. A team of scientists has now uncovered evidence that suggests that the venom of three-finger snakes evolved independently from other snakes, rather than being derived from a common ancestor. This means that the three-finger snake venom is not only more toxic than its cousins, but also that it has its own unique evolutionary history.

Today, scientists have revealed the discovery of a new polyploid group of forest trees, which they believe could have a major impact on our understanding of genetic regulation. This exciting news could have huge implications for how we manage forests and trees in the future. The new group of trees, known as the ‘Quercus Polyploid Group’, was discovered in a study led by researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz.

If you’ve ever bit into a juicy, ripe pineapple, you know how delicious the fruit can be. But what makes it so sweet? Scientists have been researching this question for years, and now, a new study says they have the answer.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, reveals that the main compound responsible for pineapple’s sweet flavor is a sugar called fructose. Fructose is found in nearly all fruits and vegetables, but in pineapple, it is especially high.
In a breakthrough discovery, scientists have recently managed to observe the emission of a photon from a black hole for the first time in history. This discovery provides a major advancement in our understanding of black holes and the complex phenomena that occur within them. The photon was observed using a new and powerful telescope, allowing us to observe the intricate details of the black hole’s dynamics. This is an exciting development in astrophysics and one that will help us better understand the mysterious phenomena of black holes.

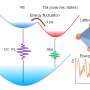
Research conducted by a team of scientists has revealed a new mechanism for efficient upconversion in two-dimensional materials. Upconversion is a process that converts low-energy photons into higher-energy ones, which has potential applications in the fields of optoelectronics and photonics. The team’s findings offer a new insight into the physics of upconversion, which could ultimately enable the development of more efficient and cost-effective upconversion devices.
Recent advancements in two-dimensional materials have enabled researchers to study new and exciting physical phenomena, including the phenomenon of upconversion.
A new study published this week in Nature Chemistry has demonstrated the potential of a new type of molecular machine that could help scientists better understand how changes to our DNA can influence our health. The molecular machine, or mof (metal organic framework), is an example of epigenetic technology, a type of research that looks at how environmental factors can change the expression of genes. The mof was designed to target mitochondrial metabolism, the process by which cells produce the energy needed to survive and function.
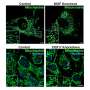
A recent study has revealed that mushroom-derived materials can have many positive benefits for nations in Africa. This research was conducted by a team from the University of Ghana and found that mushrooms can be used to create a variety of useful products, such as bioplastics, biofuel, and animal feed. Furthermore, this research showed that mushroom-derived materials can help reduce plastic pollution, create cheaper and safer products, and produce an additional source of income for African nations.
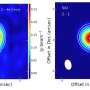
Researchers have recently made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of astrophysics that will help us to better understand the structure of our universe. They have discovered an annular form of silicon carbide (SiC2) in the circumstellar envelopes of carbon-rich stars. This is the first time this particular form of silicon carbide has been detected in space, and it is believed to play an important role in the formation of stars.
Scientists have recently made a breakthrough discovery in the field of quantum entanglement. This new phenomenon, which has been described as a “spooky action at a distance,” was discovered by a team of researchers at the University of Chicago. They were able to create an entangled state between two photons, a feat that has never been achieved before. The implications of this discovery are vast, as it could pave the way for new forms of quantum computing and communication.

A new study has revealed that the vacuum cleaner effect can be used to remove nanoplastics from bays. Researchers from the University of California, Santa Barbara, have found that fungi can be used to reproduce this effect to remove nanoplastics from the environment. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, is the first to demonstrate the efficacy of this technique.
This groundbreaking study is a game-changer for marine conservation. For years, researchers have been struggling to find a way to clean up the oceans of nanoplastics, which have been accumulating in bays and other bodies of water.
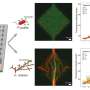
Evolutionary biologists from around the world have recently come together to discuss the long-term implications of lizard evolution. This discussion was part of a larger conference that explored the rapidly changing environment that lizards are facing today. Our understanding of the lizard evolutionary tree is growing each year, and researchers are now able to see how populations are adapting to new environmental conditions. As a result, they are able to make predictions about the future of lizard evolution.

Today, a new tool has been developed that could revolutionize the way we deliver gene therapies. This tool, which uses locally sourced materials, could make gene therapies more accessible and affordable to people all around the world. The tool, which is known as a viral vector, helps to deliver DNA to cells in order to make changes in the genetic makeup of the cells. This could potentially be used to treat a variety of diseases, from cancer to neurological disorders.
It’s no secret that the fashion industry is one of the biggest contributors to the global waste problem. But a team of scientists from Harvard University may have a solution: upcycling polyesters to create waste-free, scalable fabrics. The researchers used a process called “surface-initiated polymerization” to create a unique type of fabric made from polyester waste. The fabric is made up of small particles of polyester that are bonded together to form a strong, flexible material that can be used to make clothing, accessories, and other items.

The future of space exploration is changing, as researchers have recently found that the Moon is now surrounded by a belt of human-made space junk. This belt is made up of over a million pieces of debris, such as defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and other pieces of machinery. This discovery has sparked a discussion among scientists regarding the effects this space junk will have on future space exploration and the potential of further debris accumulation in the near future.
Today marked an incredible milestone in the history of astronomy: the 100th anniversary of the opening of the Mt. Wilson Observatory! This incredible observatory, located in the San Gabriel Mountains near Los Angeles, California, has played a pivotal role in the exploration of the Universe for the past century. It was here that astronomer Edwin Hubble revolutionized our understanding of the Universe by discovering that the Milky Way was only one of many galaxies, and that the Universe was expanding.

In a breakthrough study, scientists have developed a new method for quantifying the brightness of satellites from the ground, enabling ground-based astronomers to more accurately observe the night sky. By measuring the satellite’s reflectivity, the new method helps to reduce the brightness of a satellite to better match observations from the ground. This advancement could help astronomers to better observe fainter stars and galaxies, leading to greater discoveries.
Read Full Article Here

For years, scientists have been pushing the boundaries of what is possible with optics. Now, researchers have taken a huge leap forward with the development of free-space nanoprinting that can push far beyond the traditional optical limits. This revolutionary technique can be used to create 3D and 4D structures with nanoscale precision. This is a major breakthrough that could open up a host of new possibilities for the development of photonic devices.

