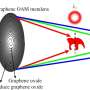
Scientists have developed a new form of broadband diffractive graphene orbital angular momentum (OAM) beam which could revolutionize communications technology. This new technology could significantly improve the speed and efficiency of wireless communication, particularly in areas where optical fiber networks are not available. The new beam is generated by a single nanostructured graphene sheet, which is capable of producing multiple OAM beams simultaneously. This could enable multiple data streams to be transmitted over the same frequency, potentially doubling or even tripling the data rate of current wireless communications.

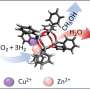
In a recent study, scientists have discovered a new way to fight bacteria using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). MOFs are a type of material made up of metal ions and organic molecules. It turns out that these materials can be used to release nitric oxide, a powerful antibacterial agent. The research team found that the MOFs were able to release nitric oxide in the presence of bacteria, effectively killing the bacteria. This could be a huge breakthrough in the fight against antibiotic resistance, as nitric oxide has been shown to be effective against a wide range of bacterial species.

It’s long been speculated that planets form from the collision of icy and rocky materials in clouds of dust and gas, but now, scientists have found evidence that collisions between two ice-rich planets can create a dimming effect that could lead to the formation of a new planet. In a new study, researchers from the University of California, Santa Cruz and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology used computer simulations to show that when two ice-rich planets collide, their combined mass can create a dimming of starlight that could indicate the formation of a new planet.

In recent years, scientists have begun to explore new ways to use carbon dioxide (CO2) as a source of energy, and the possibilities are truly exciting. One of the most promising uses for CO2 is its potential to be transformed into biofuel, a renewable energy resource that can be used in place of traditional fossil fuels. But that’s not all: the byproducts of this process may also be incredibly valuable. Here are ten ways CO2-based biofuel byproducts can be used for good:
A team of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has developed a framework for designing electromagnetic absorbers that are more efficient at absorbing electromagnetic waves than those currently available. The new absorbers are made of layered nanostructured materials, which are made up of multiple layers of metal, dielectric, and semiconductor materials. The layers are designed to interact with incoming radiation in a way that allows the absorber to capture more of the incident energy than traditional absorbers.

A new liquid reagent has been developed which can rapidly inactivate the coronavirus in just minutes! Scientists from the University of California have created a simple, cost-effective solution that can be used to disinfect surfaces and other materials. The reagent is composed of two molecules that work together to break down the virus’ outer shell, rendering it harmless. The reagent can be used in a wide range of applications, from medical equipment to everyday surfaces, and has been tested on a variety of different viruses, including SARS-CoV-2.

Today, scientists have made a breakthrough in the fight against toxic dyes that are polluting our environment. The breakthrough was made by creating a new type of titanium oxide material that can absorb and degrade dyes used in wastewater from textile industries. This new material is highly effective in removing dyes from wastewater, without the need for any additional chemicals. Furthermore, the titanium oxide material is non-toxic and can be recycled for future use.

This week, researchers from the University of Miami have announced the development of a new 3D acousto-optical scanning method that has broken the world record for accuracy and resolution. The new technique is capable of measuring objects with unprecedented accuracy and resolution. This allows researchers to capture 3D images of objects in greater detail than ever before. The new method is expected to revolutionize areas such as medicine, engineering, and manufacturing.
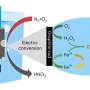
In a major breakthrough, scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have successfully developed a process for electroconverting air into nitric acid using mild temperature and pressure. This new process, which uses electricity to convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitric acid, could revolutionize the production of nitrogen-based fertilizers and industrial chemicals. The research team was able to achieve this remarkable feat with a simple, low-cost setup consisting of a small stainless steel chamber, a water-cooled electrolyte, and a high voltage power supply.
Atlas, one of the largest and most advanced particle physics experiments in the world, has recently released stringent limits on supersymmetric dark matter. This is a major breakthrough in the study of dark matter, as it can help us understand the nature of dark matter and its implications for the universe. The results show that the mass of the lightest supersymmetric particle must be greater than 1.3 TeV. This is the most stringent limit on supersymmetric dark matter to date!

Aurora Borealis, otherwise known as the Northern Lights, is set to reveal secrets of the sun in 2023. Scientists are predicting that the sun’s activity level will reach a historic low, known as the Maunder Minimum. This low level of activity is expected to be accompanied by a spectacular display of the Aurora Borealis.
The Maunder Minimum, which is expected to occur around 2023, is a period of decreased solar activity that has happened multiple times in the past.

A recent study has found that a small, specific chemical can significantly improve the bioavailability of certain drugs. This chemical, known as a prodrug, can be used to improve the amount of drug that an individual’s body is able to absorb, leading to increased effectiveness of the drug. Prodrugs have the potential to revolutionize the way that we treat certain medical conditions. By increasing the amount of drug that the body can absorb, we can effectively treat illnesses with smaller doses of more powerful medications.
On Saturday, October 14th, 2023, a total solar eclipse will travel across the United States, providing an amazing spectacle for sky-watchers. This eclipse will be the first total solar eclipse to cross the whole country in over a decade, and it promises to provide a memorable experience for those lucky enough to witness it. The eclipse will begin in the far northern parts of Maine and cross through the midwest, ending in the southwest corner of Texas.

Scientists have recently discovered an exciting new development in the field of gut health. After conducting extensive research, they have discovered a way to use grape pomace to positively affect digestive health. Grape pomace is a byproduct of wine-making and is high in dietary fibers, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds. The results of the research suggest that consuming grape pomace can help with digestive issues, such as constipation, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.
The mysteries of the outer planets are slowly becoming revealed, and now scientists are turning their attention to Neptune’s small, icy moon Triton. A team of researchers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the University of California, Los Angeles have been awarded a grant to study Triton’s atmosphere and determine what it is made of. This research will help us better understand the nature of this distant moon, and could potentially shed light on how it formed and evolved over time.

Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in understanding the key to cell reality. For the first time, an interdisciplinary team of researchers has come together to showcase the full range of cell processes. In a paper published in the journal Nature Communications, the team has identified the molecular processes that enable cells to maintain their identity and function. The findings could have far-reaching implications for the development of new treatments for diseases such as cancer.
A new study published in Nature Communications has revealed that the predator-prey defense mechanisms of certain key marine species are essential for maintaining healthy marine ecosystems. Researchers studied the interactions between various species of predators and their prey, and found that the predator-prey defense mechanisms, such as camouflage, warning coloration, and chemical defenses, play an important role in keeping the balance between predators and prey.
The research team found that certain species of predators have evolved to have unique defense mechanisms that allow them to better navigate the marine environment and catch their prey.
Lough Neagh, located in Northern Ireland, is the largest lake in the UK. It is a popular center for angling and a haven for wildlife. The Lough Neagh Partnership, a local environmental group, works to conserve and protect the lake and its surrounding area. Recently, the partnership has been focusing on restoring the lake’s water quality, which has been suffering from human pollution and sediment buildup. The group plans to build a new wetlands area to help clean the water and provide a habitat for a variety of wildlife.

It’s official! Scientists have reported groundbreaking results from a recent galaxy cruise! Using a specialized telescope, astronomers discovered a variety of intriguing phenomena, including hundreds of new exoplanets, eight new supernovae, and a supermassive black hole. This is the first time a galaxy cruise has been used to uncover such an exciting array of findings. It’s a huge breakthrough in the field of space exploration, and could lead to even greater discoveries in the future.

Today, scientists have made a breakthrough in the fight against bird flu. A team of researchers have successfully gene edited chickens to make them immune to the virus. This could potentially save millions of chickens that are used in the poultry industry, as well as preventing the virus from spreading to humans. The gene-edited chickens were created by inserting a gene that makes them resistant to the virus, and the results have been successful.
A new study has revealed exciting new insights into 3D printing with the help of X-rays. The study found that X-rays can be used to detect the microstructural fingerprints of 3D printed objects, allowing researchers to better understand the characteristics of 3D printed objects. This research could pave the way for more reliable 3D printing and advances in additive manufacturing. With the help of X-rays, researchers could gain a better understanding of how 3D printed objects are affected by heat, pressure, and other environmental factors.

NASA has recently announced that they plan to develop a new system for sending data from deep space missions. This system, known as Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC), will utilize laser communication technology to send data at unprecedented speeds. The technology will allow data to be transmitted at rates up to 100 times faster than current systems, which will enable scientists to send larger amounts of data from deep space missions.

NASA’s Roman mission is gearing up for its upcoming launch in 2023 and the anticipation is building! The mission is the first of its kind and is set to study the atmosphere of Venus in an effort to understand the environment of Earth’s closest neighbor. With its combination of high-tech instruments and a spacecraft designed for the harsh Venus environment, the mission is sure to be a spectacle. Its goal is to gather new data and insights about Venus’ atmosphere, its clouds, and its potential habitability.
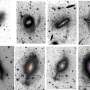
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has recently captured a remarkable view of a distant star-forming region in the constellation Auriga. This ethereal, wispy image reveals a region of glowing interstellar gas and dark dust where stars are born. The region is illuminated by the intense light of bright stars, creating an interstellar light show. This image showcases the incredible detail and sensitivity of the JWST, which will soon be used to explore the depths of outer space.

Recent research has revealed that Neanderthal gene variants may lead to greater pain sensitivity in modern humans. According to a study published in the journal Cell, Neanderthal versions of two genes — CACNA2D3 and TBX15 — are associated with higher pain sensitivity. The scientists also found that the Neanderthal gene variants are more common in East Asian populations than in European populations. This suggests that the Neanderthal variants may have helped modern humans adapt to the colder temperatures of East Asia.

