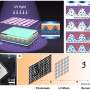
Scientists have developed a new type of microlens array that can be electrically tuned, allowing for faster and more precise control of the focusing of light. The new device consists of a series of tiny lenses, each of which can be adjusted individually to focus light in a specific direction. This technology could have a wide range of applications, from medical imaging to robotics. The development of this device marks a major breakthrough in the field of optoelectronics.

In a new study, scientists have discovered a paradigm-shifting way to identify and correct errors in quantum computers. The research, which was recently published in the journal Nature, reveals that quantum computers can be used to identify and correct errors in a more efficient way than previously thought possible. This breakthrough could lead to more reliable and powerful quantum computers.
Quantum computers are still relatively new technology, and one of the biggest challenges in building them is identifying and correcting errors.

In a recent breakthrough in computational physics, scientists have developed an alternative method for the simulation of absorption spectra. This new method, called the “multi-oscillator superposition” approach, is much faster than traditional methods and more accurate in predicting absorption spectra. The ability to accurately simulate absorption spectra is important in many areas of physics, including computational chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology. This new method promises to revolutionize the way absorption spectra are simulated, with the potential to save scientists time and resources.

Have you ever wondered what the Sun’s plasma is like? Scientists have recently been able to detect the energization of the plasma in the heliosphere, and the results are fascinating! Using two spacecraft orbiting the Sun, the Parker Solar Probe and the Solar Orbiter, scientists were able to detect the energization of the plasma in the heliosphere. The energization of the plasma is a result of the solar activity, and it is responsible for the acceleration of particles in the heliosphere.

Have you ever dreamed of flying in space? Well, if you’ve ever wanted to experience zero gravity firsthand, then get ready for the future of space travel. On October 14th, 2023, the International Space Station (ISS) will be launched into low Earth orbit, making it the world’s first commercial space station. The ISS is designed to provide a safe and comfortable environment for astronauts and space tourists alike, and will offer a variety of activities and services, such as educational programs, scientific research, and recreational opportunities.

Scientists at the Institute of Quantum Computing (IQC) recently released a study exploring a new parameter shift rule for quantum Fisher information. This new rule could potentially revolutionize quantum computing, allowing for the efficient optimization of quantum algorithms. The study was conducted by analyzing the behavior of a two-qubit system, and its results could be applied to larger quantum systems. This could open the door to solving complex problems faster and more efficiently than ever before.

NASA’s Psyche mission, launching in 2023, is set to embark on a journey to a metal-rich world unlike any other in our solar system. After a four-year-long journey, the spacecraft is expected to arrive at its destination in 2027. Psyche is a unique mission that will explore a metal-rich asteroid, nicknamed “Psyche 16”, located in the Main Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter. Psyche is believed to be the exposed core of an early planet, making it a one-of-a-kind world that scientists have been eager to explore.

If you’ve ever wondered what it would be like to fly over the surface of Mars, then you’re in luck! A new video released by NASA offers us a stunning glimpse of the planet’s terrain, and it’s like nothing you’ve ever seen before. The video, titled “Fly Over Mars Labyrinth of the Night”, was created using images taken by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and shows the amazing landscape of the Red Planet in unprecedented detail.

In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the relationship between underfunded urban schools and corporate influence. As corporate involvement in education has grown, so too has the realization that the interests of corporations are often in direct conflict with the needs of students and educators in these schools.
This article looks at the current state of urban schools and how corporate influence has impacted them. It examines the challenges faced by urban schools—such as inadequate funding, lack of resources, and lack of support—and how corporate involvement has both exacerbated and alleviated these issues.

A new approach to studying microbial diversity in the wilder places of the world has been proposed by a team of researchers. Their research focuses on the combination of high-throughput DNA sequencing and the use of environmental DNA (eDNA) to analyze microbial communities in their natural habitats. This novel approach could provide a more accurate understanding of the microbial populations in the wild, and could help to inform conservation efforts. The researchers are currently testing their method in a variety of natural habitats, including coastal ecosystems, mountain lakes, and tropical rainforest soils.

A new study has found that providing students with extra lessons in calculus can improve their understanding of the subject and increase their grades in the course. Researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, surveyed over 1,000 college students who took calculus classes and found that those who received additional instruction outside of the regular classroom were more likely to pass the course and receive higher grades than those who didn’t receive the additional support.

A new antibiotic medicine has been developed that can selectively target bad bacteria while leaving the good bacteria alone. This new medicine has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat bacterial infections. By selectively targeting the bad bacteria, this medicine can reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance while still providing effective treatment. It also has fewer side effects than traditional antibiotics, making it a safer option for treating bacterial infections.

Veterinarians have a crucial role to play in helping dairy farmers increase their herd health and productivity. A newly developed tool can help them identify key management areas for improvement. The tool presents 10 cues that can be used to identify and monitor the health and productivity of a dairy herd. These cues are divided into four main areas: animal health, animal environment, cow comfort, and herd management. By monitoring these cues, veterinarians can help dairy farmers improve their herd health and productivity.
In a recent study, researchers have taken a closer look at how precision agriculture (PA) is influencing farm profitability. The study found that PA is indeed helping farmers increase their profits, but the effect is not as dramatic as one might expect. While PA technologies can help increase yields, they can also be expensive and time consuming to implement. As such, the researchers concluded that PA should be viewed from a profitability perspective, meaning that farmers should carefully consider the costs and benefits before investing in any PA technology.

The future of tomatoes is here, and it’s looking bright! Scientists have recently discovered a way to engineer tomatoes to produce more antioxidants, which can help reduce the risk of certain diseases. These new tomatoes are expected to be available in supermarkets in just a few years. This breakthrough will have a huge impact on the tomato industry, as it could help increase production and improve the quality of tomatoes. Moreover, these new tomatoes could be a major boost for the health of consumers all over the world.

The Hubble Space Telescope has captured a stunning image of a barred spiral galaxy. The galaxy, known as NGC 1672, is located in the constellation Dorado, approximately 65 million light-years away. The spiral arms of the galaxy are filled with bright stars, while its center is filled with a bar of stars and gas clouds. The bar structure is thought to be formed by the gravitational influence of the central supermassive black hole, and is a common feature of spiral galaxies.

A recent study from the University of California San Diego has identified similar features in disease-related gene groups. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, used machine learning techniques to examine the gene expression in 5,721 different disease-related gene groups. The researchers found that the gene expression of these gene groups can be clustered into groups with similar features, providing insights into the underlying causes of diseases. The findings could lead to new treatments for diseases and provide a better understanding of the genetic basis of diseases.
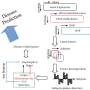
We are entering an exciting new era of optical chip technology! A team of researchers from the University of California, San Diego has developed a brand new type of optical chip that can self-configure its functions. This chip is designed to be extremely easy to use, allowing users to quickly and easily create complex optical networks with just a few clicks. The chip can be used for a variety of applications, including high-speed data transmission and remote sensing.
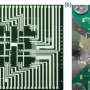
Scientists have developed a new type of fuel cell that is powered by a cobalt-modified nano-material. The new fuel cell is capable of producing electricity with a much higher efficiency than current fuel cell technologies. The new fuel cell has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce energy, making it more efficient and environmentally friendly. The fuel cell works by using a cobalt-modified nano-material to reduce the amount of energy needed to create a reaction.
NASA has announced a major breakthrough in its exploration of asteroids. In a mission scheduled for 2023, NASA will be sending a spacecraft to the asteroid Psyche, where it will collect a sample to study the origins of life on Earth. The sample will be critical in understanding how the asteroid formed and how it can provide insights into the formation of carbon-rich compounds on Earth. This discovery could have a profound impact on our understanding of the origins and evolution of life on our planet.

It looks like the skies above Los Angeles may soon be filled with huge and powerful rocket motors! A new project funded by the US Air Force is set to install a series of massive rocket motors in the city as part of an effort to develop a new generation of rocket-powered aircraft. The motors will be capable of generating up to 1.5 million pounds of thrust, making them the largest and most powerful rocket motors in the world.

Today marks a monumental day in human history. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has unveiled the first ever images of an asteroid, captured by the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. After a two-year journey, the OSIRIS-REx successfully rendezvoused with the Bennu asteroid, located over 200 million miles away from Earth. The incredible images reveal never-before-seen details of the asteroid’s surface, including boulders, craters, and ridges. Scientists and astronomers have been eagerly waiting to get a better understanding of the asteroid’s composition, as it could provide invaluable insights into the formation of the Solar System.

The search for extraterrestrial life has been ongoing for decades, and now a new breakthrough may help us find it. Scientists have developed a new technique that uses highly magnetized spacecraft to detect contamination from extraterrestrial samples. The technique, called “magnetomagnetic contamination detection”, uses the spacecraft’s magnetic field to detect any particles that have been transferred from other planets or asteroids. This could be a game-changer for the search for extraterrestrial life, as it could allow us to detect signs of life on distant worlds or moons that were previously inaccessible.
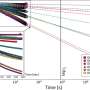
In a recent breakthrough, researchers have developed ultra-wideband heterogeneous photodiodes using thin-film lithium niobate (LiNbO3). This technology could enable applications in sensing, communications, and imaging, such as high-resolution imaging, ultra-fast data transmission, and spectroscopy. LiNbO3 is an optically nonlinear material that can convert light into electrical signals and is capable of operating at ultra-wide bandwidths. The new photodiodes are fabricated on a single chip, using a process that is compatible with commercial CMOS processes.

Recent advances in quantum dot and organic LED technology have caused the focus to shift to perovskite light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for applications in blue light-emitting devices. Perovskite LEDs are made from a combination of organic and inorganic materials, and their unique properties make them ideal for use in a variety of applications. Perovskite LEDs have a long lifetime and are highly efficient in converting electrical energy into light. They can also be used in a variety of colors, including blue, green, and red.

