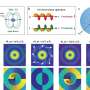
Scientists have recently made a major breakthrough in uncovering the secrets of spin-orbit optical Rabi oscillations. This discovery could revolutionize the ways in which we use light to manipulate spins in quantum systems, leading to exciting new applications such as quantum computing and ultra-fast optical communications. The research team, led by scientists from the Tokyo Institute of Technology, has used a combination of theoretical and experimental methods to study the phenomenon of spin-orbit optical Rabi oscillations.

The era of brain science is upon us! Scientists have been working hard to unlock the mysteries of the human brain, and in a few short years, it looks like we will finally get our answers. By 2023, the secrets of the brain will be revealed and the implications for medicine, technology, and humanity at large will be tremendous. This research holds the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the mind and, ultimately, our lives.

Are you looking for a way to make your microswimmer more fuel-efficient? Scientists at the University of Chicago and Northwestern University have developed a theorem that could help you do just that! Their newly-developed theorem, which was recently published in the journal Science, is based on the principle of “optimal swimming,” which states that the most fuel-efficient path is the one that minimizes the energy spent on swimming. The theorem can be applied to any type of microswimmer, such as bacteria, algae, and nanomotors, allowing them to reach their destination faster and with less fuel.
A group of scientists have recently made a groundbreaking discovery that could lead to a better understanding of the biological secrets behind aging. Through their experiments, they have been able to identify a key protein involved in the aging process and how it works. This protein, called the “aging clock”, is responsible for slowing down cell division and thus influencing how quickly we age. The team believes that by targeting this protein, they can potentially develop treatments to slow down the aging process and improve the quality of life for older individuals.
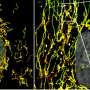
Recently, researchers have discovered a new nanostructure technology inspired by the Morpho butterfly. This technology is incredibly bright, with the potential to revolutionize the way we use light and color in everyday life. The nanostructure is created by using a combination of two types of materials: a transparent material with a reflective layer. This technology is capable of producing light in a variety of colors and intensities, allowing for a wide range of applications.
Cancer is a complex disease that is caused by changes in the behavior of individual cells. A new study published in Nature Communications has identified a mathematical model that can accurately predict the dynamics of cell behavior in cancer. The model can be used to better understand the complexity of cancer and may lead to new treatments.
This groundbreaking research has the potential to change the way we view cancer. By being able to accurately predict the behavior of individual cells in cancer, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of how cancer develops and how it can be treated.
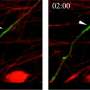
Astronomers have just made a groundbreaking discovery about exoplanets: they believe that some of them may have actual volcanoes! This discovery came about after the team of astronomers, led by Dr. Elizabeth Tasker of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), used computer simulations to study the volcanic activity on exoplanets. The simulations showed that the volcanoes on exoplanets could potentially be up to three times larger than those found on Earth, and may even spew out a variety of different types of gases.

Recent studies have revealed that a genetic mutation of the gene responsible for Raynaud’s phenomenon, a disorder characterized by abnormal constriction and dilation of blood vessels, can now be identified. This discovery could lead to improved diagnosis and treatments for this condition.
For those who suffer from Raynaud’s phenomenon, a new breakthrough in genetics could offer hope for better treatments and diagnosis. Recent studies have identified a genetic mutation responsible for the disorder, which causes abnormal constriction and dilation of blood vessels.

Scientists have just made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of energy. After years of research, a team of scientists have finally deciphered the central mechanism of energy. This discovery has the potential to revolutionize the way we use energy, and could result in major advances in energy efficiency and production. The research team found that energy is created by a sequence of interactions between particles and fields. These interactions are the basis for all energy in the universe, and can be used to create new and improved energy sources.

Scientists have discovered a new way to create materials with site-specific chiral geometry, enabling them to control the electronic and optical properties of two-dimensional heterostructures. By using a novel technique to fabricate AuCu heterostructures, researchers at the University of California, Irvine have created materials with the ability to control their chiral geometry in a design-driven manner. This breakthrough could pave the way for the development of novel optoelectronic devices with unprecedented functionality.
It’s no secret that Mindanao Island in the Philippines is one of the most biodiverse places in the world. It is home to a variety of species, many of which are found nowhere else in the world. To help protect this unique environment, researchers have created an extensive database of all species found on the island. This database will help scientists better understand the biodiversity and ecology of the island, and help inform conservation efforts to protect these species.

A new breakthrough in the field of phonon lasing has been announced: scientists have successfully observed phonon lasing in a crystal for the first time. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way we use light and sound in many applications.
Phonon lasing is a process of creating stimulated emission of phonons, which are the particles of sound. This is similar to the process of lasing, which creates stimulated emission of light particles, or photons.

In a major breakthrough in the field of quantum computing, researchers have developed a self-correcting quantum system that may pave the way for the development of large-scale, error-free quantum computers. This system is capable of automatically detecting and correcting errors in its quantum calculations, allowing it to perform complex calculations with high accuracy. This breakthrough could be a major step towards the development of powerful, reliable quantum computers.
Read Full Article Here

It’s been a long-awaited breakthrough in the scientific community - scientists have discovered a way to use electrical current to induce chemical reactions that previously could only be accomplished through the use of catalysts. This discovery could revolutionize the way we think about and use chemical reactions in the production of materials, pharmaceuticals, and other materials. This research was conducted by a team of scientists from several universities, and published in the journal Nature.

In a landmark discovery, scientists have recently sequenced the DNA of deep-sea marine worms. This breakthrough provides a unique insight into the evolutionary history and ecology of the deep sea, as well as the creatures that live there. The marine worms, known as ‘bobbit worms’, live in the dark depths of the ocean, and can reach lengths of up to 3 meters.
Using this newly-sequenced DNA, researchers were able to identify genetic pathways that are unique to bobbit worms, and compare these with pathways found in other species.

Today, scientists from around the world have made a breakthrough discovery in the field of genetics and primates. For the first time, they have generated a single-cell atlas of a primate, offering unprecedented insights into the biology of these animals and potentially paving the way for treatments of various diseases. This single-cell atlas is the first of its kind, and it has been created using gene expression data from 6,211 cells taken from two different species of primate.
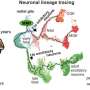
Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in the world of chemistry. They have discovered a way to convert nitrogen gas into a solid phase. This is an incredibly important development as nitrogen is essential to all life on Earth and is one of the most abundant elements in the universe. By converting nitrogen into a solid, scientists can now take advantage of its unique properties and use it to create new materials and products.
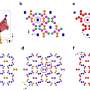
Recently, a team of scientists has made a breakthrough in quantum computing that could revolutionize the computing industry. They have developed a new technique that can erase quantum errors in quantum systems, allowing for more reliable and powerful quantum computing. This technique could have far-reaching implications for the future of computing, enabling quantum computers to operate more efficiently and with greater accuracy. By successfully erasing quantum errors, the research team has opened up a host of possibilities for quantum computing, allowing it to reach its full potential.
In a major breakthrough, scientists have developed simulations that can be used to predict the behavior of complex scientific systems. These simulations are powered by advanced artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, allowing researchers to rapidly test different scenarios and gain a better understanding of how the system works. This could prove to be a major boon for scientists and engineers, as it could lead to faster and more accurate results. Moreover, the simulations could also be used to develop new technologies and products, or to better understand climate change and other environmental challenges.
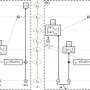
Recent advances in stem cell research have produced exciting new research into optimizing tet on homogeneous induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived myogenic cultures. By optimizing the tet on system, researchers are able to create more homogenous cell populations for studying the biology of muscle development. This system has the potential to revolutionize how scientists study and treat muscle diseases and disorders. Through this system, researchers can observe the development of muscle cells in a controlled and reproducible manner.
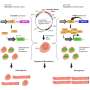
Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a new method for high-throughput identification of Toxoplasma gondii effector proteins. This new method has the potential to revolutionize the way researchers study this important parasite, which is responsible for a range of disease states in humans and other animals. The method uses high-throughput sequencing technologies to identify T. gondii effector proteins from a variety of host cell types. This new method could lead to the development of novel treatments for T.

A new method of predicting adverse drug events has just been developed, and it could revolutionize patient safety. This method, developed by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, uses data from electronic health records to create a personalized risk assessment for each patient. This could help doctors better assess the potential risks of a medication before prescribing it to a patient, potentially reducing the number of adverse drug events and improving patient safety.
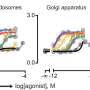
A groundbreaking new form of immunotherapy has been proven to be incredibly effective in mice. This therapy, developed by a team of scientists at the University of California San Diego, involves the use of nanocapsules that are filled with a special type of drug. The nanocapsules are designed to target the tumors in the mice, and when they come into contact with the tumors, they release the drug, which is then able to fight the cancer.

Recently, astronomers have discovered something special about a central star of a planetary nebula - a star that is beginning to die. The star is located in the constellation of Aquila, and is surrounded by a beautiful nebula, which can be seen with a telescope. What makes this star special is that it is one of the very few known stars that is giving off a particularly high rate of X-rays.

Today, a team of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley has made a breakthrough in the field of astrophysics. They have managed to decipher the mysterious behavior of gravitational waves, which are ripples in the fabric of space-time. These waves can provide us with new insights into the universe and its origins. With this newfound knowledge, scientists can use gravitational waves to study black holes, neutron stars, and other objects that were previously too small or too distant to observe.

