
European astronomers are taking on a new galactic challenge: exploring a galaxy cluster 4 billion light-years away. The team of astronomers, led by the European Southern Observatory (ESO), will use the telescope array at the La Silla Observatory in Chile to observe the cluster, which is known as Abell 2744. The team hopes to uncover the secrets of the cluster, which is believed to be one of the most massive and complex structures in the universe.

A revolutionary new gene-editing tool has been developed by a team of scientists at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The tool, called CRISPR-Cas3, is a DNA shredder that can rapidly and precisely edit genetic material. This technology has the potential to revolutionize gene editing by making it faster, more accurate, and more affordable than current gene-editing techniques.
The CRISPR-Cas3 system works by using a combination of an enzyme called Cas3 and a guide RNA molecule to search for specific DNA sequences.

In a recent study, scientists have discovered that the death of a single cell billions of years ago had a major impact on the evolution of life on Earth. The research, published in the journal Nature Communications, shows that this single-cell death event allowed for the development of complex life forms, such as animals and plants, and led to the creation of the complex ecosystems we see today. The findings provide insight into how life on Earth has evolved over time and could help scientists better understand the evolution of other planets.

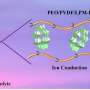
Today, scientists have discovered a groundbreaking development in the field of energy storage. Polyoxometalates, a type of inorganic compound, have been found to be effective ionic liquids in solid-state lithium-ion batteries. This finding could revolutionize the way we store energy, allowing us to charge our phones, computers, and other devices faster and more effectively. Scientists are now looking into ways to optimize the use of polyoxometalates so that we can make the most of this new discovery.
Honey bees are renowned for their altruistic behavior, and now researchers have discovered that this behavior is passed down from one generation to the next. In a new study published in the journal Science, scientists from the University of Sussex have found that when a honey bee colony is faced with a shortage of resources, the bees in the next generation are more likely to be altruistic. This suggests that the bees are able to inherit a genetic trait for altruism, enabling them to pass it on to their offspring.

Recent advancements in astronomy have enabled us to make some incredible discoveries about the universe. Astronomers have now developed a new lens that can detect energetic particles from distant galaxies, giving us an unprecedented view of the universe. This new technology could help us answer some long-standing questions about the origin and evolution of the universe.
The lens works by detecting the energetic particles that are generated by the most distant galaxies in the universe.

Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in using cow manure to produce a synthetic gas that can be used to optimize the process of energy production. The gas, called methane, will provide a clean and renewable source of energy that can be used to replace traditional sources like coal, oil, and natural gas. By converting cow manure into methane, scientists have found a way to reduce the amount of greenhouse gases produced in the process of energy production.

A recent study by researchers at the University of Utah has discovered a link between alcohol use and the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) genes. According to the study, the IGH genes appear to play a role in how individuals respond to alcohol. The study found that individuals with certain IGH genes had an increased risk of developing alcohol dependence and abuse. Furthermore, individuals with a particular IGH gene variant had a decreased risk of developing alcohol dependence and abuse.

This week, a revolutionary new program has been launched to help struggling students get back on track in their studies. The program, which is being funded by the National Education Foundation, will allow students to gain access to virtual tutoring sessions, as well as personalized learning plans and resources to help them work towards their academic goals. This program is here to help students who are struggling due to a variety of factors, including the transition to online learning, the need to balance work and school, and a lack of support from teachers and family members.

NASA is set to embark on an exciting journey to a metal-rich asteroid in October 2023. The mission, called Psyche, is part of NASA’s Discovery Program and is designed to explore a unique and unexplored world in the solar system. Psyche will be the first mission to explore an asteroid of this kind and will provide scientists with a better understanding of how planets and other bodies in our solar system formed and evolved.

Today, researchers have made a remarkable discovery. For the first time ever, they have identified electron nanostructures. These nanostructures are incredibly tiny and measure only a few nanometers in size. They are also incredibly complex, containing hundreds of millions of individual electrons.
The discovery of electron nanostructures could have major implications for the field of nanotechnology. By controlling the behavior of these tiny structures, scientists can potentially create new materials with unprecedented properties.
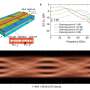
A team of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley have developed a new technology that could revolutionize high-speed data transfer. The technology, called high-speed electro-optic modulation at the topological interface, utilizes the unique properties of topological insulators to transmit data at the speed of light. This breakthrough could enable lightning-fast data communication for a variety of applications, from artificial intelligence to the Internet of Things. By utilizing topological insulators, the data transmission can be performed with minimal loss of energy, making it more efficient than traditional methods.
Recent research from a team of international scientists has revealed an astonishing discovery about the size of marine crocodiles during the Jurassic period. The findings show that some of these prehistoric creatures could grow up to 17 meters in size, making them some of the largest predators ever to inhabit the Earth. The research also suggests that these ancient marine crocodiles had a high level of intelligence, allowing them to hunt and survive in the oceans of the Jurassic period.
A recent study published in the journal Animal Behavior has demonstrated that homosexual behavior has evolved in humans and animals. The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Cambridge and the University of Exeter, found that homosexual behavior is common in a variety of species, and is often seen as an adaptive trait. This suggests that homosexual behavior is likely to have evolved in humans and animals as a way of increasing reproductive success, rather than as a byproduct of other evolutionary processes.

Advances in technology have now enabled us to customize our air purification systems so that we can better protect ourselves from toxic air pollutants. A new study has demonstrated how air purification systems can be designed to filter out specific pollutants. This technology could have a major impact on air quality in heavily polluted areas. The study found that the air purification systems could reduce levels of particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide by up to 80 percent.
Recent research has revealed that the loss of pollinators, such as bees and other insects, could have a significant impact on the production of two of the world’s most popular beverages, coffee and cocoa. Scientists from the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and the University of Cambridge found that pollinators are essential for the production of beans in both coffee and cocoa plants, and that their loss would have dire consequences for farmers who rely on these crops for their livelihoods.

In a breakthrough that could revolutionize the way scientists produce DNA molecules, researchers have developed a new technique that could make the process faster and more efficient. The team was able to synthesize large DNA blocks from smaller fragments, using a technique they call Radical Production of DNA (RPD). The RPD system works by linking together smaller DNA fragments in a single step, allowing for the assembly of large DNA blocks quickly and efficiently.

Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a new self-wrinkling coating that could revolutionize the way that impact resistance and mechanical robustness are achieved in materials. The new coating is composed of two layers, one that is rigid and one that is soft, which allows it to deform and absorb energy when subjected to an impact. This means that it can withstand much higher forces than a conventional coating would be able to, and could prove to be an invaluable tool in the development of materials with enhanced mechanical properties.

Synthetic horseshoe crab blood, known as Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL), has been used in medical diagnostics and research for decades. It is an essential component in detecting the presence of bacterial toxins in a wide range of products, such as medical devices, vaccines, and drugs.
Today, scientists have developed a new alternative to LAL: a synthetic version of horseshoe crab blood. This synthetic blood has the same ability to detect bacterial toxins, but without the need for harvesting or exploiting horseshoe crabs.

Recent research has suggested that building small roads on the Moon may be an effective way to explore its surface. The idea, proposed by a team of scientists from Purdue University, is to construct a network of tiny roads on the Moon using 3D printing technology. This would allow astronauts and robotic vehicles to easily traverse the lunar surface, possibly opening up new areas for exploration that are currently inaccessible. The team believes that this type of infrastructure could be a major game-changer for the future of space exploration.

It’s no surprise that with climate change, marine life is increasingly threatened. A new report released by the International Program on the State of the Ocean (IPSO) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has confirmed this, finding that the world’s oceans are more vulnerable than ever. The report, which was compiled by over 70 leading marine scientists, has concluded that a global scientific consensus exists that we are in a state of “ocean crisis”.

For decades, scientists have sought new ways to fight cancer, and now they believe they may have found an answer in nanosabers. These microscopic machines, each measuring less than a millionth of a meter long, are being developed to target tumors and potentially deliver treatments directly to cancer cells. The nanosabers could be used to deliver drugs or radiation to tumors, providing a minimally invasive alternative to traditional treatments. In addition, the nanosabers could also be used to detect cancer at an early stage, by sensing changes in the tumor environment.
Recently, a key portrait by the Flemish artist Anthony van Dyck has been discovered in an art gallery in the Netherlands. This portrait captures the likeness of an unknown man wearing a blue frock coat and holding a book in his hands. It is a remarkable piece of art, estimated to have been painted in the mid-1600s. Not only does it capture the man’s physical features, but it also conveys his intelligence and nobility.

Astronomers have recently discovered an extremely massive white dwarf in the Hyades star cluster. This dwarf star is the most massive white dwarf ever observed, and is nearly twice the mass of the previously known record holder. This discovery is particularly exciting because it could provide insight into how massive stars evolve, and could help us better understand stellar evolution in general. It also has implications for understanding how stars form in dense star clusters.

For the first time, researchers have managed to sequence the entire genome of a 10-year-old fossilized fly! This breakthrough was made possible by a new technique developed by an international team of researchers, which allowed them to extract and sequence DNA from a specimen that was almost ten thousand years old. The discovery is remarkable, as it provides an unprecedented look into the genetics of an ancient species, and could help us better understand the evolution and adaptation of species over time.

