
Scientists are exploring the genetic potential of eggplant’s wild relatives in their efforts to create new varieties of the popular crop. By studying the genetic diversity of the wild relatives, scientists hope to find new genes that could be used to create hardier, more resistant varieties of eggplant. This could help improve yields and make the crop more resilient to disease and pests. The research could also help to reduce the use of chemical inputs, such as pesticides, in eggplant production.

DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism that helps control gene expression. Scientists have now uncovered a new hidden mechanism of DNA methylation, which is enabling cells to more quickly respond to environmental changes. This discovery could help to explain why some diseases are passed down through generations, and could pave the way for more effective treatments.
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego have uncovered a new hidden mechanism of DNA methylation that could explain why some diseases are passed down through generations.

Have you ever wished you could unlock your door with just the touch of your skin? It’s no longer a dream– scientists have developed a new technology that uses your skin like an octopus!
The breakthrough technology, known as “skin-octopus,” is set to revolutionize the way we access secure areas like homes, offices, and even banks. The innovative system utilizes a special type of sensor attached to the door that will recognize the unique patterns of your skin.
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have created a neural network that can accurately predict the moment when a star will go supernova. Using data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, the team trained a convolutional neural network (CNN) to accurately predict the timing of a supernova event with a precision of up to one day. This finding is an important step forward in the field of astronomy, as it can help scientists better understand how stars evolve and the processes that lead to their death.

A recent study conducted by a team of researchers has revealed that nonlinear exciton-polaritons can be generated in a single-layer of WS2. This is a remarkable discovery that could open up new avenues for the study of optoelectronic devices and photonic circuits. The study, published in the journal Nature Physics, shows that nonlinear exciton-polaritons can be generated in a single-layer of WS2 when illuminated with a low-intensity laser. This is an important breakthrough which could lead to the development of new types of optoelectronic devices and photonic circuits.
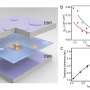
In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers at the University of Cambridge have unveiled a new method to use the orbital Hall effect in spintronics. Spintronics is a rapidly-growing field of technology that uses the spin of electrons to store and manipulate information. The orbital Hall effect is a phenomenon that occurs when electrons flow around a curved path in a magnetic field, resulting in a transverse voltage. By harnessing this effect, the researchers have been able to create a device that can control the spin of electrons at the nanoscale.
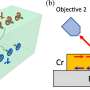
Tomatoes are a popular and versatile food, but scientists have long sought to understand why some varieties are more cold-tolerant than others. In a new study, researchers have uncovered the molecular secrets of cold-tolerance in tomatoes, paving the way for new varieties that can survive in cooler climates. The findings, published in Nature Communications, could help unlock the potential of tomatoes to be grown in regions traditionally too cold for them.

The coronavirus pandemic has been hard on all of us, but scientists have been hard at work trying to find a cure. In a major breakthrough, researchers have identified a key ion channel in the outer membrane of the virus that may be responsible for its ability to cause COVID-19. This discovery could lead to new treatments and vaccines for the virus. By studying the ion channel, researchers were able to determine that it is essential for the virus to infect cells and cause disease.

In a recent study, scientists have discovered that fin whales, a species previously thought to be solitary, actually form small groups of two to three individuals. This finding is an important revelation that could have important implications for how fin whales are managed and protected. The research shows that these whales have complex social structures and behavior, and could be more vulnerable to disturbance than previously thought. This research is a step forward in understanding the behavior and social interactions of fin whales, and could lead to better conservation efforts.

Scientists have recently developed a new method for localizing the source of respiratory droplets. This technique is based on collecting and analyzing droplet properties, such as size and velocity. By using this method, scientists can determine the direction and distance of a droplet’s source. This could be incredibly useful for tracking the spread of airborne diseases, and helping to inform public health decisions. This breakthrough in droplet science could lead to more effective methods of controlling the spread of respiratory illnesses like the flu.
A recent breakthrough by scientists at the University of Science and Technology of China has unveiled a new application of lanthanide-doped KMGF upconversion nanoparticles (UCNs). These nanoparticles are able to convert low-energy infrared photons into higher energy visible photons, a process known as upconversion. This ability could open up a wealth of new possibilities for photonics applications, such as medical imaging, laser projection, and optical communication. By taking advantage of the unique optical properties of lanthanide-doped UCNs, researchers have developed a novel strategy to generate visible photons from low-energy infrared light.
In June, the city of Hamilton, Ontario celebrated Latin American Heritage Month. This month-long celebration highlighted the diverse Latin American culture in the city, as well as the contributions of Latin American people to the community. The celebration was organized by the Hamilton Latin American Heritage Council, a group of community members who are passionate about promoting Latin American culture and heritage. Throughout the month, the city hosted a variety of events such as concerts, art exhibitions, and educational workshops.

Today, scientists are announcing a breakthrough discovery in the fight against HPV. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have identified a new protein, known as HPV-5, which could potentially lead to the development of new treatments for the virus. This new protein was discovered through an analysis of the human papillomavirus (HPV) genome and is believed to be involved in the early stages of the virus’ life cycle. The discovery of HPV-5 could potentially lead to the development of new therapies and vaccines that could help prevent and treat HPV infections.
The future of radio astronomy is at our fingertips with the development of the next generation of large array antennas. Scientists have been working on this project for over two decades, and it is now ready to come into fruition. The new system will be able to observe the universe in an unprecedented level of detail, allowing astronomers to gain a deeper understanding of the cosmos. This new array of antennas will be comprised of hundreds of individual antennas, and will be able to detect radio signals of the entire sky with greater resolution than ever before.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed a method for studying nuclear reactions involving short-lived isotopes. These isotopes, which are unstable and have a very short lifespan, have traditionally been difficult to study due to their limited availability. However, this new method could revolutionize the study of these isotopes and provide valuable insights into nuclear physics and energy production. The method involves the use of a laser-based technique that can create and detect the isotopes quickly and efficiently.
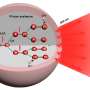
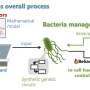
Today, scientists have taken a major step forward in bioprocessing with the development of a proof-of-concept method that promises to make bioprocessing smoother and more efficient. This method utilizes genetic engineering to create cells that can respond to environmental cues, allowing them to be easily manipulated and controlled. This breakthrough could have significant implications for bioprocessing, as it could enable the production of complex molecules for use in pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and other biomedical applications.
Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery: there are lots of galaxies out there in the Universe - but some of them might be astronomically distant! A new survey of the sky has revealed a large number of galaxies that are much farther away than previously thought. The results are a surprise to scientists, who had assumed that the most distant galaxies would be much closer to us.
Today, we have a thrilling update: astronomers have discovered a huge number of galaxies that are farther away than expected!

Scientists have just announced a major breakthrough in laser technology. By using a breakthrough design, they were able to create the world’s first widely tuneable terahertz laser. This new laser has the potential to revolutionize many fields, including medical imaging, communications, and sensing.
The laser is able to generate a wide range of frequencies, from 0.2 to 1.2 THz, making it the most tuneable terahertz laser ever created. This means that it can be used to detect a wide variety of objects and substances, from tiny biological molecules to larger objects like people or cars.
China is making history by becoming the first country to build a space station of its own! This will be the third space station to exist in the world, after the International Space Station (ISS) and Russia’s Mir space station. The Chinese station is expected to be completed by late 2023 and will be the size of a football field, with a mass of approximately 66 tons.
This is a monumental achievement for China and a huge step forward in space exploration.

Today, a revolutionary development in neuromorphic computing has been announced. Scientists from the University of Central Florida have developed a new way to control filaments in vanadium dioxide using lasers. This can be used to create an artificial neural network, similar to the way neurons communicate in the human brain. The technology allows for faster and more efficient computing, and could potentially revolutionize the field of neuromorphic computing. This development has the potential to revolutionize computing speed and efficiency, by allowing for more complex computations to be carried out in less time and with less energy.

NASA is embarking on an exciting new mission to explore a mysterious metal world located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The mission, named Psyche, will launch in 2023 and set out to explore the metal asteroid 16 Psyche, a 130-mile-wide object made of iron, nickel, and other metals. This will be the first mission of its kind, as 16 Psyche is thought to be the exposed core of a protoplanet, which is a planet that failed to fully form in the early days of the solar system.

In a groundbreaking mission to explore the metal-rich asteroid Psyche, a spacecraft is set to launch in 2023. Equipped with a suite of sensitive instruments, the mission will be the first of its kind to explore an asteroid that is believed to be composed largely of metal. The spacecraft will use its instruments to investigate Psyche’s surface and interior, allowing scientists to learn more about the formation and evolution of our solar system.

Do you ever wonder what secrets our galaxies may hold? Well, a new field of study called ‘galactic archaeology’ is helping us uncover the secrets of our own Milky Way! This exciting new field of research uses advanced technology to study the stars and galaxies around us, and to piece together the history of our own galaxy. Scientists are finding unique and interesting patterns that provide insight into our Milky Way’s past.
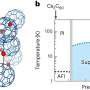
In a remarkable discovery, scientists have found an “afterglow” from an explosive collision between two giant planets. The afterglow, or post-collision debris, was detected in the form of a bright ring of light around a distant star. The findings, published in the journal Nature, provide insight into the formation and evolution of planetary systems and could help explain the origins of our own Solar System.
This week, astronomers made an incredible discovery: an afterglow from an explosive collision between two giant planets.

In a recent research study, scientists have discovered that even in some of the most extreme and inhospitable habitats on Earth, microbial life is still able to survive. From the dry valleys of Antarctica and the boiling hot springs of Yellowstone National Park, to the deepest trenches of the ocean and even within the clouds of Venus, these microorganisms have been found to be remarkably resilient. This discovery has strengthened our faith in the potential of life to exist in other extreme habitats throughout the universe.

