Scientists have recently made a breakthrough with the development of photonic crystals that can manipulate gravity. This could have a major impact for a range of industries, from aerospace engineering to medical technology. Photonic crystals are made of light-manipulating materials that have unique properties that allow them to interact with gravity in ways that have never been seen before. The crystals can be used to levitate objects, detect gravity waves, and even create artificial gravity fields.

Astronomers have recently discovered that pulsars may be the key to understanding dark matter, the elusive substance that makes up the majority of our universe. This discovery could potentially revolutionize our understanding of the universe and its origins. Pulsars are small, rapidly spinning stars that emit regular pulses of energy, and they are thought to be the result of a supernova explosion. By studying the properties of these pulsars, scientists are now able to infer the presence of dark matter in the universe.

Today, a team of researchers from the Institute of Chemical Physics at the Czech Academy of Sciences has made a major breakthrough in the field of ultrafast photoemission spectroscopy of carbon. Using a novel ultrafast laser system, they have achieved unprecedented temporal resolution of the carbon photoemission process. This breakthrough could have far-reaching implications for the development of new technologies and materials based on carbon. With this technique, the team was able to observe the dynamics of the electrons emitted from carbon with an unprecedented time resolution of 10 fs.

Scientists have long debated when animals evolved and how they evolved. Recently, a team of scientists have made a breakthrough in this debate by uncovering fossils that shed new light on the evolution of animals. The fossils, which were discovered in the Canadian Arctic, date back to the Cambrian period, around 541 million years ago. They provide evidence that animals were more diverse and widespread in the Cambrian period than previously thought.

The potential of genetic glycoengineering to advance vaccines has been gaining increasing attention in recent years. Scientists are exploring ways to modify the carbohydrates present on the surface of cells to improve vaccine efficacy and stability. By manipulating the sugar molecules on the surface of cells, researchers hope to create more effective vaccines that can target a wider range of diseases. One promising area of research is the development of glycoengineered vaccines that can induce a stronger immune response against certain pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria.

Have you ever wondered what the future of space exploration looks like? Well, the answer may be closer than you think! Scientists have recently identified 10 unique metallic signatures of space-age spacecraft, which could be used to help identify space debris from a distance. This could be a major breakthrough in the field of spacecraft monitoring and tracking. The signatures, which were discovered using X-ray spectroscopy, could also help scientists to better understand the composition of space objects, as well as the impact of space weather on spacecraft.

A new bi-functional catalyst made from a single metal could make hydrogen production from methanol more efficient, according to a study published recently in the journal Science Advances. The catalyst, which is made of a cobalt-manganese mixture, is more effective at producing hydrogen than traditional monometallic catalysts, with the added benefit of being able to produce the hydrogen at lower temperatures than typically required. This could potentially lead to lower production costs and more efficient fuel cell technology.
New research has found a revolutionary method to analyze the microbiome of the human gut. The method, developed by scientists at the University of California, Santa Cruz, uses a combination of high-resolution imaging and machine learning algorithms to gain insights into the microbiome’s structure and function. This breakthrough could potentially revolutionize the way doctors diagnose and treat diseases related to the human gut microbiome. The team’s findings have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
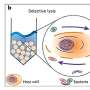
A recent breakthrough in the field of microbial ecology has revealed the function of microbial communities in a much simpler way than previously thought. Scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have discovered a novel way to understand the role of microbial communities in different habitats, including the human gut. By examining the environment and the structure of microbial communities, they have developed a mathematical model that can accurately predict the functions of these communities.
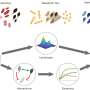
In a groundbreaking new study, scientists have discovered that ancient microbes could have played a key role in the environment’s ability to store important metals. Researchers from the University of Leicester, in collaboration with researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have discovered that microbial communities could have been responsible for the storage of metals in the environment for between 700 million and 1 billion years. The findings could have implications for our understanding of the environment, and the management of metals in it.

In a groundbreaking development, scientists are now applying artificial intelligence to create a new type of polymer membrane that offers greater efficiency and energy savings in the production of oil and gas. This new membrane technology could revolutionize the energy industry and significantly reduce the cost of oil and gas production while also reducing environmental impacts. The new polymer membrane is composed of a material that is both light and strong, and is capable of filtering out impurities in oil and gas.

A new study by researchers at the University of California, San Francisco has revealed that deep sleep may be an effective way to prevent hospital-acquired infections. The study, which was published in the journal Nature Communications, found that deep sleep in mice significantly reduced the number of hospital-acquired infections. The researchers found that when mice were kept in a state of deep sleep for several hours each day, they had significantly fewer infections than mice that were kept awake.

In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have found that inequality is an inevitable consequence of mammalian evolution. By studying the evolutionary histories of mammals, the team was able to identify traits that lead to the development of inequality in the species, and how this has shaped the diversity of life we see today. From their findings, the team concluded that the development of inequality isn’t necessarily a bad thing, but rather it has helped drive the evolution of mammals in a positive direction.

As the effects of climate change continue to take their toll on the global food system, a new research project has begun to explore the potential of adapting traditional methods of corn growing in the American Midwest. The “Growing Zone Corn” project, led by researchers from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, will focus on the development of corn varieties that can thrive in a variety of climates and soil types. This would give farmers the ability to choose from a variety of corn varieties that are suited to their specific growing conditions, allowing them to maximize production and ensure that their crops are resilient in the face of changing weather patterns.

The coffee and cocoa industries have been feeling the effects of habitat loss for pollinators like bees, butterflies, and other insects. A recent study by the University of Exeter found that the loss of pollinators could have a significant impact on production of these important crops. Without pollinators, the study estimates that coffee production could fall by an average of 50%, and cocoa production could drop by an average of 30%.

In an exciting breakthrough, scientists at the Korean Consortium (KC) have developed a strategy for light-driven superconductivity. This means that superconductivity, which is usually achieved by cooling materials to extremely low temperatures, can now be achieved using light instead. This new strategy could revolutionize the way we use and create superconductors, making them much more efficient and accessible. With the potential to revolutionize technology and energy consumption, the potential of this new strategy is truly groundbreaking.
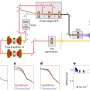
Recently, a group of scientists have announced a breakthrough in green hydrogen production. Green hydrogen is produced by using renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectricity, and is a clean and efficient alternative to traditional hydrogen production methods. The new breakthrough enables the production of green hydrogen to be accelerated by up to 300 times, making it a much more viable and cost-effective option for the manufacturing industry. This new development could be a major step towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future!

On August 21st, 2023, the United States of America will witness its first total solar eclipse in seven years. This eclipse will be the first of its kind to move from coast to coast since 1918. Starting in Oregon and ending in South Carolina, this total solar eclipse will cast an awe-inspiring shadow across the entire nation.
As the day of the eclipse approaches, Americans across the country are preparing to witness this incredible event.

An astronaut has broken the record for longest amount of time spent in space, with an incredible 1057 days in Earth’s orbit! Russian cosmonaut, Oleg Kononenko, returned to Earth on December 20th, 2023 after more than three years in space. During his time in space, Kononenko made a total of six space walks, four of which were from the International Space Station. He also completed several experiments, including the first-ever in-space repair of a satellite.

Today, a team of scientists announced the first ever Saturday citations of a simulated universe. This simulated universe, which is powered by a sophisticated computer program, is able to recreate the complex physics of gravity. The results of this simulation have provided researchers with unprecedented insight into the behavior of matter and energy in the universe. Through this simulation, scientists have been able to observe how gravitational fields interact with matter and how these interactions affect the overall structure of the universe.

NASA recently announced that the Osiris-Rex spacecraft has revealed evidence of carbon-bearing material on the surface of the asteroid Bennu! This is an exciting discovery, as Bennu was the first asteroid visited by NASA’s spacecraft. The samples collected by the spacecraft confirmed the presence of organic molecules, which are necessary for the formation of life. This discovery could open up new possibilities for understanding the origin of life in our universe.

NASA is preparing to launch an incredible mission to explore a mysterious metal-rich asteroid known as 16 Psyche. This exciting mission will provide us with an unprecedented look at the interior of an asteroid, which will allow scientists to study the origin and evolution of our solar system. The spacecraft is set to launch in 2023 and travel to 16 Psyche, which is located in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, for a detailed exploration.

On October 14th, 2023, a total solar eclipse will be visible across parts of the Americas. Starting in Oregon, USA, the eclipse will travel south across the continent, before eventually ending in northern Brazil. This once-in-a-lifetime event will be a spectacular sight, and a great opportunity for astronomers and eclipse-chasers to witness the awe-inspiring power of a total solar eclipse. Make sure to mark your calendar and plan your trip to the eclipse’s path of totality!

New research suggests that European summers are likely to become significantly hotter and drier in the coming decades. This could have a devastating impact on crops and other forms of agriculture, leading to an increased risk of famine and water shortages for many countries. To help tackle this problem, scientists are now looking at the possibility of using traditional craft techniques to help farmers adapt to the changing climate. This could involve using traditional methods such as terracing and irrigation systems, as well as more innovative approaches such as the use of soil-less farming methods.

A new study has found that the introduction of “climate flies” could help reduce global warming. Climate flies are flies that are genetically modified to consume more carbon dioxide than regular flies. According to the study, these flies could reduce global temperatures by up to 0.5 degrees Celsius over the next decade.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, suggests that releasing billions of climate flies into the atmosphere could reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which would in turn reduce global temperatures.

