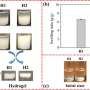
Recent advances in digital technology have opened up exciting new possibilities for the art world. In a groundbreaking project, researchers have now succeeded in producing a million pieces of artwork, all created using nothing but chemistry and digital technology.
The team used a combination of DNA nanotechnology, 3D printing and digital imaging to generate a huge library of unique artworks. The process starts by encoding a pattern into a strand of DNA which is then inserted into a 3D printed sculpture.

Recently, scientists have discovered a way to control the spread of bacterial pathogens, by triggering a “door” that helps keep them contained. Using a combination of high-powered lasers and computer algorithms, researchers were able to manipulate the cell wall of a bacterium, opening and closing the door to the pathogen. This could be the first step in controlling the spread of harmful bacteria, and could even lead to new treatments for bacterial infections.

Geospatial technology is being used to unlock the potential of corn fields across the globe. By using a combination of satellite imagery, drones, and artificial intelligence, farmers are able to gain insights and develop strategies to maximize their crop yield and minimize environmental impact. This technology can help detect crop health issues, identify areas of soil fertility, and monitor the growth of the plants. Not only does this technology improve the productivity of the crop, but it also helps identify and prevent potential problems such as pests, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies.

Recently, scientists have developed a deep learning-based biosensing platform that promises to revolutionize the way we observe and monitor the natural world. This platform is able to detect and identify various biological entities, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, with unprecedented accuracy and speed. The platform works by utilizing a combination of machine learning algorithms and innovative hardware to isolate and identify these organisms. This technology is expected to have a huge impact on the field of environmental science, as it can provide a much more detailed and accurate view of the world around us.

The future of communication is here! Researchers from the University of Cambridge have just announced the development of photonic chips that can enable high capacity transmissions, ushering in a new era of communication technology. These chips are capable of transferring data at a rate of up to 1 terabit per second - that’s 100 times faster than the fastest internet connections available today! The chips are constructed using silicon, and use light-based signals instead of electrical signals to transfer data, meaning that they are much more efficient and reliable than current technology.
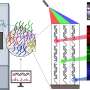
In a breakthrough study, researchers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a new imaging technique to visualize the unique glycans bound to biomolecules. Glycans are complex carbohydrates that can be found on cell surfaces and are essential for modulating the biological activity of proteins. By using this new imaging technique, researchers are able to determine the structures of glycans within the context of the bound biomolecule. This has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of protein-glycan interactions and lead to new therapeutic strategies.

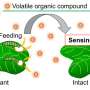
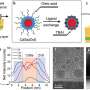
Today, scientists have discovered a way to observe the communication between plants in real-time. Using advanced technology, researchers have developed a method to visualize airborne molecules exchanged between plants in their natural environment. This new technology is revolutionizing the way we understand how plants interact with each other and how they communicate. The implications of this discovery could lead to new breakthroughs in the fields of agriculture and environmental conservation. By being able to observe plants and their communication patterns in real-time, we can gain an unprecedented insight into the complex dynamics of the natural world.
As the world moves toward an increasingly digital future, the need for reliable and efficient memory solutions is greater than ever before. Now, researchers have developed a new type of memory that is powered by light and can store multiple levels of information in a single cell. This breakthrough is ushering in a new era of light-powered multi-level memories that offer unprecedented levels of efficiency and reliability.
The new memory, called a “multi-level memory cell” (MLMC), is made up of a single cell that can store multiple bits of information at once.
AI is revolutionizing biodiversity research in tropical rainforests! Scientists at the University of York are using AI to help identify and conserve animal species in the rainforest. By combining AI and traditional methods of biodiversity research, scientists are able to detect animal species that are often hard to spot in the wild. This technology has the potential to help protect species from extinction, as well as improve our understanding of tropical ecosystems.

Today, economists have developed an algorithm that offers a way for businesses to become more flexible and sustainable. The algorithm, designed by a team of economists from the University of California, Irvine, allows businesses to adjust to changing market conditions in a way that optimizes their profits. The algorithm uses a combination of predictive models and machine learning to analyze data and make decisions about how to respond to changing market conditions.

Harnessing the power of molecules to generate electricity is the goal of an exciting new research project. Researchers at the University of Cambridge are working on a new technology that could revolutionize the way we generate electricity. The project involves manipulating molecules in a way that could potentially generate electricity without the need for traditional fuel sources such as coal, oil, or natural gas. The research team is using a combination of synthetic biology and nanotechnology to create molecules that can produce electricity when exposed to light or temperature changes.
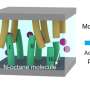
A new enzyme molecule has been discovered by researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) that could have a major impact on the way marine bacteria are able to degrade plastics. This new enzyme, called Methylomarinovorans methylothermobutyricum (MMT), was discovered in a sample of seawater collected near the Japanese coast. This enzyme has the potential to break down plastic polymers, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), much more quickly than other known bacterial enzymes.
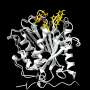
The future of cancer immunotherapy is looking brighter than ever! A new study conducted by researchers from the University of Illinois at Chicago has revealed a promising new approach that uses mRNA nanovaccines to trigger an anti-tumor immune response. The study, which was recently published in the journal Nature Communications, details the development of a rational mRNA nanovaccine that can be used to target and destroy tumor cells. The nanovaccine is composed of a small, non-coding RNA molecule that is able to penetrate the tumor cell membrane and activate an anti-tumor immune response.
A new breakthrough in bioprinting technology promises to revolutionize medical treatments across the world. Scientists have now developed a cell-friendly bioprinting method that allows for high-fidelity medical implants to be printed with unprecedented precision. This breakthrough has the potential to open up a whole new field of personalized medicine, where treatments can be tailored to the individual patient’s needs. This technology could also make it easier to fabricate complex organs and tissues, allowing for more successful organ transplants and tissue engineering.

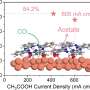
A new strategy to boost the efficiency of carbon monoxide electrolysis has been discovered by scientists. Carbon monoxide electrolysis is a promising route for the production of fuels such as hydrogen. The team found that the addition of a catalyst known as a layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly can increase the efficiency of the electrolysis process by up to 25%. This could be a major step forward in improving the efficiency of energy production from carbon monoxide.
Recently, a flesh-eating illness that is caused by bacteria has been discovered along the coast of Florida. The disease is called Vibrio vulnificus and it is a naturally occurring bacteria found in warm coastal waters. This bacteria can cause severe illness and even death in individuals who have a weakened immune system or open wounds that are exposed to the contaminated water. Symptoms include fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhea, and severe skin infections.

China is about to make history in particle physics. In 2023, a new underground site in the Sichuan province will become the home of the world’s largest and most advanced neutrino detector, the China-based Trident Neutrino Observatory. This massive facility will be the first of its kind in China and will revolutionize our understanding of the universe and the fundamental forces that govern it.
The Trident Neutrino Observatory is a collaboration between the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the University of Michigan, and other international institutions.

Are you an older adult looking to demystify biology? If so, you’re in luck. In this article, we’ll be exploring some of the key questions and answers surrounding biology as it applies to older adults.
The aging process is something that affects us all, but it can be especially confusing when it comes to understanding biology. It can be difficult to make sense of the complex biological processes that come with aging, and it can be challenging to learn how to maintain your health and wellness as you age.

The world of electronics is on the precipice of a new era—the approach of advanced electronics storage through ferroelectricity. Scientists have just developed a new ferroelectric material that can store information in a much more efficient and stable way than traditional semiconductors. This new material, called hafnium oxide, can store data for a much longer period of time without losing its charge. Additionally, it can switch between two different electrical states much faster than traditional semiconductors, meaning that it can process information much more quickly.

NASA is set to launch a groundbreaking mission to a dwarf planet in our solar system. The mission, called Hypervelocity Impact Probe (HIP), will send a spacecraft to the dwarf planet Makemake to study its surface and composition. The spacecraft will use a combination of imaging and spectroscopy to map the dwarf planet. It will then use a “hypervelocity impact” to penetrate Makemake’s surface and collect samples of the material beneath it.
Astronomers have just made a fascinating discovery about pulsars in the globular cluster NGC 6624. Using the Very Large Array, a powerful radio telescope, they detected 10 pulsars in the cluster, making it the first time that pulsars have been discovered in such a dense stellar environment. This discovery could help scientists better understand how these objects form and evolve in such an environment. It could also provide new insights into the formation and evolution of globular clusters in general.
In a remarkable breakthrough, scientists and philosophers have come together to uncover the nature of evolutionary law. Through rigorous research and analysis, they have been able to identify the fundamental principles that govern the process of evolution. These principles, known as the Universal Laws of Evolution, provide unprecedented insight into how evolution works and how it shapes the world around us. The discovery of these laws has implications for many areas of science, including biology, ecology, and even philosophy.

A team of astrophysicists and nuclear engineers have made a breakthrough in understanding the reaction paths of nuclear reactions in stars. This finding could have a major impact in the development of nuclear power sources and could help us to better understand the physics of our universe. The team was able to map out the specific reaction paths of the most commonly used nuclear reactions in stars, and this could revolutionize our understanding of how stars produce energy.

New research conducted by scientists at the University of Arizona has revealed a revolutionary discovery in space exploration: quartz crystals in clouds of hot gas could be used to detect the furthest corners of the universe. Using the James Webb Space Telescope, the team of researchers observed quartz crystals in clouds of gas in the Milky Way, and in other galaxies, finding that these crystals are sensitive to the light from distant stars and galaxies.
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have successfully created a gel-like material that mimics the adhesive properties of a bird’s feet. This gel, which consists of cellulose, is able to hold onto surfaces and then detach from them without leaving any residue. The discovery could lead to a new generation of applications in robotics and adhesive technologies. The gel is able to stick and unstick without leaving any residue and can be reused countless times.