Agronomists have recently made a groundbreaking discovery that could revolutionize the way we approach hormone therapy. By utilizing heavy metals in soil, agronomists have found a way to naturally regulate hormones in the human body. This discovery could have far-reaching implications, potentially opening the door to new treatments for a variety of conditions related to hormone imbalances. In addition, this discovery could also help reduce the risk of adverse side effects associated with synthetic hormone treatments.

Astronomers have made a stunning discovery of the closest known ultraluminous supernova to date. Located in the constellation of Pegasus, the supernova is approximately 200 million light years away from us, making it one of the most nearby ultraluminous supernovae seen to date. The supernova, which is classified as a Type Ia, is about 10 times brighter than a typical supernova of its type. Scientists have been able to observe the supernova in great detail, which provides valuable insight into the properties of ultraluminous supernovae and how they may differ from typical supernovae.

For centuries, scientists have been trying to understand the nature of the physical world and the laws that govern it. But a new study suggests that some of the most fundamental laws of quantum mechanics may need to be rethought. A team of researchers has identified 10 “thought laws” that could potentially redefine our understanding of the universe. These laws could help us to explain some of the most mysterious aspects of quantum physics, such as entanglement and the uncertainty principle.

Recent research has suggested that the combination of hybridization and polyploidization could play a major role in the evolution of species. Hybridization, or the mating of two different species, and polyploidization, or the increase in the number of chromosomes that occurs when two sets of chromosomes fuse, have long been seen as major forces in the evolution of new species. However, until recently, their exact role in the evolution of species was unclear.
For parents of preschoolers, there is exciting new research that suggests that engaging in activities that involve rhythm can help boost brain development! A new study conducted by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill found that preschoolers who participated in rhythmic activities such as music, dance, and sports showed significant increases in their executive functioning skills, which are important for learning and development. These results provide a great opportunity for parents to incorporate rhythm-based activities into their children’s daily routines.

Astronomers have made a remarkable observation about protostars – the earliest stage of a star’s life cycle. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, astronomers have discovered that protostars are able to ‘siphon’ off material from their surrounding environment in order to fuel their growth. This process, known as accretion, is the same mechanism that powers stars throughout their lives, and it appears to start much earlier than previously thought.

It’s a momentous day for the food industry: a pathogen that has been a source of great destruction for centuries has finally been eradicated! Scientists are celebrating the news that the blue plague, a food-destroying pathogen that has been plaguing farmers for generations, has been completely eliminated. This is a huge win for the food industry, as it can now guarantee that food production will be free of this dangerous pathogen.
In recent years, scientists and engineers have been hard at work developing more efficient, cost-effective solutions for treating wastewater generated from industrial processes and urban areas. A new technology developed by researchers at the University of California, Riverside, is making it possible to treat wastewater more quickly, more efficiently and more cost-effectively than ever before. By using a combination of innovative processes, the team was able to create a treatment system that not only meets all local and federal regulations, but also does so in a fraction of the time and cost of traditional systems.

An international team of scientists has just announced a major breakthrough in astronomy. After years of study, they have finally identified the source of the largest single explosion ever detected in the universe. The colossal blast, known as GRB 190114C, was detected in April 2019 and is the result of two neutron stars colliding and merging together. The team was able to determine the explosion’s origin by studying the afterglow of the blast, which was seen across the entire electromagnetic spectrum.

NASA is in the planning stages of a revolutionary new project: a vast, billion-hub “space gateway” orbiting the moon. This gateway will be a major waypoint for astronauts and spacecraft on their way to the moon, Mars, and beyond. It will provide a permanent presence in space, featuring a communication system, research facilities, and a refueling station. It will also act as a staging area for future deep space exploration. The gateway is set to be complete by 2023, and will be a major milestone in humanity’s exploration of the universe.

Today, NASA announced that its Lucy spacecraft is on track to make history. The spacecraft is set to approach its first of 12 targeted asteroids in 2023. This is the first mission of its kind to explore the Trojan asteroids, a group of asteroids orbiting the Sun near Jupiter. With its groundbreaking mission, Lucy will be able to shed light on the early days of our Solar System - providing us with an unprecedented look at the formation of our planets.
A new breakthrough in biotechnology is set to revolutionize how we detect and treat diseases. Scientists have developed a hydrogel-based material that is capable of binding to a target molecule with high specificity, similar to an antibody. This material, known as an aptamer, is made of a strand of DNA or RNA, and has the potential to be used as a chemical antibody, allowing for the detection of diseases and toxins in a much faster and more accurate way than traditional methods.

Researchers from New Zealand and Australia have just completed the first-ever genomic sequencing of the common Brushtail Possum. This is an exciting breakthrough as the Brushtail Possum is a species of marsupial found in both New Zealand and Australia, and by understanding its genome, scientists can gain further insight into the unique biology of marsupials. Possums are important to both countries’ ecosystems, so this research could help inform conservation and management strategies in the future.

In recent years, math disabilities have become increasingly common among students in schools all across the country. Despite their prevalence, however, many schools are still not properly equipped to handle the needs of students with math disabilities. This lack of support has led to a great deal of frustration among students and their families, as they struggle to find ways to help their children succeed in math.
The issue of math disabilities is especially concerning given that math skills are essential for academic success.

Scientists have discovered something remarkable about longevity in marine mammals—they can live for much longer than previously thought. A new study published in the journal Nature Communications has revealed that some species of dolphins, whales, and manatees can live much longer than previously believed. The research team studied the lifespan of over 1,000 marine mammal species and found that some lived up to five times longer than previously estimated. The findings suggest that marine mammals may have evolved a unique ability to age slowly, allowing them to live longer and healthier lives.

Today marks a historic moment for SpaceX, as the company has announced that it is now equal to the entire Space Coast in terms of launch capability. This means that SpaceX can now launch more than any other single provider in the world. The announcement comes after a series of successful launches, including the launch of the Crew Dragon spacecraft earlier this year. This milestone is a testament to SpaceX’s relentless commitment to making space exploration more accessible and affordable.

In the world of technology, tribotronics have recently emerged as a promising prospect for creating functional devices that are self-powered. Tribotronics is a combination of tribology, the science of friction, and electronics, combining the two to create a unique form of energy harvesting. Tribotronic devices are capable of capturing the energy from sliding friction to power themselves, eliminating the need for a power source. This means that the devices can be used in areas without an external power source, such as in remote or rural areas.

Good news for chocolate lovers! A new study has found that cocoa pods could become a source of chocolate in the future. Scientists have discovered that cocoa pods can be used to produce a kind of ‘chocolate-like’ substance that could potentially replace cocoa beans. This discovery could revolutionize the chocolate industry and make chocolate more sustainable, as cocoa pods are much more abundant than cocoa beans. The researchers believe that cocoa pods could be used to make chocolate more cheaply and even be used to create new flavors and textures.

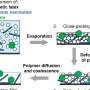
In a world where agriculture is an increasingly important part of our lives, it is essential that we consider the environmental impact of our farming practices. With this in mind, researchers at the University of California, Davis, have developed a new approach to sustainable and smart agriculture. This approach, known as “biodegradable soil,” is designed to reduce water and chemical use while increasing crop yields. The soil is composed of a mix of organic matter, minerals, and beneficial microorganisms which work together to create a nutrient-rich environment for plants while also providing a natural buffer against disease and pest outbreaks.
Researchers have identified a multi-drug resistant strain of E. coli bacteria that could be a serious public health threat. The strain, known as ST11-MDR-AmpC, is resistant to nearly all antibiotics and is able to spread from person to person. This marks a significant development as it is the first time a multi-drug resistant strain has been identified in humans. The strain has been found in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, and is believed to be responsible for a number of outbreaks in recent years.

The future of medicine is bright, and new discoveries continue to be made every day. A new study has found that polyalthic acid from Copaiba, a tree native to South America, could potentially be used as an antimicrobial agent. This could be a breakthrough in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, as polyalthic acid has been shown to be effective in killing a wide variety of bacteria, including some which are resistant to antibiotics.

The role of memory in cognitive functions has been studied extensively for many years, but there has been relatively little research conducted on how memory contributes to the successful acquisition of English as a second language. A new study has revealed that memory plays a significant role in the understanding and retention of English language skills. The study found that individuals with better memory were able to learn and retain English grammar and vocabulary much more easily than those with poorer memory.

A new species of orchid-pollinating bumblebee has been discovered on a remote island off the coast of Scotland. The bee, Bombus muscorum, is the first bumblebee to be described from the island of Islay in over a century. This discovery is an exciting addition to the already diverse bee population of Islay and represents a unique example of island evolution.
This new species of bumblebee is remarkable not only for its discovery on Islay, but also for its unique method of pollination.
Scientists from around the world have recently collaborated to uncover some incredible insights about 2D materials. After forming an international collaboration, they have discovered that these materials have some remarkable properties that could lead to a whole range of new applications. One of the most exciting findings is that these materials can be used to create electronic devices that are faster, more efficient, and even more flexible than ever before. This could revolutionize the way we interact with technology, potentially leading to a world of applications that are more powerful and more convenient than ever before.

Recent groundbreaking research has revealed that bacteria could be the key to effectively capturing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen for our planet. The study, conducted by scientists at the University of Bristol, UK, has found that certain bacteria can be used to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen while also capturing the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This could provide a major step towards reducing carbon dioxide levels and helping to combat climate change.