
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed a new method that allows people to play musical instruments without any prior knowledge of the instrument. The new method, developed by a team of scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, uses artificial intelligence to interpret the movements of a person’s hands and feet, and translate them into music. The team used this method to create a piano-playing robot that was able to play simple melodies without any prior instructions.

Recent research has uncovered that modern salamanders may hold the key to understanding the behavior of their ancient ancestors. By looking at the behavior of living salamanders, scientists are able to gain insight into the ecology of their ancient relatives. The research team found that salamanders are surprisingly active animals, exhibiting a variety of behaviors including foraging, mating, and predator avoidance. These behaviors have remained relatively unchanged since the time of the ancient salamanders.

The dynamic relationship between transcription and epigenetic processes has been the focus of many studies within the scientific community, but now researchers at the University of California, San Francisco have developed a new method to more fully understand this relationship. By combining single-cell RNA sequencing and epigenomics data, the team was able to map out the dynamic transcriptional and epigenetic landscape of cells in unprecedented detail. This new approach could provide insight into the mechanisms of gene regulation, which may be useful for the development of new treatments for various diseases.
Researchers have recently discovered new evidence that sheds light on the evolution of mosquitoes and their hosts. By studying a group of mosquitoes, they were able to uncover the genetic basis for host preference and adaptation in the insects. This research could have implications for how we control and prevent mosquito-borne diseases.
Our understanding of the evolution of mosquitoes and their hosts has taken a giant leap forward. A team of researchers has identified the genetic basis for host preference and adaptation in the insects.

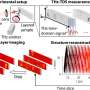
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered an entirely new form of imaging – Terahertz (THz) imaging. This is a revolutionary form of imaging that allows us to see objects hidden beneath the surface of other materials. THz imaging works by producing a beam of electromagnetic radiation that is able to penetrate through a variety of materials, including plastics, wood, and even human skin. This allows us to see objects that would normally be invisible to the naked eye.
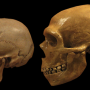
In a recent study, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology have revealed evidence of a previously undocumented encounter between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens. This encounter likely took place approximately 120,000 years ago in the Middle East, significantly earlier than the previous estimates of between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago. This discovery has significant implications for our understanding of the timeline of human evolution. It suggests that the two subspecies of humans, Homo sapiens and Neanderthals, coexisted in the same area for a much longer period than previously thought.
In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers from the University of Lorraine have unearthed the remains of a new species of plesiosaur, Lorrainosaurus. This ancient marine reptile lived during the Middle Jurassic period, approximately 170 million years ago, and is the earliest known member of the group of plesiosaurs that evolved into modern species. The fossil remains were discovered in the museum’s own fossil collection and were only recently identified as belonging to a new species.

Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in quantum physics: the ability to generate quantum entanglement and teleportation. This exciting new discovery could revolutionize the way we communicate, travel, and even think.
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where two particles become linked together in a way that any change in one particle is reflected in the other. This means that if one particle is moved or altered, the other particle will instantly change as well, no matter how far apart they are.

A new method for accurately analyzing body fluids at crime scenes has been developed by scientists. The breakthrough technology could help investigators to quickly identify the type of fluid involved in a crime, without the need for traditional lab testing. The research team has developed a method that uses a combination of infrared and Raman spectroscopy to analyze body fluids in a much shorter time than traditional techniques. This could be a crucial tool for forensic investigators, as it could help them to quickly identify the type of fluid at a crime scene and determine whether it is blood, saliva, or another type of body fluid.
A recent study has revealed a unique and hitherto unknown bacterial transcriptional response to changes in its environment. The research, conducted by a team of scientists at the University of Cambridge, has revealed that certain bacterial species can respond to environmental stressors by altering their gene expression in ways that had been previously unknown. The findings could have important implications for understanding how bacteria adapt and respond to changing environments, as well as how to design better treatments and vaccinations for infectious diseases.

An international research team led by the University of Melbourne has made a breakthrough discovery that could lead to a better understanding of how cancer cells grow and spread. The team has revealed the structure of a key protein involved in cancer growth and metastasis. This discovery could open the door to the development of new treatments for cancer in the future. The protein, called a NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE), plays an important role in the growth and spread of cancer cells, and this new research has provided a three-dimensional view of the protein’s structure.
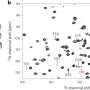
Recently, a team of scientists from the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have made some incredible new discoveries about the genetics of the common octopus. After sequencing the genome of the common octopus, the team was able to identify some truly remarkable insights into the evolution and development of this species.
One of the most interesting findings of the research was that the common octopus has a large number of genes that are involved in the development of its unique tentacles.

Space exploration is about to reach a new level of precision! A team of astrophysicists recently announced their discovery of a new method for accurately measuring distances between relatively nearby galaxies. This new technique, dubbed the “space-time interferometer,” combines space-based and ground-based data to create an incredibly precise measurement of distances between galaxies within 2.5 million light years of the Milky Way. This breakthrough will enable researchers to study galaxies in a much more detailed way and help us to understand more about the nature of our universe.

Today, scientists have discovered a groundbreaking phenomenon that could revolutionize the way we think about spin-based electronics. The phenomenon, known as the Vectorial Spin-Orbital Hall Effect, is a key to unlocking higher efficiency and lower energy consumption in spintronic devices. This effect was observed in tight-binding numerical simulations of a two-dimensional electron gas in a perpendicular magnetic field. These simulations revealed that when the spin-orbit coupling is strong, electrons with opposite spins move in opposite directions, creating a “spin-orbit current”.

Scientists have discovered a breakthrough in medical imaging technology that could revolutionize the way diseases are diagnosed in the future. Using a combination of nanoparticles and contrast agents, researchers have found a way to create detailed images of cells and tissue in the human body. This is a major advancement in medical imaging, as it will provide more accurate diagnoses and potentially even enable early detection of diseases. This breakthrough could be the first step towards a new era of medical imaging.
The world of technology is being revolutionized with the advent of high quality diamonds. Researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a technique for producing high quality diamonds that can be used in a variety of applications, including in narrowband deep learning. This new technology promises to greatly improve the accuracy and speed of deep learning algorithms. The diamond-based technology has the potential to increase the accuracy of deep learning by up to 50% and reduce the time needed to run the algorithms by up to 90%.

Scientists have discovered a new way to make a rare form of electronic material: a five-layer graphene sandwich. This new material could have a huge impact on the electronics industry, as it has the potential to improve the performance of current electronic devices, as well as enable the development of entirely new applications.
The new graphene sandwich consists of five layers of graphene, a sheet of carbon atoms, stacked on top of each other.

Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in the world of medicine: the discovery of yeast-derived compounds that could revolutionize the way we treat diseases. This breakthrough was discovered during a study conducted by scientists at the University of California, Berkeley and aims to provide new methods for producing medicinal compounds that can be used to treat a variety of illnesses.
The research team discovered that a specific type of yeast, called Candida glabrata, is capable of producing compounds that could be used as treatments for a variety of diseases.

A team of scientists has recently discovered a new pattern in the layers of the Sun. The pattern is believed to be caused by the Sun’s magnetic field, and it could help us better understand solar activity and the Sun’s influence on Earth. The research, which was recently published in Nature Astronomy, used data from solar observatories to identify the pattern. The pattern is made up of complex shapes and could offer insight into how the Sun’s magnetic field affects its layers and how its layers interact with each other.

Today, scientists have announced a breakthrough in particle physics research. A technique known as “near-miss” has been used to study the particle known as the tau lepton. This particle is essential to understanding the Standard Model of particle physics, as it is the only lepton that interacts with other particles through the strong nuclear force. Using this technique, scientists were able to determine the properties of the tau lepton with unprecedented accuracy.

An exciting new discovery on the Red Planet has been found! Scientists have discovered evidence of what could be biosignatures from an ancient lake on Mars, a finding that could drastically change our understanding of the planet’s past. The biosignatures, which were found in an ancient mud rock, suggest that Mars was once capable of supporting life. This is huge news for astrobiologists and planetary scientists alike, and could lead to a greater understanding of the history of the planet and its potential for life.

A recent study has revealed a potential new opportunity for Greenlanidic agriculture that could revolutionize the industry’s sustainability: glacial flour. Glacial flour is a type of sediment created when glaciers grind against bedrock, and it is rich in nutrients like potassium, calcium, and phosphorus. These nutrients have the potential to be used as fertilizer for plants, and could thus dramatically reduce the amount of synthetic fertilizers used in Greenlandic agriculture. This could result in improved crop yields, and pave the way for more sustainable agricultural practices in the region.

Scientists have recently discovered a new way of enhancing the sensitivity of a fiber optic system. Known as the “exceptional point enhanced sensitivity paradigm,” this method has the potential to allow fiber optic systems to achieve a record-breaking level of sensitivity. The EPESP utilizes the principles of two coupled waveguides and the phenomenon of exceptional points to create a unique system in which light is transferred between the two waveguides with extraordinary precision.
Today, a group of rogue scientists have made a breakthrough in nanometric mechanics. Using a giant 3-D printer, they were able to create nanometric parts that are nearly impossible to replicate with traditional methods. The parts they created are so precise that they can be used for a variety of applications, from medical implants to miniature robots. This breakthrough opens up a new world of possibilities and could revolutionize the way we think about manufacturing processes at the nanoscale.
Every year, around 10 billion birds collide with glass windows in the United States alone. That’s a staggering 10,000 birds per hour, all of whom lose their lives in this preventable tragedy. Glass windows are especially dangerous to birds, as they often mistake the reflection of the sky and trees for an open space. This leads to birds crashing into the glass at full speed, resulting in broken wings, concussions, and even death.

