A new study published in Nature Genetics has revealed that the genome of the tomato contains natural mutation variations that determine the size and shape of the tomato. By understanding the relationship between the genome and the physical characteristics of the tomato, researchers have discovered that the genetic basis of tomato size and shape is much more complex than previously thought. This could have major implications for breeding programs aimed at developing better tomatoes.

Scientists have recently found a way to control chaos in optical fiber systems using Raman amplification. This discovery could revolutionize the way we use and store information, making it faster and more reliable. By using Raman amplification, researchers were able to reduce the amount of noise in the system, allowing them to control chaos and create a more stable environment for data transmission. The use of this technique could lead to new and improved ways of sending and receiving data, potentially improving internet speeds and reliability.

Enzyodynamic therapy, a new and innovative form of nanoscale medicine, has been gaining traction as a potential treatment for a wide variety of diseases and medical conditions. This groundbreaking new therapy uses nanoscale particles to target and manipulate biological enzyme systems within the body. By using nanoscale particles, these enzymes can be manipulated to achieve a desired medical outcome. In the most basic sense, enzyodynamic therapy is a form of nanoscale medicine that has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat medical conditions.

A new breakthrough in immunotherapy has been made by researchers at the University of Southern California. They have discovered a way to use mRNA-filled extracellular vesicles (EVs) to boost the body’s immune response to fight cancer. By packaging mRNA into EVs, the researchers were able to deliver the mRNA directly to immune cells, allowing them to recognize and respond to cancer cells more effectively. This could be a huge step forward in the fight against cancer and other diseases that rely on a strong immune response.
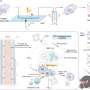
A recent breakthrough in medical engineering has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of macular degeneration, the leading cause of vision loss in older adults. Researchers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a new type of protein-like polymer that can be injected directly into the eye. This polymer is able to reduce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are a major factor in macular degeneration. The polymer is also able to increase the supply of oxygen to the retina, which helps keep it healthy and functioning normally.
Quantum computers are on the horizon. They promise to revolutionize computing power and open up new possibilities for research. In a recent breakthrough, scientists have made a major step forward in understanding how quantum computers will work. They’ve succeeded in using two qubits to form a basic logic gate, which is an essential building block of quantum computers. This is a huge step forward in the development of a quantum computer, and could eventually lead to a quantum computer that is much more powerful than any classical computer.

Today, a team of scientists announced the development of a revolutionary new technology: super-bright light sources powered by quasiparticles. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize the way we view our world and has the potential to improve a wide range of applications, from medical imaging to quantum computing. Quasiparticles are particles that can be generated using certain materials, and their unique properties make them ideal for powering these new light sources.

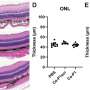
Recent research has revealed a new function of protein condensates that are involved in numerous cellular processes. Protein condensates are assemblies of proteins that are denser than normal cellular material. They are known to be involved in a variety of processes, such as gene expression, metabolism, and cell signaling. Now, a study published in Nature Communications has uncovered a new role for protein condensates—they can act as a ‘rigidity sensor’ to control the dynamics of their associated proteins.
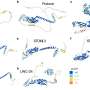
Today, an international team of researchers announced a major breakthrough in the field of nanotechnology. By combining DNA nanostructures with optical components, the team has created a system that could revolutionize the world of nanotechnology. This new system could be used to create nanoscale devices with unprecedented precision and control. With this new system, scientists will be able to create components that are smaller than ever before, with the potential to revolutionize fields such as medicine and communications.
A recent study conducted by a team of researchers has uncovered a gene that could potentially unlock a longer life for humans. This ‘golden gene’ was found to lengthen the lifespan of fruit flies by up to 20 percent. Previous studies have suggested that this gene, known as Induced by Loss of Expression of Longevity Assurance Gene 1 (ILE1), could also be present in humans and could possibly lead to a longer life.

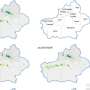
In a new breakthrough in precision agriculture, scientists have achieved a meter-level resolution for mapping cotton fields in Xinjiang, China. With this new technology, farmers can identify the exact areas of their fields that are in need of attention and can then use the data to manage their crops more effectively. This technology is set to revolutionize the way farmers interact with their land and provides a much needed boost to the agricultural industry.
In a new study, scientists have discovered a new way to understand how electrons move through a solvent. By studying the motion of electrons in a polar solvent, they found that electrons can move quickly and interact with molecules in the solvent in a variety of ways. This new understanding of electron motion will allow scientists to better understand how electrons interact with different materials, and could lead to more efficient energy storage solutions.
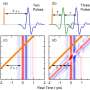
It’s official: X-ray lasers are getting brighter and darker. Scientists have recently discovered a way to amplify the power of X-ray lasers, making them brighter than ever before. This breakthrough could revolutionize scientific research by allowing scientists to observe the inner workings of molecules and atoms in unprecedented detail. With this new technology, scientists will be able to study the dynamics of chemical and biological reactions, and explore the limits of quantum mechanics.

Astronomers have recently discovered a new type of cataclysmic variable star, designated as Swift J05037.3-6737, located in the constellation Carina. This star is a binary, meaning it is composed of two stars in close orbit around each other. One of the stars is a white dwarf, while the other is a low-mass red dwarf. The white dwarf is pulling material from its companion, causing X-ray flares and powerful outbursts. This star is the first of its kind to be observed in X-rays, opening up a new field of research for astronomers.
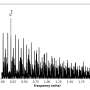
A breakthrough discovery has been made in the chemistry world: 10 new chemical compounds have been discovered! These compounds, found in the world’s most remote and unreachable places, have never been seen before. Scientists believe that these compounds could lead to new treatments for diseases, as well as new materials with unique physical and chemical properties. This is an incredible discovery that could open up a world of possibilities!
Read Full Article Here

It’s been nearly 17 years since the last emergence of adult periodical cicadas - and now, the wait is almost over! In 2023, periodical cicadas from Brood X are expected to emerge, covering much of the eastern United States. This is an exciting event for scientists and citizens alike, as Brood X is one of the largest and most widely distributed broods of periodical cicadas. It is estimated that 1.5 million cicadas per acre will emerge from the ground and fill the air with their loud buzzing sound.

Today, scientists from the University of California, Berkeley have announced a major breakthrough in 3D isotropic microfabrication in glass. This new technique enables a wide range of applications in optics, medicine, and other fields. By using femtosecond laser pulses to create extremely precise and isotropic 3D microstructures, this new technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach many challenges in science and engineering.
The technique begins by using a femtosecond laser to create two-dimensional patterns in a glass substrate.
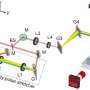
Have you ever wanted to get a better view of the universe? Well, now you can! Scientists have developed a new telescope that provides a clearer and more detailed view of the stars and galaxies than ever before. This incredible telescope will allow us to study the universe in unprecedented detail, giving us an up-close look at the stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects that make up our universe. With this telescope, we can now explore the vastness of the universe in ways that were simply not possible before.

Recent advances in quantum computing have been made, thanks to the development of a new type of nondestructive ytterbium qubits. This breakthrough technology is aiding the development of a scalable quantum computing architecture.
These qubits are based on a single ytterbium (Yb) ion and can be precisely controlled, allowing for the manipulation of single quantum states. This control has enabled researchers to create a new kind of “quantum logic” that allows for the manipulation of qubits without destroying them.
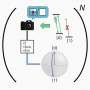
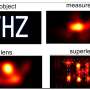
Physicists have successfully developed a new type of “super lens” that has the potential to revolutionize the way we look at the world. This new lens is called “superlensing” and it is capable of focusing light more powerfully than any lens before it. Superlensing allows us to see details that were previously invisible to the naked eye, and could have applications in medical imaging, astronomy, and more. This breakthrough could help us gain a better understanding of the world around us and could lead to new discoveries and inventions.
Astronomers have recently discovered a new magnetar, SGR J1830-645, located in the constellation of Sagittarius. Magnetars are a type of neutron star with an incredibly strong magnetic field, hundreds of times more powerful than a regular neutron star. This magnetar is particularly interesting because it is the first one to be discovered in the Milky Way outside of the Galactic Center.
Astronomers are excited to explore this new magnetar, SGR J1830-645, located in the constellation of Sagittarius.
A major breakthrough in treating sulfur mustard poisoning, a deadly chemical agent used in warfare, has just been revealed. Developed by researchers at the University of Colorado, the treatment is non-toxic and effective at neutralizing the effects of sulfur mustard exposure. This discovery is a major boost in the fight against chemical weapons, as sulfur mustard poisoning has been a major cause of death and injury in conflicts across the world.

Today marks an important milestone in the world of physics - a team of scientists have created a miniature particle accelerator, the first of its kind! This revolutionary device is capable of accelerating particles up to speeds nearly a million times faster than those of conventional particle accelerators. This breakthrough could transform how we study particles at the smallest scales, and could be used in the development of new technologies such as medical imaging and cancer treatments.
Scientists have recently come together to create a collaborative effort in order to develop artificial intelligence algorithms that could be used to create more efficient methods of finding treatments for COVID-19. This project, known as the Molecular AI for COVID-19 (MAIC19) initiative, is a global effort that involves experts from various disciplines, including computational biology, structural biology, and computer science. Through this project, the researchers seek to create algorithms that could help them make more rapid progress in developing treatments for the virus.
The future of neighborhoods is looking greener! This is thanks to a new initiative from USAT Cellular, which is installing solar-powered charging kiosks in communities across the US. These kiosks provide a free, clean, and reliable charging station to the public, allowing people to charge their mobile devices with energy from the sun. This is a great step towards a more sustainable future, as it reduces our dependence on fossil fuels and helps us move towards a zero-carbon economy.