
In the year 2023, a new era of space exploration will begin. For the first time ever, a human mission will embark on a journey to Mars. The mission, known as the Mars One, will be led by a team of six astronauts and will last for an estimated 500 days. The goal of the mission is to establish a permanent human presence on the red planet. The astronauts will be equipped with state-of-the-art technology to explore and study the Martian environment.

In a recent press conference, health officials in South Africa answered questions from the public about the bird flu outbreak in the country. The most important facts to be aware of are that the bird flu strain, H5N8, is highly contagious and that it can spread to humans. Thankfully, the virus is not believed to be highly pathogenic, meaning it does not cause serious illness. The South African government has taken the necessary steps to contain the virus, such as closing live poultry markets and culling infected birds.

The future of AI-enabled technology is rapidly approaching, and with it comes a need to consider the implications it will have on society. One of the most important questions to consider is the role that intermediaries will play in this future. Intermediaries are third-party entities that facilitate the exchange of information, goods, or services between two parties. They can be in the form of organizations like governments, businesses, or educational institutions, or they can be individuals such as lawyers, brokers, and consultants.

Recently, scientists discovered that electrons can quickly adapt to their environment, much like a quick-change artist. By studying molten salts, they discovered that electrons can switch from one type of behavior to another in a mere fraction of a second. This discovery could have implications for the development of new materials with unique properties.
The behavior of electrons in a material is an important factor when considering the properties of that material.

A new device that combines virtual and augmented reality technology is allowing researchers to scan tropical forests in real-time. The device, which was developed by researchers at the University of Arizona, uses a combination of virtual reality, augmented reality, and 3D imaging systems to create a full 3D map of a tropical forest. The device works by using the 3D imaging systems to scan and record the forest environment while the augmented reality and virtual reality systems provide an immersive experience, allowing researchers to explore the forest in a realistic way.

A new study has revealed that cockroaches suppress the immune system of their offspring at birth. Researchers from the University of Michigan found that a protein produced by the mother cockroach is passed on to their eggs, which helps the newborns survive in a hostile environment. This protein is believed to play a role in the newborns’ ability to survive in conditions where the immune system would normally be activated. The findings of this study could lead to new insights into how the immune system works and how it can be manipulated for medical purposes.

Today, a new study conducted by researchers from the University of Michigan has found that grouping English learners together in classrooms can have a positive impact on their academic achievements. The study looked at data from over 400,000 English learners in grades 3-8 and found that grouping English learners together in classrooms can lead to better test scores and improved English proficiency. The researchers also found that grouping English learners together in classrooms can help to reduce the achievement gap between English learners and their peers.

“A new study published in the journal Science has found that large language peer review is a key factor in the success of scientific research. The study, conducted by a team of researchers from Harvard Medical School and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), examined the publication records of more than 500,000 scientific papers and found that those with a higher number of peer reviews were more likely to be cited by other scientists and to receive more attention from the scientific community.
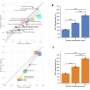
New research has found that the vitamin C present in kiwifruit may help mitigate copper toxicity. According to the study, conducted by a team of researchers from New Zealand, the vitamin C in kiwifruit acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from the toxic effects of copper. The researchers tested various kiwifruit cultivars and found that the vitamin C levels varied significantly, with some cultivars having as much as four times the amount of vitamin C as others.

A new discovery out of South Korea could revolutionize the production of calcium chelates. Researchers have discovered that peptides extracted from mung beans can be used as an effective and eco-friendly alternative to traditional calcium chelates. This new method to produce calcium chelates could have wide-ranging applications in food, pharmaceutical, and agricultural products. The peptides extracted from mung beans are not only more cost-effective to produce than traditional calcium chelates, but also have a higher bioavailability, meaning that they are more easily absorbed by the body and provide more nutritional value.
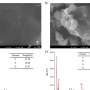
A team of researchers at the University of Miami has made a breakthrough in materials engineering: they have developed a new type of metal-ceramic combination that is both incredibly strong and highly conductive. This new material could revolutionize the way electronics and materials are manufactured, as it has the potential to be used in a wide variety of applications, from consumer electronics to aerospace components.
The team developed this new material by combining metal alloys with ceramic particles.

Introducing the new Miniature Magnetic Resonance Imager (MMRI): the world’s first diamond-based MRI scanner. Developed by scientists at the University of Manchester, the MMRI offers MRI scans with unprecedented resolution and accuracy. With its microscopic size and superior imaging capabilities, the MMRI will revolutionize medical diagnostics and imaging. Its diamond core is not only incredibly durable, but also allows for an unparalleled level of precision and accuracy, allowing doctors to detect and diagnose conditions sooner and with greater accuracy than ever before.

NASA is set to launch its historic Lucy mission in October of 2023. The mission will see the spacecraft fly past seven asteroids in the Trojan asteroid group, which are located near the orbit of Jupiter. This is the first time a spacecraft will be visiting a group of objects like this, and the mission could provide unprecedented insight into the history of the solar system. Scientists hope to gain valuable information about the formation of planets and the early stages of our solar system.

A new type of electrocatalyst has recently been developed that could revolutionize the way we generate energy. This new catalyst is composed of totally non-noble metal elements, which makes it both more affordable and more efficient than traditional electrocatalysts. The new catalyst has been proven to decrease the amount of energy required in fuel cells, making them more efficient and cost-effective. This could have a huge impact on the way we generate energy in the future.
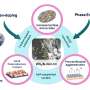
Engineering researchers have developed a novel self-powered and flexible multi-color electrochromic device (ECD) that could be used in a wide range of applications, such as smart windows and displays. The device is composed of a flexible polyimide substrate, a graphene-based transparent electrode, and a few layers of electrochromic materials. This structure allows the device to be self-powered, meaning that it does not require any external power source or battery to operate.

A recent study published in Nature Climate Change outlines the potential threat to remote high latitude wilderness areas due to the effects of climate change and agricultural practices. The study found that these areas could be subject to significant changes in land cover, biodiversity and ecosystem services due to the combined effects of human-induced climate change and agricultural activities. In particular, the study highlighted the potential for widespread conversion of tundra and boreal forests to low-productivity agriculture, leading to the loss of important habitat for plants and animals, as well as reduced carbon sequestration.

Today, a new synthetic tape, designed to be more sustainable and eco-friendly, has been flagged as unsustainable. The tape is made from a combination of plastic and other synthetic materials that are not biodegradable. This means that the tape will remain in the environment for years, potentially polluting our oceans, rivers, and land. Scientists are now trying to find a more sustainable solution that won’t have a negative impact on the environment.

In a recent study, a team of scientists explored the strategies used by fish harvesters in the Pacific Northwest. The study found that fish harvesters use a variety of methods to increase their catch, such as adapting to changing regulations, employing creative strategies to avoid detection, and using technology to their advantage. This research provides insight into the ways in which fish harvesters have adapted to their environment in order to survive and thrive in the face of increasingly stringent regulations.

Today, scientists have discovered a new structure-destabilizing mutation in BCL-2, an antiapoptotic protein found in humans. This mutation has the potential to open up a new avenue of research for treating cancer and other diseases. Researchers have long known that BCL-2 is important for protecting cells from apoptosis and that mutations in this protein can lead to cancer. Now, scientists have identified a particular mutation that destabilizes the structure of the protein and increases its susceptibility to proteolysis, meaning it is more easily broken down and degraded.
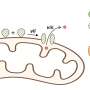
Today scientists have unlocked a new discovery that could revolutionize our understanding of human biology - the function of a human cell surface protein. Researchers at the University of California, Irvine, have recently identified the key role that this protein plays in cell-to-cell communication. The protein, known as CD3, is a member of the T-cell receptor family and is found on the surface of both T-cells and B-cells, which are important components of the immune system.
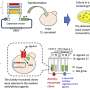
Scientists have recently unveiled an exciting new microscope platform that promises to revolutionize the way researchers study the intricacies of skeletal muscle. This platform, called the Skeletal Muscle Imaging and Analysis Platform (SMIP), allows scientists to image the entire skeletal muscle system in unprecedented detail. SMIP is a combination of advanced microscopy techniques and powerful software that enables researchers to study the structure and function of individual muscle fibers, as well as the interactions between them.

In a groundbreaking archaeological discovery, scientists have uncovered evidence of a long-forgotten Inca Empire. The ancient city of Machu Picchu, located in the Andes Mountains of Peru, was home to a powerful ruling dynasty from the mid-15th century until the Spanish conquest of 1532. What makes this discovery so remarkable is that the city appears to have been built during a period of intense heat, with temperatures exceeding even modern-day readings.

A recent study conducted by an international team of researchers has revealed a surprising discovery: some genes have been ‘stolen’ from their hosts and are actually contributing to a parasitic behavior within them. The team found that the stolen genes, known as ‘mobile genetic elements’, are actually driving the evolution of some species by allowing them to borrow traits from other species and adapt to their environment more quickly. These genes are enabling the species to survive in their environment, and the researchers believe that this phenomenon could be seen in many more species in the future.

A recent discovery of a fossilized skull in South Africa has revealed a vital piece of the puzzle in understanding human evolution. The skull, estimated to be between 1.8 and 2.0 million years old, is believed to belong to a previously unknown species of early human ancestor – one that is closely related to the Homo genus. The new species has been dubbed Homo gautengensis, and it could provide researchers with valuable insight into the evolution of the Homo genus, and eventually, Homo sapiens.

The future of seafood is looking murky. It’s not just an issue of sustainability; it’s a matter of taste. A new study finds that the emergence of muddy flavors in fish, a phenomenon known as “muddy flavor syndrome,” is making fish and seafood less appealing to consumers.
Have you noticed that your favorite seafood dish isn’t tasting quite the same? That’s because a phenomenon known as “muddy flavor syndrome” is on the rise.

