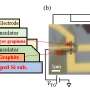
A new high-speed electrical readout method for graphene has been developed by a team of scientists, which could pave the way for graphene-based devices with unprecedented performance. The new readout method uses a combination of electrical and optical techniques to measure the properties of graphene in a fraction of the time of traditional methods. This could enable graphene-based devices to operate at higher speeds, and to be used in a variety of applications, including communications, computing, and sensing.

As the world continues to grapple with the pandemic, one of the most pressing questions is how to ensure that students in Europe receive a quality education despite not being able to attend school in person. To answer this question, a new report from the European Commission has outlined 10 science lessons that can be used to ensure that students continue to learn and grow despite school closures. These lessons include emphasizing digital skills, providing innovative and supportive online learning experiences, and improving access to resources for students of all backgrounds.

According to a recent study from the European Space Agency (ESA), there are potentially dangerous, city-killing asteroids that have been left undetected. The study estimates that there are currently over 1,000 asteroids larger than 140 meters in diameter that are still orbiting close to Earth’s atmosphere. These asteroids are of particular concern due to their size and potential to cause catastrophic damage if they were to hit Earth. The study also found that the number of undetected asteroids has increased over the past few years due to the advances in technology and detection methods.

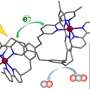
Scientists have recently discovered a revolutionary new photocatalyst capable of converting CO2 into fuels and other useful products. The photocatalyst, called a dinuclear ruthenium complex, is a molecule composed of two ruthenium atoms with a “bridge” between them. This bridge is called a triazole ligand, and it allows the two ruthenium atoms to interact with each other in a way that makes the conversion of CO2 into valuable products possible. Excitingly, the photocatalyst works under visible light, meaning that it can be used in a wide range of applications, from solar energy to fuel cells.
Recent research has revealed a new strategy to tackle tuberculosis infections: cord-like aggregates of bacteria. These aggregates, or “bacterial cords,” have been found to be more resistant to antibiotics and, as a result, more difficult to eliminate. In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Manchester and the University of Edinburgh have demonstrated the potential of using bacterial cords as a means to combat tuberculosis infections.

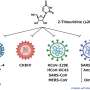
A group of researchers from the University of Texas Medical Branch have developed a promising new antiviral drug candidate that could potentially treat a broad spectrum of viral infections, including dengue, SARS-CoV-2, and Zika. The new drug candidate, called EP67, is a small molecule that has been shown to be effective in inhibiting the replication of several viruses in laboratory studies. EP67 works by blocking the activity of an enzyme called a helicase, which is essential for many viruses to replicate.
Recently, researchers have developed a new gel mat that can be used to grow muscle cells in a lab. This gel mat is made of a protein known as collagen, and it provides a three-dimensional scaffold that helps muscle cells to grow and develop. This is a game-changer for scientists and researchers who can now use the gel mat to study muscle development in a more natural setting. The gel mat also provides a much more cost-effective way of growing muscle cells than previously used methods.
A new study conducted by researchers at the University of California, Irvine has uncovered a surprising connection between rancid food and tools used by AI scientists. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, found that rancid food can provide AI scientists with valuable insights and data that can be used to develop more complex AI systems. The researchers believe that the rancid food can act as a kind of “simulated reality” that can be used to train AI systems to interpret complex data more accurately.

A new study has revealed a harsh workplace climate in many organizations around the world. The researchers analyzed data from thousands of employees and found that a significant number of employees experience a negative work environment. This includes feeling unsupported, unappreciated, and overwhelmed. The study also found that negative climates are more common in larger organizations, and that the effects of this climate can lead to decreased employee engagement, decreased productivity, and increased turnover.

Scientists have recently made a groundbreaking discovery: certain species of worms can regenerate their bodies. This is an exciting development that could lead to the creation of treatments to help humans regenerate lost body parts. In a recent study, researchers found that by manipulating the genes of certain species of worms, they were able to stimulate the regeneration of their entire bodies, from the head to the tail. This could potentially lead to treatments that could help humans with the same issue.

In recent years, physicists have been uncovering some of the biggest unsolved mysteries of the universe, from dark matter to the origin of the universe. While these mysteries remain unsolved, there are still major problems in physics that scientists are working to solve. Here is a list of the 10 major problems in physics that scientists are currently tackling:
Unifying the four fundamental forces of nature Understanding dark matter and dark energy Explaining the origin and evolution of the universe Bridging the gap between quantum mechanics and general relativity Explaining the properties of materials at the nanoscale Understanding the behavior of matter in extreme conditions Developing a theory of quantum gravity Developing a unified theory of quantum fields Finding a way to accurately describe black holes Exploring the nature of time For centuries, physicists have been trying to uncover the mysteries of the universe.

In the world of sustainable cosmetics, we have a new revolutionary way of producing natural products without damaging the environment. This new method involves harnessing the power of cyanobacteria, a type of microscopic bacteria found in aquatic environments, to produce natural cosmetics.
By taking the natural pigments of cyanobacteria and using them as a starting material, scientists can create a wide range of sustainable cosmetics without the need for synthetic ingredients or harsh chemicals.

Researchers have developed a new strategy to spin acoustic phonons in silicon vacancies in 4H-SiC with a promising outlook for future quantum technologies. By controlling the spin of acoustic phonons, the research team was able to modify the spin of the silicon vacancy at room temperature, which could lead to more efficient, secure, and reliable quantum devices. The breakthrough was made possible by a combination of experimental and theoretical techniques, providing a new platform to study and manipulate phonon spins.
The rise of children facing difficulties related to anxiety is a growing concern for many parents. According to a recent study, one in four children aged four to 17 in the United States have been diagnosed with an anxiety disorder. In light of this, it is important that parents are aware of the signs and symptoms of anxiety in their children and are equipped to provide them with the necessary support.

Recent research has revealed that the maternal microbiota can influence fetal development. This means that the composition of the mother’s microbiome, the collection of microorganisms living in her body, can affect the health of her unborn child. This is significant since a healthy microbiome is essential for the development of the fetus, and the mother’s microbiome can have a significant impact on the infant’s health in the long-term. The study found that the maternal microbiome can influence the development of the placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic sac, all of which are essential for a baby’s healthy growth.
If you’ve ever seen an algae bloom, you know that it can cause a lot of stress to the environment. But what if we could use soft materials to help alleviate some of this stress? A team of scientists in Australia has been researching a new way to use soft materials to help protect the environment from algae blooms. They have developed a new method of using soft materials that can absorb the excess nutrients in the water, which can help reduce the amount of algae growth.

Today, on October 10th, 2023, the Juno spacecraft has made its closest flyby of Jupiter’s moon Io! This marks the fifth flyby of the moon for the spacecraft, with the first being on August 5th, 2016. Scientists are excited to use the data collected from this flyby to gain a better understanding of Io’s composition and its unique volcanic activity. Juno’s flyby today was only 2,200 miles away from the surface of Io, granting researchers the opportunity to collect extremely detailed images of the moon.

Scientists have discovered a new species of marine bacteria that has lost its ability to swim. The bacteria, dubbed “Tekayea staleyi”, was found in ocean sediment off the coast of Japan by researchers from the University of Tsukuba. They discovered that the bacteria had lost its flagella, a tail-like structure used for movement in most bacteria, indicating that it had lost its ability to swim. The researchers also found that the bacteria had adapted to its environment in other ways, such as by using a new type of gas-filled vesicle to move around.

NASA recently announced the successful development of a new rocket nozzle that will allow for deeper space exploration than ever before. The rocket nozzle is the result of a five-year research project and is the first of its kind. The nozzle is designed to withstand the extreme temperatures and pressures of deep space, allowing for the launch of payloads to far-off destinations. It is expected to revolutionize deep space exploration, giving us access to previously unreachable places.

NASA’s Voyager team is focusing on software upgrades for their spacecraft, which have now been traveling through space for over four decades. Upgrades are being made to both the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft, which were originally launched in 1977. These upgrades will enable the spacecraft to communicate more effectively with Earth and to continue their exploration of the outer reaches of our solar system. The goal of these upgrades is to extend the life of the spacecraft and ensure that they can continue to gather valuable data about the outer planets.

In an effort to help ensure sustainable fishing practices, a new tool has been developed to tackle the problem of overfishing. The Foreshore Fishing Tool, developed by scientists at the University of Edinburgh, aims to provide fishers with information about which fisheries are best for sustainable fishing. The tool uses a range of data, such as the type of fish and its potential size, to help fishers decide which areas are most suitable for fishing, as well as which fishing practices are most sustainable.

Scientists have developed a new type of semiconductor laser diode that emits vertical ultraviolet (UV) B light. This breakthrough could lead to a new wave of applications for UV lasers, such as medical treatments and data storage. The research team used a combination of nanostructures and advanced epitaxial growth techniques to successfully create the new laser diode, which is capable of emitting light with a wavelength of 320 nanometers. The team believes this type of laser diode could be used for a variety of applications, including medical treatments, data storage, and environmental monitoring.

Recent advances in biotechnology have enabled researchers to develop a better understanding of how to optimize the cytochrome P450 network. This network is responsible for the detoxification and metabolism of drugs and toxins, and its optimization is essential for the effective functioning of the liver. In a new study, researchers have used a high-level mathematical model to predict how different combinations of drugs and toxins will interact with the cytochrome P450 network.

Radar technology is revolutionizing to provide more precise measurements than ever before. A new Terahertz (THz) emitter has been developed that could be used to measure the distance between objects with extreme accuracy. The THz emitter is a special type of laser that emits THz radiation, which is a type of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate through materials such as wood, plastic, and paper. This new technology is promising for applications in transportation, military, and medical fields.

A recent study published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology has found that exposure to low levels of organophosphorus flame retardants (OPFRs) during pregnancy can cause malformations in the developing embryo. The study’s authors looked at data from 6,000 pregnant women and their newborns and found that those exposed to even low levels of OPFRs had a higher risk of malformations compared to those without exposure. These malformations include cleft lip, cleft palate, and heart defects.

