A piece of the moon may soon be orbiting near Earth. Scientists have discovered an asteroid that is believed to be a piece of the moon, broken off during a large impact event some 4 billion years ago. The asteroid, named 2021 AG5, is currently in an orbit that passes close to Earth, making it the closest known moon fragment of its kind. This rare near-Earth asteroid could help scientists better understand the formation of the moon and how it has changed over time.

A team of researchers from the University of Manchester have recently identified a group of genes that are responsible for ultra-low glycemic index foods. These foods are incredibly beneficial for those with diabetes, as they are absorbed slowly by the body, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. The research has indicated that specific genes in certain fruits and vegetables are responsible for this low glycemic index. This exciting discovery has the potential to revolutionize how we treat diabetes, and could drastically improve the lives of those who suffer from it.

Have you ever wondered why, when you get a haircut, you never get the same exact cut twice? It’s all thanks to a process called apoptosis, or programmed cell death, which is a normal part of the hair growth cycle. Apoptosis is the process by which cells in the hair shaft die and are eventually shed, making room for new hair to grow in their place. This process is essential for maintaining healthy hair growth, and without it, our locks would become unmanageable.

A new study has revealed a surprising insight into the genetic makeup of the Dutch bluetongue virus. Researchers at Utrecht University have used a combination of traditional and modern methods of genetic analysis to uncover new information about the virus. This includes the fact that the virus possesses a unique genetic element, not previously observed in other bluetongue viruses. The discovery could help scientists better understand the virus, and possibly aid in the development of future control strategies.
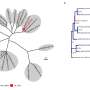
A new study published in Nature Plants has found that multifactorial stress can lead to divergent responses in citrus. The study looked at two citrus species, orange and grapefruit, grown under varying levels of water, nitrogen and potassium. The results showed that the two species responded differently to the changing environmental conditions. The orange trees had higher relative growth rates when nitrogen levels were low, while the grapefruit trees had higher relative growth rates when potassium levels were low.
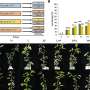
DNA metabarcoding is revolutionizing the way we understand soil composition and its effect on crop production. A new study published in Nature Communications has shown that DNA metabarcoding can be used to accurately identify the microbial communities that live in soil and the abundance of different bacteria, fungi, and other organisms that make up the soil. The study also demonstrated how these microbial communities can affect crop production. For example, the researchers found that the abundance of certain bacterial species was associated with higher yields of certain crops, while other species were associated with lower yields.
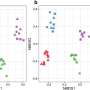
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed a way to program particles to exhibit unexpected behaviors. This means that particles, such as electrons, can now be programmed to interact differently with their environment than their natural behavior. This new technology has the potential to revolutionize the way particles interact with each other, as well as the way we measure and control them. This breakthrough could have a huge impact on the development of new materials, medical technologies, and more.

Nowadays, researchers are beginning to unlock the potential of the microbiome — the collection of bacteria and other microorganisms that inhabit our bodies — to revolutionize the way we diagnose and treat a wide variety of diseases. In a breakthrough study, researchers at the University of California, San Diego have found that analyzing the microbiomes of both the skin and gut can be used to identify therapeutic targets for diseases like cancer, allergies, and psoriasis.

Recent advancements in nanotherapeutic delivery to tumors have opened the door to more efficient treatments for cancer. A new strategy developed by researchers at UC San Diego and the University of Pennsylvania has now been proposed to further increase the efficiency of nanotherapeutic delivery. This strategy would use a combination of two nanotechnology approaches to more effectively target tumors and reduce side effects. The researchers believe that this approach could be the future of nanotherapeutic delivery for tumors.
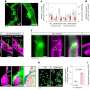
Scientists have discovered a new mechanism that could be used to create water-repellent surfaces. The study found that the combination of surface nanostructures and a liquid-infused coating can cause a surface to become highly water-repellent. This new mechanism could be used to create surfaces that are resistant to water and oil, making them useful for a variety of applications, including outdoor coatings, anti-icing materials, and self-cleaning surfaces.
This breakthrough could revolutionize the way we treat surfaces.

Scientists have just uncovered an exciting new role of muscular lacunae in the body. Muscular lacunae are small cells that make up musculoskeletal tissues in humans and other species. The new discovery reveals that these cells play a role in the repair of damaged tissues, allowing for quicker recovery and improved physical performance. This new information could lead to new treatments and therapies for individuals with musculoskeletal injuries. The findings were recently published in the scientific journal PLOS ONE, and could have a profound impact on the future of sports medicine.
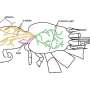
In a major breakthrough, scientists have developed a system of environmental sensors that can detect dangerous chemicals in the air. These sensors, which are the size of a cube, have been designed to monitor air quality in industrial areas, cities, and other places where hazardous materials may be present. With the help of these sensors, it is now possible to detect tiny amounts of hazardous chemicals that may have been previously undetectable.

We are all familiar with fungi – the mushrooms on our dinner plates, the mold on the bread in our pantries, and the mushrooms that sprout up in our gardens after a rain. But there is a new type of fungus that has been discovered and is being used in a surprising way – to help clean up oil spills. Scientists have found that by combining the special, oil-eating fungus with bacteria, they can create a powerful ally in the fight against oil spills.

A new study has revealed the formation of fast-moving black hole binaries in the universe. These binary black holes are formed when two black holes merge together, and the resulting black hole has a velocity much higher than that of the individual black holes. This newly discovered phenomenon could help us better understand the evolution of galaxies and the physics of black holes.
Researchers used simulations to examine the characteristics of these fast-moving black hole binaries.

Visiting the nuclear fuel facility in Mexico just got easier! Starting this week, the public is now able to explore the facility, which is located in the Gulf of Mexico, through guided tours. This is the first time in history that visitors will be able to experience the site first-hand and learn about the important role it plays in powering Mexico. The tours will be led by a knowledgeable guide and will include a look at the nuclear fuel fabrication area, reactor core, and other parts of the facility.

Astronomers have recently made a mind-blowing discovery: a distant radio source located three billion light-years away. This is the most distant radio source ever detected, and it could provide important insights into the nature of the universe.
This radio source was discovered by a team of astronomers from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, using the Very Large Array (VLA) in New Mexico. The source is located in the constellation Cetus, and has an estimated age of 11 billion years.

Scientists have made a major breakthrough in the fight against plastic pollution. For the first time, they have discovered a way to break down and recycle the plastics that are currently clogging up our landfills and oceans. This breakthrough is a major step forward in reducing the amount of plastic waste that ends up in nature and will help keep our planet healthy for generations to come.
Researchers from the University of California, Davis have developed a method that breaks down plastic into its component parts, which can then be recycled into new products.

The coin toss, the simplest of all random events, is not so random after all. A new study has revealed that when flipping a coin 10 times, there is a slight bias towards heads. This means that if you flipped a coin 10 times, you would be more likely to get heads than tails, although the difference is very small. This finding is special because it goes against the assumption that coin tosses are completely random.

In a recent breakthrough, researchers have discovered evidence of pairs of black holes in the universe. By studying the gravitational waves emitted by these black holes, the researchers were able to get an unprecedented look into the inner workings of these mysterious objects. This discovery has opened up the possibility of further exploring the behavior of black holes, and the physics of the universe in general. It is an exciting time in the world of astrophysics, as we continue to uncover more and more about the mysteries of the universe.

A new study published in Nature Climate Change has revealed that Bordeaux red wines produced in the future will likely be more alcoholic and higher in tannin than those of today. Researchers predict that, due to climate change, the average maturity date of Merlot grapes in the Bordeaux region of France will shift two weeks earlier by 2023, resulting in a higher sugar content and a higher alcohol concentration in the wine.
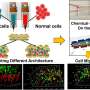
3D printing has revolutionized the medical field in countless ways. A new breakthrough in 3D printing technology has facilitated faster and more cost-efficient cancer treatment. Researchers from the University of Zurich have developed a 3D printed tumor model which can be used to replicate a tumor faster and more accurately than traditional methods. This technology could lead to more precise treatments and better outcomes for cancer patients. The 3D printed tumors are created using a 3D printer and a special material that can accurately replicate the size and shape of a tumor.
India is making history as the nation prepares to launch its first ever space flight mission with astronauts on board. The mission will be conducted by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). This mission will be the first time ever that Indian astronauts will travel into space. The mission is scheduled for launch in October of 2023 and will send a crew of three astronauts into space for a period of seven days.

A major breakthrough has recently been made in cosmology, with the announcement that Saturday citations of ‘Golden Humans’ have been discovered in the universe. This remarkable discovery has enabled us to gain a much deeper understanding of the composition of the universe and the workings of cosmological phenomena. Saturday citations are thought to be the origin of the material universe, and are made up of tiny particles that form an intricate network of matter and energy throughout the cosmos.

A new simulation of the Matrix Law of Physics is showing promise in developing a revolutionary new idea. According to the study, the Matrix Law is a mathematical equation that describes the behavior of particles on a very small scale, and could potentially open up new possibilities for understanding the laws of nature. The simulation, which was conducted by a team of researchers from the University of California, San Diego, suggests that the Matrix Law could be used to create a new model of physics that could describe the behavior of particles on the atomic scale.

In a recent study conducted by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, it was found that air purifiers can be used to reduce concentrations of wildfire-generated gases in indoor air. The study found that air purifiers can help reduce the amount of smoke and other harmful gases, such as formaldehyde, that enter our homes and businesses when wildfires occur. This is especially important in areas that are particularly prone to wildfires, as the danger posed by these gases can be greatly reduced by the use of air purifiers.

