
Today, the world is mobilizing to empower children with access to creative and free mobile technology. With this new technology, children can access the internet, create and share content, and connect with others around the world. The initiative is spearheaded by the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), which is partnering with various organizations to bring this technology to children in developing countries. The technology is designed to be both affordable and safe, allowing children to explore the digital world without the fear of exploitation.

Broccoli is much more than a vegetable side dish. It has been found to contain powerful health benefits, and researchers have just discovered a new way that it can benefit us - a small molecule found in broccoli, called sulforaphane, has been proven to have anti-cancer properties. This small molecule has been found to help fight off cancer cells in the body, making it an important tool in the fight against cancer.

Scientists have made a breakthrough in room temperature phosphorescence with an ultra-long-lasting light-emitting material. A team of researchers from the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully developed an indium-based material that can phosphoresce at room temperature for up to 10 hours. This is the longest room temperature phosphorescence that has been achieved to date, and could have a wide range of applications in displays, lighting, and optoelectronic devices.
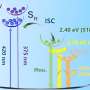
Nanostructured photoanodes are a promising technology for harvesting solar energy, but their effectiveness has been limited due to their need to be heated to extreme temperatures in the range of 160-500C and their potential to degrade over time. However, researchers have recently developed a new type of nanostructured photoanode that can be heated hydrothermally at much lower temperatures (up to 160C) and remain stable over time. This breakthrough could significantly reduce the cost and complexity of solar energy harvesting, making it more accessible to everyone.
We’ve long been fascinated by the great mystery of space, and now scientists are giving us a way to explore it: simulations! A new study published in the journal Nature Astronomy has created a new simulation that will allow us to explore the formation of galaxies, star clusters, and other complex structures in the universe. By simulating the conditions needed to form these structures, researchers can gain insight into how they were formed and what their properties are.

Today marks a new milestone in the field of catalysis: scientists have successfully achieved single-atom catalysis, a feat once thought to be impossible. This process, known as the “Holy Grail” of catalysis, involves using a single atom as a catalyst to promote a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. This breakthrough promises to revolutionize the way we think about catalysis, as it offers a highly efficient and cost-effective way to drive chemical reactions.

A new astronomical event, a kilonova, has been detected by scientists. It is the most energetic type of explosion known to exist in the universe and is created when two neutron stars collide. This extremely powerful event releases a staggering amount of energy and is capable of producing heavy elements like gold and platinum. It is estimated that a kilonova is some 10 billion times brighter than a supernova and can be detected from up to 1.

A new tool is emerging that could revolutionize fish farming: hormones. Scientists at the Institute of Aquaculture Research in London have developed a tool using hormones to help farmers and researchers better understand the behavior of their fish. By administering hormones, they can alter the behavior of the fish, allowing them to observe the changes in the fish’s behavior and better understand their needs. The tool could also be used to regulate the growth of the fish, helping to ensure that the fish are healthy and that the fish farm is providing the best environment for them.

Scientists have developed a new technique to measure greenhouse gases in the atmosphere with unprecedented accuracy. Called laser heterodyne spectroscopy, it uses lasers to measure the absorption of light from molecules in the air. This allows scientists to measure concentrations of greenhouse gases like methane and carbon dioxide with an accuracy of better than 0.1 parts per million. The technique could be used by researchers to better understand how climate change is affecting our atmosphere.
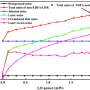
The ability to identify and characterize particles down to the nanoscale has been a long-standing challenge in the scientific community. In a recent breakthrough, researchers have developed a new method for deep and long-standing identification of nanoparticles – a process that could revolutionize the field of nanotechnology. Using a combination of advanced imaging techniques and machine learning algorithms, the researchers were able to accurately identify and classify nanoparticles within a single image.
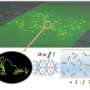
In recent years, scientists have become increasingly interested in the potential of platinum nanoparticles (PNPs) for accelerating the electrochemical process in sodium-ion batteries. A team of researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has now discovered the synergistic roles of PNPs and sodium ions in the electrochemical process, which could lead to improved energy storage capacity in sodium-ion batteries. The team’s findings, published in the journal Nanoscale, could help to further advance the development of sodium-ion batteries for use in electric vehicles and other applications.
A revolutionary new way of tracking wildlife has been developed by researchers from the University of Oxford, using airborne DNA. This new technology, which is expected to be available in 2023, will enable scientists to monitor wildlife populations more accurately and at a larger scale than ever before. By collecting and analysing environmental DNA from the air, researchers will be able to quickly identify the presence of different species and their size and movements.

The search for a sustainable source of nitrogen is over! Scientists have found a way to use ammonia in a reaction to produce a sustainable source of nitrogen. This means that the production of nitrogen-based fertilizers, essential for sustaining life on earth, can now be done without relying on fossil fuels. This is a major breakthrough in environmental sustainability and could lead to a more secure future for food production.
Astronomers have recently made an exciting discovery in the depths of space - they have found 10 red dwarfs that are similar to the sun! These stars are relatively small, but they have the potential to host Earth-sized planets in their habitable zones. This could be a huge breakthrough in the search for life beyond our planet. The discovery shows that there are many more stars that may be able to support life in the universe than previously thought.

3D printing technology has taken a giant leap forward with the announcement that a professor from MIT has developed a way to 3D print human hair. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way that tiny sensors are created and used in a variety of applications. Instead of using traditional manufacturing methods of intricate parts, which often require expensive tooling and time consuming assembly, Professor Chae-Hwan Park has used 3D printing to create tiny hairs that each contain a sensor.

A new video developed by a team of researchers from the University of California is giving people a chance to save themselves from a potentially deadly mistake. The video, which is meant to act as an antidote for mushroom poisoning, is a powerful tool that could potentially save lives. The video focuses on identifying and avoiding poisonous mushrooms, as well as providing information on how to treat mushroom poisoning. The researchers hope that by providing this knowledge to the general public, they can help reduce the number of cases of mushroom poisoning and save lives.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have succeeded in creating a lab-made material that mimics human tissue! This lab-made material is made up of two layers of a substance that is similar to collagen, the main component of human connective tissue. This material is incredibly resilient, and has the potential to be used in a variety of medical applications, such as creating artificial skin for wound healing and creating implants for bone repair.

Astronomers have just completed the largest cosmological simulation ever made, providing a new window into the evolution of the Universe. The simulation, run at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, is the first of its kind to accurately reproduce the distribution of matter in the Universe. It was created using data from the Planck satellite mission, which has been used to map the cosmic microwave background (CMB)—the relic radiation left over from the Big Bang.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have developed an artificial protein capable of degrading a common plastic pollutant. This discovery could have far-reaching implications for our environment, as plastic pollution has become a major global issue. The artificial protein, called PETase, is capable of breaking down the plastic polyethylene terephthalate (PET) into its component parts. This could provide a way to clean up plastic pollution from the environment, and may even be used in the recycling process.
Today marks the 90th anniversary of the birth of Carl Sagan. Sagan was a world-renowned astronomer, astrophysicist, and cosmologist who changed the way we think about the universe and our place in it. His life and work has had an immense impact on science and society.
Carl Sagan was born on November 9th, 1934 in Brooklyn, New York. He went on to pursue a Ph.D. at the University of Chicago and became a widely respected and admired scientist, author, and educator.

Chemists have recently developed a new technique for creating adjustable arrays of microscopic objects. This innovative method is a major breakthrough in the field of nanotechnology, allowing for the precise manipulation of individual components on the nanoscale. Using this technique, chemists can manipulate objects as small as a few hundred nanometers, making it possible to create tiny machines and circuits. Furthermore, the technique enables the creation of three-dimensional structures, allowing for more complex nanoscale devices.

Today, scientists have announced a revolutionary new cargo-carrying system. The system is able to transport both tethered and untethered soft payloads to a variety of destinations. This is a major breakthrough in the world of cargo transportation, as the ability to transport soft payloads will open up many new possibilities. Scientists are now able to transport items such as fragile foods, delicate machinery, and other items that were previously impossible to transport.
New research has revealed that mining asteroids could offer a way to increase economic viability in space. A team of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, has identified 10 groups of asteroids that could provide resources for space exploration and other activities. The researchers studied hundreds of asteroids and found that these 10 groups of asteroids could be mined for valuable materials such as water, iron, and platinum. This could potentially revolutionize space exploration and the mining industry, as these asteroids could provide a much-needed source of resources.

Fungi have been around for over 400 million years, but a new study has revealed that their evolution has been anything but static. In a new paper, researchers describe how a newly discovered species of Mycena fungus has evolved to invade the bodies of its hosts and how this will alter the way we think about fungal evolution.
The study found that Mycena pteridis, a species of fungus native to Africa, has evolved to become a parasite of its hosts.

In a major breakthrough, scientists have discovered a powerful radio source located over 12 billion light-years away from Earth. Dubbed YETI (Youngest and most energetic Extragalactic Transient in the Universe), the source was identified using the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) telescope located in the Netherlands. YETI is the most distant radio source ever detected and is believed to be associated with a rare type of astronomical object known as a fast radio burst (FRB).

