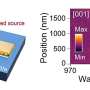
In a recent study conducted by researchers from the University of Gothenburg, it was found that high-quality, nanocrystalline resonators can have a significantly higher resonance frequency in the infrared spectrum than previously thought possible. The findings could have major implications for the development of new technologies, such as infrared laser communication systems and infrared spectroscopy.
The researchers used nanocrystalline resonators made of zinc oxide, which is an abundant, low-cost material. By using a combination of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and other techniques, they were able to measure the crystal resonances with an unprecedented level of accuracy.

In a study published in the journal Physical Review Applied, scientists from the University of California, Riverside have discovered that applying stress to a metal can cause it to become both electronically and magnetically conductive. This opens up a new avenue for engineering materials that can be used in a variety of electronic and magnetic devices. By applying stress to the metal, the scientists were able to create a strain-induced electronic and magnetic conductivity that could be used to create more efficient and effective devices.

Today, scientists have announced an incredible breakthrough in semiconductor technology: the creation of a ‘superatomic’ semiconductor structure that has been shown to enable unprecedentedly efficient energy transport. This superatomic semiconductor structure is composed of a lattice of atoms arranged in a spherical ball, which has been nicknamed the “atomic ball.” This new structure has been shown to enable the transport of energy with almost perfect efficiency, making it an ideal candidate for a variety of applications.
A new nanopore platform developed by Japanese researchers using artificial intelligence (AI) has demonstrated the ability to accurately and quickly identify nucleic acids. The platform, developed by researchers at Osaka University and Waseda University, could have a major impact on the way nucleic acid analysis is performed, as it can identify nucleic acids with high accuracy and in a fraction of the time of current methods. The platform, which uses a combination of AI and nanopore sequencing, could be a game changer for medical diagnostics, as it can rapidly detect and identify nucleic acids from samples such as saliva, urine, or blood.

Recent scientific research has uncovered an exciting new development in the fight against viruses. A team of researchers has discovered that mammalian cells can consume bacteria in a process that kills viruses. This finding has the potential to revolutionize the way we fight viral infections, providing a more effective alternative to traditional antiviral treatments. The research, published in Nature Communications, found that mammalian cells can use a process known as phagocytosis to consume bacteria, which can then be used to produce compounds that are toxic to viruses.

New research suggests that nanoparticles could be an effective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. A study conducted by researchers at Stanford University found that by using nanoparticles to deliver drugs to affected areas, they were able to reduce inflammation and joint swelling, while decreasing the amount of drugs needed. This is exciting news for those suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, as it could potentially provide a new way to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
NASA has announced a new breakthrough in space communication technology! For the first time ever, they have successfully demonstrated a two-way, end-to-end laser communications system between an Earth ground station and a spacecraft orbiting the planet. This new system, which they have dubbed the Optical Payload for Lasercomm Science (OPALS), is capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 50Mbps—a tremendous improvement over the current record of 622 Kbps. OPALS will allow researchers to send and receive large amounts of data to and from space much faster than ever before.

NASA is set to revolutionize space exploration with the help of their new Giant Optical Telescope. This telescope has an unprecedented resolution and accuracy, allowing for a deeper exploration of the universe than ever before. This will open up exciting opportunities for scientists to uncover new information about our universe and the objects within it. With the help of this new technology, NASA will be able to observe far-off galaxies, stars, and other celestial bodies in greater detail than ever before.

Imaging technology is advancing at a rapid pace, and a new method has been developed that can reveal the structure of cells within the bone. A team of researchers at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg in Germany has developed a new imaging method that combines high-resolution microscopy with a technique called multiphoton microscopy. The new method is capable of imaging cells within the bone without damaging the tissue, making it possible to study the structure of cells in great detail.
The iconic New York Natural History Museum is set to open its doors to thousands of visitors in October 2023. After a lengthy renovation and expansion, the grand reopening of the museum will feature a variety of new and exciting exhibits to explore. From interactive displays about the natural world to a stunning array of wildlife specimens, the museum promises to be a must-see destination for locals and tourists alike. Get ready to explore the wonders of nature and the science behind it - the New York Natural History Museum is sure to be an unforgettable experience!

NASA is gearing up for an adventure on the Red Planet! On October 5, 2023, the space agency is set to launch the Mars 2020 rover, the first rover to feature a high-resolution panoramic camera. This camera will allow us to experience the Red Planet like never before, with stunning images of the Martian landscape. This mission is part of NASA’s larger effort to explore Mars and search for signs of life.

Researchers have found an important new protein that could lead to the development of a new antimalarial drug. This protein, called ZAP36, is essential for the survival of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum, which is responsible for the majority of malaria cases worldwide. The discovery of this protein could open up new avenues for drug development and bring us one step closer to developing a much needed new antimalarial drug. This is great news for the millions of people affected by malaria every year.

Today, scientists have made a remarkable discovery in the world of microscopic organisms. After searching through hundreds of samples collected from deep-sea vents, they have identified a new species of predatory worm, dubbed Minorisa species. It is thought to be the smallest predatory worm ever observed, measuring just 0.4mm in length. This groundbreaking find has implications for our understanding of the evolutionary history of the microscopic world and the interactions between different species.

A new study has found that female students are more likely to have higher grades than their male counterparts in certain specializations. The study, conducted by the University of Bristol, looked at gender differences in grades across all undergraduate degree specializations and found that female students consistently outperformed males in people-oriented specializations such as psychology, sociology, and nursing. This is the first study to uncover such a strong gender difference in academic performance across the full range of specializations.

It is estimated that over the next decade, up to 10 UK species of seabirds will have developed a natural immunity to avian influenza. This remarkable breakthrough is the result of years of research by the British Trust for Ornithology (BTO) and the University of East Anglia (UEA). The team studied the behavior of seabirds in their natural habitats and discovered that some of the birds had developed a natural immunity to the virus.

For those of us who are curious about the effects of hypoxia on our bodies, a new study has revealed some interesting insights. Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh have found that hypoxia (low oxygen levels) can cause periosteal stem cells to become more active, leading to increased bone growth and healing. This is an exciting discovery because it could lead to the development of new treatments for bone-related diseases and injuries.
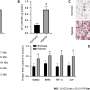
Astronomers have made a major breakthrough in understanding the formation of galaxies in the early universe. By using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile, scientists were able to observe an incredibly distant galaxy, dubbed SPT0418-47, located 12.4 billion light-years away from Earth. This marks the first time a galaxy has been observed so early in the universe’s history, a mere 1.4 billion years after the Big Bang.
The discovery of SPT0418-47 provides a stunning new window into our cosmic past.

Physicists have recently simulated interacting polarons, quasiparticles that form when an electron interacts with a phonon. This simulation is a breakthrough for researchers, as it allows them to better understand the behavior of these quasiparticles, which could have implications for nanoelectronics. By simulating the behavior of these quasiparticles, physicists have opened up a new world of possibilities for further research.
Read Full Article Here
source: Phys.org

In a revolutionary new study, researchers have discovered a way to measure the mobility of sperm cells, which could help improve infertility treatment for those struggling to conceive. By creating a new type of nanomembrane, the researchers were able to measure the movement and speed of the sperm cell, which can be an important factor in fertility. This new technology could help doctors better identify and treat patients who are struggling to conceive, as well as improve the chances of successful pregnancies.

Scientists have recently made a major breakthrough in understanding the genetic triggers of root growth. A team of researchers at the University of Oxford have identified a gene, named ‘PENNYWISE’, which is responsible for the growth of lateral root formation in plants. This gene is believed to play a key role in the development of a wide range of plants, from crops to ornamental flowers. This discovery could potentially lead to improved yields for farmers and the development of more resilient plants.

In a recent breakthrough in nanotechnology, scientists have developed a graphene-based supercapacitor that can withstand mechanical stresses and strains. This is a major breakthrough in the field of energy storage, as most graphene-based supercapacitors can only handle a limited amount of strain. The researchers have designed a graphene-based supercapacitor that is capable of withstanding up to 10,000 times the strain of traditional graphene-based supercapacitors. This means that it can be used in a variety of situations, such as in wearable electronic devices, which need to be able to withstand mechanical forces.

Scientists have made an exciting breakthrough in the search for high temperature superconductivity in carbon materials. In a new study published in Nature Materials, researchers have developed a new form of carbon-based material that can superconduct electricity at temperatures over 200 degrees Celsius. This is the highest temperature at which superconductivity has been observed so far in a carbon-based material. Superconductivity is a phenomenon in which a material can conduct electricity with almost zero resistance.
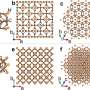
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have been able to combine Raman Spectroscopy and Electrochemistry to study the properties of single crystal surfaces. This new technique, called Raman Spectroelectrochemistry, enables researchers to study the chemical properties of single crystal surfaces at the molecular level. It provides insight into the structural and chemical changes that occur when a single crystal surface is exposed to an electric field. This technology can be used to investigate the behavior of materials under various environments, including those found in batteries, fuel cells, and solar cells.
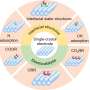
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers have developed two new approaches to treating spinal cord injuries with a molecular scaffold. This scaffold is a three-dimensional structure that helps support the cells in the injured area of the spinal cord while promoting the regeneration of nerve cells. The study found that the scaffold could be used to effectively repair damaged nerve cells, and that it was compatible with other treatments such as stem cell therapy.
Recent research has revealed a potential future where magnets and superconductors could be used together to create new and innovative technologies. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics in Germany have discovered a way to combine magnets and superconductors to create a powerful new type of magnet. This new magnet is created by combining magnets with a thin superconducting material, allowing the materials to interact and produce a powerful magnetic field.

