Microalgae has been touted as a potential tool to help us reach our goal of net-zero carbon emissions. In a recent breakthrough, scientists have made advances in using microalgae to capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into biomass. This biomass can then be used to produce biofuels, fertilizers, and other products. This process of using microalgae to capture and convert carbon dioxide is known as algal photosynthesis. The potential for microalgae to help us reach our goal of net-zero carbon emissions is huge, as it could provide a renewable, sustainable, and cost-effective way to reduce emissions.

Today, a groundbreaking new application of artificial intelligence (AI) has been announced that could revolutionize the way we fight tree disease. Scientists have developed an AI system that is capable of predicting tree disease before it even begins to bud. This AI system is a significant breakthrough in the fight against tree disease, as it could potentially save countless trees and prevent devastating losses to forests and other natural habitats. With this new system, scientists can detect disease before it even begins to spread, allowing for early intervention and prevention.

We’ve all heard the news about how climate change is impacting our planet, but did you know that it could be affecting your wheat crop too? Scientists have been working to understand the effects of climate change on wheat, and they are now beginning to uncover some interesting insights. In this article, we will explore 10 of these insights and how they can help farmers arm their wheat against climate stress.

Today, astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery that will revolutionize our understanding of the universe. By capturing the formation of a powerful cosmic jet, they have observed a phenomena that was previously thought to be impossible. This powerful jet can be seen blasting from a supermassive black hole located millions of light years away from the Milky Way. It is believed that this jet is the result of a supermassive black hole consuming matter from its surrounding environment.

Astronomers have recently made a groundbreaking discovery, using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), to uncover hundreds of previously unseen stars in the core of the Milky Way. The JWST, launched in October 2023, is the most powerful space telescope ever launched and its capabilities have allowed astronomers to observe the stars in the Milky Way’s core in unprecedented detail. By combining near-infrared images from the JWST with data from the Gaia space observatory, astronomers were able to identify hundreds of faint stars that were previously hidden due to the intense brightness of the Milky Way’s core.

As space exploration continues to grow and technology advances, so does our presence in space - and the potential for collisions with other objects in orbit. A new report by the European Space Agency (ESA) predicts that by the year 2023, the space around Earth will be so filled with satellites and debris that collisions between them will become more and more common. The ESA anticipates that failure to take proper measures to manage the space environment will lead to an increase in collisions, which could have a devastating effect on our ability to explore and use the space around us.

China has recently announced plans for its first mission to a space station. The mission is set to launch in 2023 and will be the first of its kind for the Chinese space program. The mission, which will be jointly conducted with the United Nations, will involve a crew of four astronauts living and working on the station for a period of 30 days. The mission will focus on conducting research and experiments in microgravity, astrophysics, and space biology.

Today, we are closer than ever to understanding how Venus became the hellish planet it is today. Researchers have used data from NASA’s Magellan mission to discover evidence of plate tectonics on Venus, similar to the movements seen on Earth. This finding suggests the planet may have had an Earth-like climate billions of years ago.
This is a major breakthrough in our understanding of Venus and its history, as it means the planet may have had much more in common with Earth than previously thought.

It is now widely accepted that the universe is home to many civilizations, but until recently, it was believed that these life forms were far too spread out in space and time to ever interact. However, a new study published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics suggests that some of these civilizations may be much closer than we thought.
The study, led by researchers from the University of Rochester, suggests that civilizations could form on planets in just a few million years, meaning that life could exist in our own cosmic neighborhood.
Recent research has revealed a fascinating discovery in the world of neuroscience: tiny networks in the brain behave similarly to the networks of neurons that control the behavior of birds. Scientists have found that these tiny networks intertwine with each other in a way that mimics the behavior of birds. This could have implications for human behavior, as well as artificial intelligence and robotics. By understanding how these networks interact, we could gain insight into how the brain works and how to better control robotic behavior.
The search for subsurface ice on Mars is a hot topic in the world of space exploration. A new set of tools developed by scientists could revolutionize the way we explore this alien world. The tools could help us better understand the potential for life to exist beneath the Martian surface, and open up new possibilities for exploration. The tools, developed by researchers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and the University of Southern California, enable the detection and characterization of subsurface ice on Mars from orbit.

A new study has revealed some interesting insights into the effects of surface treatment on antibacterial wood. The study, conducted by researchers at the University of Helsinki, found that the application of a special surface treatment to wood can drastically reduce the growth of bacterial and fungal colonies. The surface treatment, which involves the application of a high pressure air stream, is capable of killing up to 99.9% of bacteria and fungi on the wood surface.

Astronomers have discovered a new population of massive protostars in the Carina Nebula. This discovery confirms long-standing theories of how stars form in the universe. The team of researchers used powerful infrared telescopes to observe the Carina Nebula, a region of intense star formation located about 7,500 light-years away from Earth. They discovered a new population of massive protostars, which are stars in the earliest stages of formation. This discovery marks a major breakthrough in understanding the process of star formation and how stars are born in the universe.

New research has revealed that volcanic hotspots on Jupiter’s moon, Io, could be linked to global climate changes on Earth. Scientists at the University of Arizona have discovered that massive outbursts of lava from Io’s volcanoes can produce a powerful electrical current that can travel through the atmosphere and react with Earth’s atmosphere. This could result in changes in global temperatures and weather patterns that could last for centuries. The findings have been published in the journal Nature.

Space exploration continues to make incredible strides forward, as researchers recently announced the successful deployment of the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission. This is the world’s first mission to demonstrate the capability of deflecting an asteroid by colliding a spacecraft into it at high speed. The target of the mission was the asteroid Didymos, which is part of a binary asteroid system composed of two asteroids, Didymos A and Didymos B.

A new study published in the journal Nature Physics has revealed that even when populations of birds have different abilities and characteristics, they still exhibit the same flocking behavior. The research team, led by Professor Roberto Di Candia from the University of Rome, observed flocks of starlings and found that the birds with different sizes, colors and flying abilities still moved together in the same manner. This suggests that even when a flock is made up of heterogeneous bird populations, they still display the same collective motion.
Quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize computing as we know it, and a major breakthrough has been made to bring us closer to realizing this potential. A new quantum architecture has been developed that can store a single electron qubit for up to a millisecond, which is an incredible feat that could lead to the development of quantum computers that are faster and more efficient than ever before. This architecture utilizes a combination of a silicon quantum dot and a microwave resonator, allowing for the qubits to be manipulated and stored in a controlled environment.

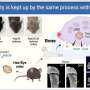
This week, scientists from the University of California, San Francisco revealed a groundbreaking discovery linking proteins involved in bone density to hair growth. For years, researchers have been puzzled as to why and how hair grows, yet this study has provided key insight to this mystery. The research team experimented on mice and found that when a protein known as sclerostin was blocked, mice experienced increased hair growth due to increased bone density.
Do you ever wonder what mysteries lie beyond our own galaxy? Scientists have just discovered something extraordinary. A team of researchers has identified what is believed to be the deepest known galaxy in the universe. This ancient galaxy, known as GN-z11, is located around 13.4 billion light-years away from Earth. This discovery has implications for how we understand the early universe and could provide insight into how galaxies form and evolve over time.

Farming rice and crayfish together can have positive effects on soil biodiversity according to a new study from the University of Oxford. The team of researchers found that the combination of the two crops led to an increased abundance and diversity of soil organisms, which could help to improve the soil quality and promote sustainable farming practices. This could have important implications for food security, as it could help to maintain the health of agricultural soils and reduce the need for chemical inputs.
For years, scientists have explored the diversity of sulfur cycling at the largest scales, from the global sulfur cycle to the role of sulfur in ecosystems. Now, a new study has taken a closer look at the diversity of sulfur cycling at the smallest scales.
The study, published in Nature Communications, was led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology and the University of Bremen. It examined the diversity of sulfur cycling at the scale of individual sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, which are found in many different environments, from the ocean to soils and sediments.

In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have detected mysterious transmissions coming from deep underground. The signals, which have been dubbed “Dark Scientists,” originate from an unknown source and have been described as “unlike anything we’ve ever seen before.” Researchers believe the signals could be evidence of an unknown form of life living beneath the Earth’s surface. The source of these transmissions is still a mystery, but the potential implications of this discovery are immense.

This week, scientists from all over the world announced the successful launch of the first-ever Atmospheric Space Station (ASS), a revolutionary new research platform designed to study the mysterious phenomenon of airglow in Earth’s atmosphere. The ASS, which is now orbiting Earth at an altitude of about 400 km, is equipped with advanced instruments developed to measure the composition and behavior of airglow particles from space. This new research platform will provide unprecedented insight into this remarkable phenomenon that has long puzzled scientists.

The possibilities for exploration of space are now greater than ever. In October 2023, a team of researchers from the University of Washington will launch the first-ever mission to explore the outer edges of our solar system. The mission, named Project Space-1, will use a new type of spacecraft, designed to travel farther and faster than any previous mission. The spacecraft will be propelled by a combination of ion engines, solar power, and a unique new propulsion system, capable of accelerating the ship to speeds up to 20 times faster than traditional spacecraft.

In a breakthrough for wearable technology, researchers have developed a novel multimodal graphene-based e-textile platform that can be customized for a variety of applications. This platform, which consists of a graphene-based nanomaterial, can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a variety of applications, such as energy harvesting, sensing, and communication. The platform has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with our environment by providing real-time information about our surroundings.