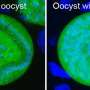
Today, researchers have made an exciting discovery in the fight against malaria: they have identified a gene in the malaria parasite that could be targeted with drugs, potentially leading to an effective treatment. This gene, called MOB2, is a crucial part of the malaria parasite’s life cycle, and when it is disrupted, the parasite can no longer survive. This discovery is a major step forward in the battle against malaria, as it could lead to the development of drugs that target the MOB2 gene and effectively treat the disease.

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is set to explore Jupiter’s moon Ganymede in 2023. This will be the first time ever that a telescope has been used to explore this moon, which is the largest in our solar system. During its mission, JWST will take detailed images, measure the moon’s composition and search for signs of life. It will also measure the temperature and pressure of the moon’s atmosphere, allowing astronomers to gain new insights into its geology and atmosphere.

Robotics technology is revolutionizing the agricultural industry by providing farmers with new and innovative solutions to increase efficiency in crop production. A team of researchers from the University of Georgia have recently developed an end-effector robotic system that can autonomously harvest cotton with minimal human intervention. This technology will be a major asset to farmers, as it can save labor costs and time spent on harvesting cotton. The system is composed of two different robots, one to pick the cotton and the other to monitor and ensure the quality of the harvested product.

In a recent announcement, Russian President Vladimir Putin declared plans to separate a segment of the International Space Station (ISS) to create an autonomous Russian space station in its own orbit. Putin stated that Russia aims to move the station to a higher orbit that would allow the station to remain operational for an extended period of time. The move would mark a major milestone for the future of Russian space exploration.

Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in the world of atomic physics. By utilizing electric fields, they have successfully managed to control atomic transitions. This could have huge implications for quantum computing and communication. The research team used electric fields to manipulate the transitions between two energy states in an atom. By doing this, they were able to control the rate at which the atom moved into another energy state. This could potentially open the door to creating more efficient and faster quantum computing and communication.
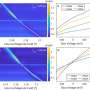
Scientists have been working to uncover the mysteries of the universe for centuries, and it appears that they may be close to a major breakthrough. A recent study has revealed that there may be a “universal bound” of topological entanglement in the universe. This means that all matter in the universe is fundamentally connected in a way that has never been seen before. By understanding this universal connection, scientists may be able to unlock new theories and possibilities that could revolutionize how we understand the universe.
Space debris has been a growing concern for the last few decades with the number of objects in low-Earth orbit estimated to be in the millions. Now, a new study suggests that our current approach to space debris may not be enough and that we could be facing a dangerous tipping point in the next 100 years. The study, published in the journal Scientific Reports, suggests that the amount of debris in orbit is approaching a tipping point where even small amounts of added debris could cause an exponential increase in the amount of debris in orbit.

Today, tracking bees is becoming a whole lot easier thanks to a robotic hive created by researchers at the University of Sussex. The robotic hive is capable of tracking the movements of bees and their behavior with unprecedented accuracy, providing new insights into how the insects interact with their environment. The robotic hive is equipped with sensors that measure the bees’ locations, flight paths, and feeding behavior. This data is then used to generate detailed maps of the hive, which can be used to identify patterns in bee behavior and identify any potential problems.

A mysterious disease is spreading rapidly across South Africa, causing trees to die and turn orange in color. The cause of the disease is not yet known, but scientists are actively working to find out what is causing it. The disease has been reported in several provinces and is affecting a variety of species, including pine, gum, and cypress trees. Symptoms of the disease include orange needles, dead branches, and a thinning of the crown.

Have you ever wondered how hair can sense its environment? Scientists have just uncovered a hidden sensory mechanism that allows our hair to detect subtle changes in its environment. This discovery may revolutionize the field of sensory research, leading to new treatments and therapies for conditions involving hair. This new research was conducted by a team of scientists, who used advanced imaging techniques to examine the structure of hair. They found that the hair cells contain proteins that are sensitive to changes in temperature, humidity, and pH levels.
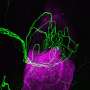
A team of scientists have just announced a major discovery: the existence of undiscovered asteroids in our solar system! These asteroids are believed to contain superheavy elements, which could potentially revolutionize the way we power our world. Scientists are now working to determine the properties of these elements and how they could be used in the future. This discovery is an exciting step forward in the search for new and potentially game-changing energy sources.

Recent research has uncovered a new role for hydrogen sulfide in the gut. Found in minute amounts in the digestive system, hydrogen sulfide has long been known to play a role in the body’s response to stress. However, new research has revealed that it may also be involved in the digestion of food, helping to break down complex carbohydrates and proteins. This finding could have implications for understanding and treating digestion problems, as well as providing insights into the body’s response to stress.
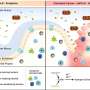
Sleep is a crucial part of our lives, and the body’s internal clock, or circadian pacemaker, plays a key role in regulating when we feel sleepy and when we feel alert. A new study has revealed some eye-opening insight into how the circadian pacemaker works, and it could have major implications for our overall health and well-being.
The study, conducted at the University of California, San Francisco, looked at how different light wavelengths affect the circadian pacemaker.

Today, researchers at the University of California, San Diego have made a breakthrough in the development of miniature robotics: they have created tiny brick-busting muscles! These tiny brick-busting muscles are made out of a type of plastic, and are capable of lifting and moving objects around that are much larger than them. This technology could revolutionize the field of miniature robotics, and could be used to create robots that can be used for a variety of applications, from search and rescue missions to healthcare.

Scientists have recently discovered a new anisotropic lattice which has the capability to produce high chiroptical responses. This new lattice combines two different materials, an organic chromophore and an inorganic lattice, arranged in a specific way to generate high optical responses with a wide range of applications. The chromophore is an organic molecule that absorbs and emits light, while the inorganic lattice is a crystal structure composed of metal ions. By arranging the two materials in a specific way, researchers were able to create an anisotropic lattice that produces high chiroptical responses.

A new study, published in the journal Nature Communications, has revealed that researchers can now use genetic methods to extract fossil lipids from sediment. This groundbreaking discovery could provide new insight into the evolutionary history of extinct organisms, and could potentially revolutionize how we understand the Earth’s ancient climate. Fossil lipids are molecules that are preserved in the fossil record and are often used to reconstruct the environment in which the organism lived.

Today, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery about protein that could help us create a more climate-proof future. It has been discovered that a specific type of protein, called a root-associated lipoprotein (RALP), is found in the roots of plants and is essential for the plants to survive in extreme climates. This protein helps the plant to access water in drier climates and to tolerate hotter temperatures. The implications of this discovery are huge — if we are able to find a way to genetically engineer plants with more RALP, then we can create crops that are more resistant to extreme weather conditions and more resilient in the face of climate change.

In a groundbreaking study published today in Nature Biotechnology, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have demonstrated a novel method for generating biomass from waste materials. Using a combination of enzymes and a novel optimization algorithm, the researchers were able to efficiently convert waste materials into biomass, which can then be used as a renewable energy source. This method could drastically reduce the amount of waste generated by industrial processes, while simultaneously promoting the use of environmentally friendly renewable energy sources.
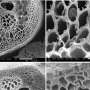
It looks like the future of materials science is here! Researchers have developed new algorithms that allow for quantum simulations of polymeric materials. This is a revolutionary breakthrough that will allow for unprecedented accuracy and precision when predicting the behavior of materials. With this breakthrough, scientists can now simulate the behavior of materials at the molecular level and accurately predict how materials will react to various conditions. This will revolutionize the way materials are studied and developed, leading to improved products and safer working environments.
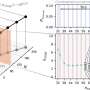
Scientists have recently discovered a new type of metal-organic complex that could revolutionize the way we think about energy storage. This complex, made up of a polyoxometalate-based metal-organic framework, or POM-MOF, is capable of storing energy at temperatures up to 200 degrees Celsius and is also environmentally friendly. The team behind this discovery is led by Professor Zhanfeng Cui of Imperial College London and hopes to use their findings to create a new type of rechargeable battery.
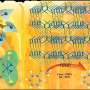
Scientists have developed a new technique that can be used to precisely tune the properties of membrane layers used in catalytic reactions. This new method, which has been developed by a team of researchers from the University of California, Riverside, could significantly improve the efficiency of catalysts used in industrial processes such as fuel cells and electrolyzers. Through this new technique, the researchers are able to precisely control the contact between the membrane and catalyst layer, allowing for more efficient and selective catalytic processes.

Researchers have recently made a shocking discovery while studying the ways in which cells communicate with one another: intercellular messengers that reveal an entirely new form of cellular communication. These messengers were found to be composed of small, lipid-based particles that can be released by cells and travel between cells to convey important information. This discovery could have far-reaching implications for our understanding of how cells interact with one another and could lead to new treatments for diseases such as cancer.
Scientists have recently announced an exciting breakthrough in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) technology, which could revolutionize the way we access remote sensing data. Specifically, researchers have created a new algorithm that allows sparse SAR images to be unambiguously reconstructed. This means that with this new technique, it is now possible to obtain high-resolution images from sparse SAR data, a feat that was previously thought to be impossible. This breakthrough has the potential to drastically reduce the cost of SAR data acquisition, as fewer SAR measurements are required to produce a clear image.

Farmer’s lives have been transformed by a new app that can control drones and increase farm efficiency. This revolutionary app, developed by researchers at the University of California, allows farmers to use drones to manage their crops with unprecedented precision. The app allows farmers to map and monitor their crops in unprecedented detail, and even to detect potential problems with their crops before they become serious. The app also helps farmers to optimize their irrigation and fertilization, and to apply pesticides and herbicides more efficiently.

As technology advances and the use of computers in the classroom grows, teachers now have access to a wide range of natural language tools to help them better communicate with their students. Natural language processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence that studies how computers can understand human language. With NLP, teachers can create interactive lessons, create automated assessments, and even provide feedback to students. In this article, we will explore 10 natural language tools that teachers can use to enhance their instruction.

