
A recent study from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology in collaboration with the Chinese Academy of Sciences has found that CRISPR/Cas9 technology can be used to effectively increase the resistance of Chinese cabbage to turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). The CRISPR/Cas9 technology was used to create a virus-resistant Chinese cabbage line, with a success rate of up to 100%. This is an exciting breakthrough that could potentially revolutionize the ability to protect crop plants from viral infections.

A new strategy for high performance small molecule near-infrared (NIR-II) photoswitching has been developed. The strategy enables the design of photoswitching molecules that are stable, non-toxic, and small enough to penetrate into cells and tissues for use in optogenetics and other applications. The strategy uses a combination of two small molecules, called a phototrigger and a photo-switchable group, to enable switching between two different photochemical states. The phototrigger is a small molecule that absorbs energy from light and releases a proton transfer agent (PTA) that, in turn, triggers a photochemical reaction in the photo-switchable group.
Today, scientists have unveiled an incredible discovery about the conjugation process of the ciliate Paramecium. This cellular process, which allows two of the same species to exchange genetic material, is vital for the species’ survival. The study, conducted by a team of researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles, has revealed new insights into how the process works, and how it’s unique from other types of cellular reproduction. Through their research, the team was able to identify several key players in the conjugation process, as well as the proteins involved.
We are on the brink of a major breakthrough in computer science: an algorithm that can solve any numerical problem with astonishing accuracy and speed. Developed by researchers at the University of Washington, the algorithm is a game changer for those who rely on numerical calculations to make decisions, from scientists to financial analysts. It uses a combination of advanced mathematics and machine learning to tackle even the most complex numerical problems with unprecedented speed and accuracy.

Recent advances in forensic science have allowed for an exciting new tool: using pet hair to catch criminals. According to a new study published in the journal Forensic Science International: Genetics, researchers have successfully used the DNA from pet hair to help identify suspects in criminal cases. This method is especially useful in cases where the suspect has been identified, but the suspect’s DNA is unavailable. By comparing the pet DNA to a database of known pet DNA, investigators can now determine if the pet hair found at a crime scene matches the pet of the suspect.

In a breakthrough study, scientists have recently discovered a way to use technology to increase soil carbon levels, which in turn can significantly boost crop yields. This new technology, developed by a team of researchers from the University of California Berkeley, has the potential to greatly improve agricultural production while also helping to reduce the amount of carbon in the atmosphere. The technology works by combining the use of anaerobic soil disinfestation (ASD) with the addition of a biochar soil amendment.

Have you ever wondered what it would be like to grow a mouse embryo in space? Recently, scientists in Japan have successfully grown mouse embryos in space for the first time. This is a major step forward in the understanding of how embryos develop in microgravity.
The experiment was conducted on board the Kibo module of the International Space Station (ISS) by Japanese scientists from the University of Tsukuba. The team was able to grow two-cell mouse embryos to the blastocyst stage, which is the stage just before implantation in the uterus.

A new study conducted by researchers from the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has uncovered a giant fluctuation-enhanced phonon-magnetic effect in a type of materials called rare-earth nickelates. The findings of the study have been published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
The team of researchers behind this study has discovered that rare-earth nickelates exhibit a giant fluctuation-enhanced phonon-magnetic effect, which could be useful for the development of next-generation devices.
Today, scientists have released a new method for creating a more stable and efficient next-generation of materials. This method is revolutionary and could have a major impact on the future of energy and resource use. By using atom-level precision to create new materials with improved stability, scientists have opened up a new world of possibilities. These materials could be used in a variety of applications from energy efficiency to improved corrosion resistance.

Today, the International Society of Limnology announced that Saturday, October 20th will be known as “Citations for Mars Limnology and Phage Day”. This marks the first day of a week-long celebration dedicated to recognizing and honoring the contributions of researchers who have advanced the study of Mars limnology and phage. Limnology is the study of inland waters, and phage are viruses that infect bacteria. This field of research is of particular interest to those studying the possibility of life on Mars.
The future of random bit generators has taken a major step forward with the announcement of a new device that can generate petabits of random numbers. This new device, which was developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge, is capable of generating random numbers at a rate of 1 petabit per second. This means that it can generate 1 million gigabits of random numbers per second, which is more than 10,000 times faster than the best existing random bit generators.
Aquaculture is quickly becoming one of the most effective and sustainable ways to produce nutritious food for the world. Recent studies and technological advancements have made aquaculture a viable option for many communities, and it’s becoming increasingly popular due to its potential for creating jobs and providing a reliable source of income. Aquaculture is a form of farming that uses water to cultivate aquatic plants and animals, such as fish, shellfish, and seaweed.
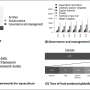
Chemists have made a breakthrough discovery in the field of anti-aromatics. They have managed to synthesize a doubly anti-aromatic C16 carbon chain that has been observed as a stable molecule for the first time ever. This is an exciting finding, as it has long been speculated that such a molecule could exist, and now, it has been proven to be true. The discovery has the potential to reshape our understanding of chemical behavior and open the door to new possibilities in the field of molecular engineering.
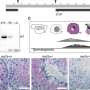
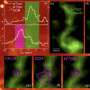
A new study has recently revealed a link between male infertility and a protein found in sperm. The research, conducted by a team of scientists from the University of California, Los Angeles, indicates that a protein known as SMCHD1 may be the key to unlocking the mystery of male infertility. The study found that when the protein is mutated or missing, it can lead to a decrease in sperm production and a decrease in sperm motility.
We are on the cusp of a new era in nanotechnology. Scientists have recently developed a DNA origami nanoturbine, which could be the basis of many new nanomotors. This nanoturbine is made up of a DNA scaffold that is folded and manipulated into a turbine-like structure. This structure can then be used to power nanomotors, which could be used for a variety of applications, such as medical treatments or energy production.
Astronomers have discovered an infant star located in a very distant galaxy, and it is the youngest star ever seen. The star, called “J1407b”, is estimated to be only a few million years old. This is a very young age for a star, as some stars can be billions of years old. J1407b is located in a spiral galaxy called NGC 613, located approximately 110 million light-years away from Earth.
Today, researchers have discovered a new mechanism that can help provide fiber-optic networks with more speed and capacity. This mechanism is known as “mode-division multiplexing,” and it is a major breakthrough in how data is transmitted via fiber-optic cables. By utilizing this new technique, the amount of data that can be sent through a single fiber-optic cable is significantly increased. This can provide fiber-optic networks with the capacity to support more users, faster speeds, and more reliable connections.
According to recent research from the University of California, Davis, there is a greater chance than previously thought that the exo-Neptune GJ 436b could have an atmosphere. This exoplanet, located about 33 light-years away from Earth, has been the subject of much speculation since its discovery in 2004. This new research, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, suggests that GJ 436b could have an atmosphere composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, similar to the atmosphere of Saturn’s moon Titan.

A new study published in Nature Energy has found that environmental PFAS is an emerging source of energy for microbial fuel cells. PFAS, or perfluoroalkyl substances, are a class of chemicals used in a variety of industrial and consumer products, including nonstick cookware, waterproof clothing, and firefighting foam. The study reveals that PFAS can be used as an energy source for microbial fuel cells, which are small devices that use bacteria to convert organic matter into electricity.

In a groundbreaking move, the world is about to recognize animals as legal persons. This means that animals will be acknowledged as having legal rights and standing in court. This monumental decision is being made in order to protect and promote the welfare of animals, which are so often overlooked and abused. The law is intended to reduce animal suffering by ensuring that the interests of animals are taken into account in decision-making.

The future of sustainability is looking brighter every day! Scientists have created a new type of nanomaterial that could be a game changer for the environment. This hybrid nanomaterial combines the best of both worlds: nanotechnology and sustainability. The nanomaterial has the potential to boost sustainability in multiple industries, from energy production to manufacturing. By using this nanomaterial, production processes can be made more efficient, leading to fewer emissions and cleaner air.

Recently, the Hubble Space Telescope snapped a photo of two galaxies that are part of the Arp-Madore catalog of interacting galaxies. This catalog was created by two astronomers in the 1970s to highlight galaxies that are interacting with each other in some way.
The two galaxies, known as UGC 695 and UGC 694, are located roughly 150 million light-years away from Earth. Hubble’s image of the pair shows two galaxies that are gravitationally interacting with each other.

Deep sea creatures have been found to possess a remarkable ability to survive in extreme conditions. A recent study has revealed that sea anemones are no exception. Scientists have discovered that certain genes from sea anemones are capable of surviving in extremely deep ocean conditions. The genes are able to remain intact and functional even at depths of up to 1000 meters. This finding not only shows the remarkable resilience of these creatures, but also brings us closer to understanding the unique genetic adaptations that enable them to survive in these extreme environments.
NASA recently announced the launch of a new rocket, set to take place in October 2023, that promises to take us further into the universe than ever before. The rocket, called the Sizzling Edge Star-Forming Rocket (SESFR), will explore the edges of galaxies and star-forming regions, giving us an unprecedented look into the creation of stars and the structure of galaxies. Scientists are hopeful that the mission will help us understand more about the evolution of galaxies and the formation of stars, and that it could even provide us with new insights into our own origins.

NASA recently unveiled a technological breakthrough that could be a game changer in the search for life beyond Earth. The newly developed technology is an advanced infrared spectrometer that can detect the presence of organic molecules in atmospheres of exoplanets, or planets outside of our Solar System. The spectrometer is designed to detect very small amounts of organic molecules such as methane and carbon dioxide, which has long been seen as a key indicator of life.

