
Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in using artificial intelligence to better understand how drugs impact the human body. Through the use of AI, researchers have been able to identify multiple new potential drug targets and gain insights into how these drugs interact with the human body. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize the way drugs are developed and used, and could lead to more effective treatments for a variety of diseases.

A new study has found that using a combination of “smart farming” and fire-resistant crops could help protect agricultural areas from the threat of wildfires. The research, conducted by a team at the University of California, Davis (UC Davis), suggests that by using smart farming strategies such as crop rotation and precision agriculture, farmers can help reduce the fuel loads on their land and make their crops more resistant to fire.

NASA recently previewed their next mission, the Lucy mission, set to launch in 2023. Lucy, named after the fossil Lucy found in 1974, will be the first mission to explore Trojan asteroids located in the Jupiter’s orbit. This mission will help us understand the formation of our solar system and provide insight into the origin of life on Earth. The mission will be made up of two probes, Lucy and Eurybates, which will survey the six Trojan asteroids located between the orbits of Jupiter and Neptune.

AI-powered investing is the future of stock trading, and new research is proving that data-limited stock selection methods can be just as accurate as those that rely on complex data sets. A recent study by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, has found that a data-limited AI-powered stock selection method can be just as accurate as one that relies on large data sets. This method, which is based on reinforcement learning, uses minimal data to make stock predictions and could be used to improve the accuracy of stock trading.

On July 7th, 2023, a large asteroid will pass uncomfortably close to Earth. This asteroid, known as 2021 KT1, is estimated to be up to 400 meters in diameter – making it one of the largest asteroids to ever pass this close to Earth. Scientists are monitoring 2021 KT1 closely and have determined that the asteroid will pass within 8 lunar distances of Earth, making this a potentially dangerous situation. If the asteroid were to collide with Earth, the impact would be devastating.

Astronomers have discovered a mysterious and massive stellar halo surrounding the Andromeda galaxy - an enormous spiral galaxy located approximately 2.5 million light-years away from Earth. This stellar halo, dubbed the “Ark,” is made up of hundreds of thousands of ancient stars and stretches nearly three times farther than the galaxy’s iconic spiral arms. This discovery provides astronomers with an unprecedented opportunity to study the origin and evolution of one of the most famous galaxies in the sky.

This week, students from an Australian school have made history as they prepared the first batch of vegetables to be grown in space. The vegetables, which include lettuce, were grown from seeds sent up on a rocket from the International Space Station (ISS), and will be harvested in the coming weeks. For the students, the project represents a unique opportunity to contribute to scientific research, and to gain valuable experience in the field of space exploration.

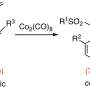
Today, scientists have successfully demonstrated the first ever Pauson-Khand reaction with atropisomeric substrates. This breakthrough is expected to have a major impact on the synthesis of natural products, pharmaceuticals, and materials. The Pauson-Khand reaction is a type of chemical reaction that is used to create cyclic compounds with multiple bonds. Up until now, the reaction has only been used with substrates that are not atropisomeric. Atropisomeric compounds are molecules that have a chiral center, which means they can exist in two different forms.
China is making history once again by becoming the first nation ever to farm on the moon. This ambitious project is set to launch in October of 2023. The small farm is designed to be self-sustainable and will include a number of plants and vegetables.
China has taken a bold step forward in space exploration by becoming the first nation to develop a farm on the moon. The farm will be located in the moon’s South Pole-Aitken Basin and is scheduled to launch in October of 2023.

In a recent study, researchers have discovered a common shrub that is more efficient at harvesting energy from sunlight than any other plant! The shrub, called Balanites aegyptiaca, is found throughout the Middle East and Africa. This remarkable plant is able to harvest more energy from the sun than any other known plant, making it an ideal source of renewable energy. Its ability to capture and store energy makes it promising for a variety of applications, from electricity generation to water desalination.

Psychologists have developed a new scale to measure students’ attitudes toward digital technology. The scale is designed to provide educators with a useful tool for gauging students’ views on the use of digital technology in their learning. The scale can be used to help teachers understand how their students feel about digital tools and how they use them in their learning. It can also help educators identify where there may be potential areas of improvement to help students become more engaged and successful with digital technology.

Recently, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has made a groundbreaking observation of the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant located in the constellation of Taurus. The Crab Nebula is a cloud of gas and dust that was formed after a massive star exploded in 1054 AD. This observation marks the first time that the Webb telescope has been able to capture such a detailed view of the nebula, providing astronomers with never-before-seen information about its structure and composition.

A new study has revealed a fascinating insight into the Denisovans, an ancient hominin species that lived in Central and East Asia from about 400,000 to 50,000 years ago. The study, published in Nature Communications, suggests that the Denisovans left a significant genetic legacy in the modern human genome, and that this legacy may have had an impact on the development of modern mental health and behavior.
The Denisovans, named after the cave in Siberia where their skeletal remains were first discovered in 2010, were an ancient hominin species that lived in Central and East Asia from about 400,000 to 50,000 years ago.
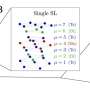
Today, scientists have uncovered a new and exciting phenomenon that could potentially revolutionize how we think about the Hall effect. Researchers at the University of Tokyo have developed a theoretical model that illuminates the nonlinear Hall effect, which is a phenomenon in which a current carrying material generates a voltage that is proportional to the product of the current and the magnetic field. This new model will allow us to better understand why this effect occurs and how we can use it to develop new technologies.
Space colonization has been a topic of science fiction for decades, and now a team of researchers is exploring how to make it a reality. Led by Dr. Tricia O’Neil from the University of Arizona, the team is looking at the latest advances in space technology to identify the best ways to colonize distant planets. The team is focusing their efforts on technology that could enable humans to live in a closed-loop environment that is self-sustaining, providing resources for exploration and colonization.
A new breakthrough in metamaterial and metamolecule fabrication has been developed, which could revolutionize the way we fabricate 3D structures using co-assembly. Scientists from the University of California, Berkeley have developed a novel method that combines the principles of self-assembly with the use of external fields to create complex 3D structures. The technique, called “Metamolecule-Metamaterial Co-Assembly,” allows for the precise manipulation of individual components to create complex, hierarchical structures. This could be used to create a variety of products, from medical implants to nanomaterials.
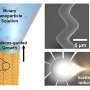
The future of computing is energy efficient. Researchers from the University of California, Berkeley have developed a new way to simulate spirals with electronic devices that are much more energy efficient than traditional devices. This new method could have a major impact on the way computer systems are designed and powered. With this new method, computers can be designed to be more efficient in terms of energy consumption, meaning longer battery life and less power use.

The well-being of teachers is in decline due to the focus on school headlines. A recent study conducted by researchers from the University of Bristol and University College London has revealed that the focus on school headlines has eroded the well-being of teachers. The research found that teachers are increasingly feeling overwhelmed by the demands placed on them, and that the focus on school headlines has meant that teachers are feeling a lack of autonomy and control in their job.

Recently, researchers have developed a new simulation method that uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to accurately simulate the behavior of powder-based materials. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize the field of materials science and could open up new opportunities for applications ranging from drug delivery to 3D printing. The AI-based simulation method combines data from X-ray diffraction experiments and computational analysis to create a detailed 3D representation of the powder material.
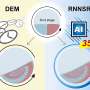
Today, scientists have discovered a new way to manipulate nanoparticles. By using a technique called “play-and-play,” scientists are able to easily move and control nanoparticles with a simple joystick. With this breakthrough, scientists are now able to use nanoparticles to tackle a variety of biological problems and diseases, such as cancer, infections, and genetic disorders. This discovery is a major milestone in the field of nanotechnology, as it provides a much simpler approach to manipulating nanoparticles.
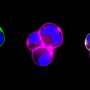
Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in understanding how parasitic diseases work, and how to combat them. A team of researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, recently discovered a way to “clamp” complex parasites to human cells, which could lead to the development of new treatments for parasitic diseases. The new technique, which uses a modified form of CRISPR, can be used to attach a parasite to a host cell, allowing scientists to observe how the parasite interacts with the host and how it takes over its functions.
Today, scientists have made an exciting breakthrough in the fight against SARS-CoV-2. New research has demonstrated the use of surveillance genotyping with the CRISPR-Cas12a enzyme, which can detect SARS-CoV-2 in sewage samples. This breakthrough could help detect outbreaks of the virus in their earliest stages, before people start showing symptoms. This would allow health care workers to take steps to contain the virus and potentially save thousands of lives. This new technique is a major step forward in the fight against this deadly virus.
The future of Apple Inc. looks to be a bright one, as the company is currently researching ways to power its devices with a revolutionary new technology known as “Genome-wide Modern Computing (GWC). GWC is a powerful form of computing that uses the human genome as its source of data. This allows for the efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of genetic data, making it a potential game-changer for the tech industry.
Today, NASA announced an exciting new discovery - X-ray telescopes have revealed evidence of bones in outer space! This is the first time we have ever seen such a phenomenon. Scientists believe these bones could be from ancient stars that have long since died. This could open up a whole new field of research and will help us to better understand our universe. Stay tuned for more information as we learn more about this unique discovery!

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is set to launch in October of 2023, and with it comes the promise of new discoveries in the field of exoplanet research. Scientists are expecting to use the JWST to explore the atmospheres of exoplanets, searching for signs of life. With its powerful infrared capabilities, the telescope will be able to look for gases like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ozone that may be present on planets orbiting other stars.

