A new study has revealed a potential method for harvesting metals from asteroids. The method, proposed by researchers at the University of Central Florida, could provide humanity with a reliable source of metals for the construction of spacecraft and other technologies. The research team discovered a way to use a combination of lasers and a process called “ablation” to extract metals from asteroids. Ablation is a process in which the intense heat from the laser vaporizes the surface of the asteroid, releasing the metals contained within.

A new discovery has opened the door to a potential sustainable alternative to synthetic materials: velvet worm slime. The slime, produced by the velvet worm, has been found to have a unique combination of properties that make it a great candidate for use as a material for clothing, footwear, and even medical applications. Scientists from the University of Oxford have been studying the velvet worm slime to determine its potential for use as a sustainable material.
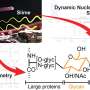
The production of detergents is one of the most important industries in the world. In order to meet the ever-growing demand for these products, manufacturers must ensure they are producing them in a cleaner and more efficient way. A new study has identified a key area of focus for manufacturers to make sure their production process is as green as possible.
The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Birmingham, found that the use of two different types of acid in the production process of detergents can drastically reduce the production’s environmental impact.
Today, scientists have developed a new algorithm that is able to successfully improve the resolution of microscope images up to 10 times the original pixel count. This algorithm, developed by researchers at the University of California San Diego, has been shown to be able to increase the resolution of images from the standard 4 megapixel count to 40 megapixels. This is a huge leap forward in the field of microscopy, as higher resolution images provide greater detail and clarity.
It’s official: three astronauts have just completed an unprecedented one-month stay aboard the China Space Station. From October 1, 2023 to November 1, 2023, the three astronauts—two Chinese and one Russian—were the first humans to stay in space for an entire month. This incredible feat of human endurance and technological prowess has been hailed as a great success for international collaboration in space exploration.
Read Full Article Here
source: Phys.org

A team of researchers from Harvard’s John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created a dual metalens that can switch between two different modes of operation. This breakthrough could enable a wide variety of applications in fields such as augmented reality, optical communications, and imaging. The metalens is a thin, flat surface with nanostructures that can focus light like a traditional lens. With the dual metalens, light waves can be manipulated in two different ways, allowing for greater flexibility and control over the optical properties.
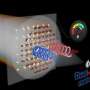
An exciting new development in the world of quantum research has been announced: scientists are one step closer to creating a new type of quantum fluid. This quantum fluid, created from ultracold atoms, could have a range of applications from quantum computing to metrology and beyond. The research, led by a team at the University of Washington, has demonstrated a key step towards creating this new type of quantum fluid: the ability to tune the interactions between the atoms.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is set to revolutionize the study of exoplanets. Its extraordinary capabilities will allow researchers to gain insight into the atmospheres of planets located outside of our own solar system. In a recent study, astronomers have used JWST to analyze the atmosphere of Fomalhaut b, a planet orbiting the star Fomalhaut in the constellation Piscis Austrinus.
The JWST is expected to provide unprecedented detail on the composition of Fomalhaut b’s atmosphere.

In a breakthrough for the art world, researchers from the University of California, San Diego, have successfully reverse engineered the painting technique of renowned artist Jackson Pollock. Using the technique of 3D printing, the researchers have been able to recreate the intricate and unique patterns that Pollock was known for, providing a new perspective on the artist’s work. The findings of the study suggest that 3D printing could be a viable tool for studying and reproducing the works of other artists, including those from the Impressionist period.

A new study from researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara, has uncovered the complex ecology of pit latrines. Pit latrines are traditional sanitation systems that are commonly found in many developing countries, and they are a major source of human waste contamination of the environment. The study, published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, shows that the composition of the microbial communities in pit latrines is highly variable and can be influenced by factors such as the type of pit latrine, the location of the pit latrine, and the age of the pit latrine.

Recently, researchers have made a breakthrough discovery that could revolutionize the way we think about the classification of living things. After decades of research, taxonomists have identified three new categories of life on Earth that could revolutionize the way we think about our planet’s biodiversity. The new categories are based on genetic similarities and represent the three domains of life, archaea, bacteria, and eukaryota. Furthermore, these categories are thought to have evolved independently from each other over the course of 3.

Gone are the days of birthday parties with clowns and bouncy castles. A new era of entertainment is here with the recent announcement of a mission to the moon by Balloon Animals. The team of scientists and engineers will be using helium-filled balloons to launch a spacecraft to the moon. This mission seeks to explore the lunar environment, and also to create a new form of entertainment on the lunar surface.

Recent findings from the Institute for Space Research have revealed that life on other planets is not only possible, but likely. After studying the atmospheres of nearby exoplanets, scientists have come to the conclusion that these planets have the potential to harbor life. This is a groundbreaking discovery that could have implications for our understanding of life in the universe. It is an exciting time for astrophysicists as we continue to learn more about our planet neighbors and the possibilities for life beyond Earth.

In a major breakthrough, scientists have discovered the mechanisms behind the reconnection of xylem in interfamily grafts. Xylem is the vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. The research was conducted by a team from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and published in the journal Science.
This research has opened up new possibilities for the use of interfamily grafts in agricultural applications.
On October 5th, 2023, a historic announcement was made - advanced reproductive techniques have been used to safely reproduce white rhinos! This is a huge breakthrough in conservation efforts, as the white rhino population has been dwindling due to poaching. Conservationists have been working diligently to find a way to preserve this species, and now they have! This reproductive technique, which is similar to in vitro fertilization, allows eggs to be collected from female rhinos and sperm from males to be used to create viable embryos.

A new study from researchers at the University of Cambridge has found that giant planets could be the death of life in their star systems. The team studied how hot Jupiters—giant planets that orbit close to their host star—can disrupt the biodiversity of their star systems. They concluded that the extreme temperatures and radiation from these planets could lead to the destruction of any life that may exist.
The researchers used computer simulations to model the effects of a hot Jupiter on the planetary system.

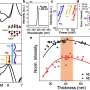
Recently, scientists have developed a new paper-based super-resolution technique for non-linear hyper-spectral imaging. This technique promises to revolutionize the way we approach imaging of small objects, such as cells, bacteria, and viruses. Using a simple paper slide, scientists are now able to capture high-resolution images of these tiny objects with unprecedented accuracy and detail. The paper-based super-resolution technique works by combining multiple images taken at different wavelengths to construct a single image of the object at a higher resolution.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of international goals and targets that aim to improve the quality of life on our planet. They are a global call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity. In October 2023, the world will come together to review the progress made in achieving the SDGs. This review will be a critical moment to evaluate the progress each country has made towards achieving these ambitious goals.

A new study by mathematician Dr. Daniel Harrison has revealed a startling truth - climate change could lead to a mass extinction event in as little as 100 years. Dr. Harrison’s research focused on the effects of rising temperatures on global ecosystems. He concluded that if the current global temperature trend continues, the Earth’s biodiversity will take a drastic hit, leading to a mass extinction event. Dr. Harrison warned that this event would cause unprecedented disruption to the planet’s ecosystems, leading to widespread famine, disease, and death.

NASA’s C-20A made history this week, becoming the first plane to ever fly over Antarctica. The C-20A, a Gulfstream III jet aircraft operated by the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, flew from Punta Arenas, Chile to McMurdo Station in Antarctica in just five hours. This groundbreaking flight marks the first time an aircraft has ever flown a scientific mission to the continent. During the flight, the C-20A collected data on the atmosphere, surface temperatures, and other environmental factors.

NASA’s Juno spacecraft has just made a groundbreaking discovery - salts on the surface of Ganymede, the largest moon of Jupiter! Scientists have long suspected that Ganymede had a salty surface, but this is the first time that salts have been found on its surface. This finding is an important step in understanding the moon’s composition and its potential for hosting life. Now that salts have been discovered, scientists will be able to study them in more detail and investigate the environment of Ganymede.

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is ready to begin its mission to explore the Trojan asteroids! This mission marks an important milestone in space exploration, as it will be the first mission of its kind to visit the Trojan asteroids. The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of instruments that will allow it to study the composition of the asteroids, as well as their formation and evolution. The Lucy mission will also look for clues about the origin of life in our solar system.

A new nanotherapeutic vaccine delivery system developed by researchers at MIT could revolutionize the way we administer vaccines. The researchers have developed a nanotherapeutic platform that uses an engineered nanoparticle to deliver not only the vaccine, but also a second molecule to boost its efficacy. This second molecule, known as an adjuvant, helps stimulate an immune response, making the vaccine more effective. The platform is designed to be highly versatile, and could potentially be used to deliver a wide range of therapeutic molecules.
Climate change is having a devastating effect on the Middle East. In just the next few years, temperatures in the region are expected to rise, leading to increased drought and water scarcity. This is a problem that affects not only the environment, but also the people who rely on the region’s resources. In response, experts are looking for innovative ways to help the Middle East adapt to a drier, hotter climate.

Scientists have developed a new type of epoxy-based, moisture-resistant phosphorescence that can remain “ultralong” for up to two months. This groundbreaking technology could revolutionize the way we use phosphorescence in the future.
Phosphorescence is a type of luminescence that occurs when a material absorbs energy from a light source and re-emits it over time. Until now, the use of phosphorescence has been limited due to its sensitivity to moisture, but this new technology could change that.