Researchers have recently discovered an unprecedented anomaly deep within the Earth’s mantle that has never before been observed. Dubbed the ‘Galle Anomaly’, the region is located around 2,900 kilometers below the Earth’s surface and is likely the remnant of an ancient tectonic plate. Scientists suspect that the anomaly is composed of several different types of rock, including some that are not usually found in the mantle, indicating that the material originated elsewhere.

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft has recently been making history! This spacecraft, which was launched in October 2021, is currently on its way to explore the Trojan asteroids. These asteroids are located in the outer region of the solar system, in the orbit of Jupiter. This is the first time a mission like this has been attempted, and Lucy is expected to make some incredible discoveries in its two-year mission. The spacecraft will fly by six of these asteroids, all of which are thought to be relics of the early formation of the solar system.

Today marks a historic moment for NASA’s Osiris-REx mission. After seven years of preparation, the spacecraft has flown by the Osiris-Apex asteroid. This is the first time a spacecraft has been sent to explore an asteroid up close. The mission’s aim is to bring back a sample of the asteroid’s surface material for scientists to analyze in the lab. This is a major milestone for planetary science as it will provide a greater understanding of our solar system and the origin of life.

Today, researchers from the Institute of Physics have announced a breakthrough in the field of electronics: a new technique for neutralizing the inhomogeneity of cleaved bulk materials. This technique could revolutionize the way we use electronics in our daily lives. By using a combination of atomic force microscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy, the scientists were able to observe and manipulate the material at the atomic scale, allowing them to precisely identify and mitigate the inhomogeneity of the material.

A recent study, published in Nature Communications, has revealed a new, innovative way to combat the Ebola virus. Researchers have discovered that the virus can be infected by cells, a finding that could help to develop treatments for the deadly virus. The study found that certain cells, when exposed to the virus, were able to take it up and replicate it. This could potentially lead to treatments that could target and destroy the virus before it can cause any harm.
Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in the development of nanowire brain networks. These networks, composed of nanowires, are capable of storing and processing information in a way that mirrors the functioning of a human brain. This breakthrough could lead to exciting new applications in areas such as artificial intelligence and robotics.
The research team, based at the University of Sheffield, was able to create a network of nanowires that can store and process information in a way that is comparable to the human brain.

The James Webb Space Telescope is set to become the most powerful telescope ever launched, and its capabilities are beyond what we can currently imagine. In order to better understand the telescope’s capabilities and applications, engineers at NASA have developed new simulation software. This software provides an interactive interface for simulating how the telescope will observe the universe and interact with its environment. With this software, engineers and scientists can explore the telescope’s performance and capabilities before its launch in 2023.

Today’s sky is becoming increasingly crowded with satellites. A new study by researchers has revealed that, on average, there are 11 satellites that create bright glints in the sky every hour. This can be a big problem for astronomers who are trying to observe the night sky, as these glints lead to significant light pollution. The authors of the study are now calling for new regulations to help reduce this light pollution.

The world of physics has recently been abuzz with the solution to an age-old thermodynamic puzzle. Scientists have found that the mysterious behavior of micro-crystals, which have puzzled physicists for decades, can be explained by a simple thermodynamic process. This process, called “surface diffusion,” involves the movement of particles on the surface of a solid crystal. By understanding this process, researchers can better understand the behavior of these materials and potentially use them in new technologies.
Today marks a historic moment for space exploration as SpaceX and NASA announce an unprecedented alliance. The two powerhouse organizations will collaborate on a mission to explore the far reaches of outer space. This mission will be the first of its kind, combining the resources of both SpaceX and NASA to create a unique opportunity for space exploration. With the help of this alliance, we can look forward to many exciting advancements in the field of space exploration.

Scientists have just announced a breakthrough in coffee technology: decaf coffee without caffeine! After years of research, coffee drinkers can now enjoy all the flavors of their favorite cup of joe without any of the associated caffeine. This new decaf coffee is created using a proprietary process that removes all traces of caffeine from the coffee beans, leaving behind only the smooth and delicious flavor. Even better, this new decaf coffee is available at a fraction of the cost of regular coffee.

Astronomers have recently discovered something rather ominous: eleven newly detected planets, orbiting a sun-like star, are doomed. The star, known as TOI-561, is a red giant and is about 60% more massive than our own sun. As the star grows in size, it will eventually envelop the eleven planets, foreshadowing their ultimate destruction. Scientists have theorized that this could be the fate of our own solar system in the distant future.

Microdiversity in species is an important factor for the health of the environment and the ecosystems in which they live, and new research has shown that intraspecific microdiversity plays an important role in the ecology of lactic acid bacteria. A new study has found that intraspecific microdiversity of lactic acid bacteria is driven by ecological factors such as resource competition, environmental conditions, and the interactions between bacterial species. The results suggest that intraspecific microdiversity could play a role in the maintenance of healthy ecosystems and could have implications for the development of new methods for preserving biodiversity.

Scientists have discovered a new species of bacteria that can eat plastic! This new species, Ideonella sakaiensis, has been found to be able to break down the chemical bonds of the most common plastic material, polyethylene terephthalate (PET). This is a remarkable discovery, as PET is a non-biodegradable material that was previously thought to be able to remain in the environment indefinitely. It is estimated that up to 12 million tons of plastic waste are not recycled each year, and this new species of bacteria could provide a solution to this global problem.

In a groundbreaking discovery, archaeologists have uncovered evidence of a great fire that swept through London in 1179. The fire was so intense that it left evidence of its destruction in the form of charred material found deep underground. This is the first time that archaeologists have been able to confirm the existence of a fire of this magnitude in London’s history. The discovery provides an insight into the city’s past and how it has changed over the centuries.

Today, researchers have discovered a new species of ancient lamprey in China that is larger than any other species of lamprey ever found. This new species of lamprey, named Lethenteron zhui, lived during the Middle Triassic, around 243 million years ago. This species of lamprey is an amazing discovery, as it reveals that large lampreys have existed for a significantly longer period of time than previously thought. Lampreys are an ancient species of fish that have been around for more than 360 million years, and Lethenteron zhui is by far the largest species of lamprey ever found.

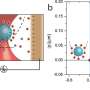
Have you ever heard of a strange magnetic material that could revolutionize the way we use and store energy? Scientists have just developed a new material that could make energy storage and use more efficient than ever before. This material is made up of two different elements, cobalt and manganese, and it is the first of its kind to exhibit a unique type of magnetism. The magnetic properties of this material could be used to create higher energy density storage devices, enabling us to store more energy in a smaller space.

Scientists have developed a new type of processor that promises to revolutionize the way Artificial Intelligence (AI) and gene sequencing is performed. The processor, developed by a team of researchers at the University of Washington, is capable of performing tasks that would normally require a supercomputer, but at a fraction of the cost. This new processor is expected to be used for a variety of applications, including AI, gene sequencing, and even medical imaging.
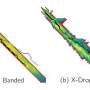
A revolutionary new approach to dissipative solitons has been discovered that could revolutionize the ability to control and manipulate light in photonic systems. This approach is called spatiotemporal mode-locking, and it could potentially enable the manipulation of multiple modes of light in a single optical source. This breakthrough could make it possible to use multiple wavelength sources in a single optical system, opening the door to new applications, including high-speed optical communications, optical sensing, and imaging.

A breakthrough study published in the journal Nature Chemistry has uncovered a new method for predicting drug-protein affinity. This method could potentially revolutionize the development of new drugs by helping to identify which proteins are likely to interact with a given drug.
The method, developed by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, uses machine learning to predict drug-protein affinity from the 3D structure of the drug and the amino acid sequence of the protein.
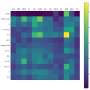
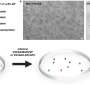
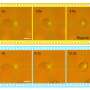
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have used supercomputers and optical tweezers to create a safer method of manipulating tiny particles. This new technique, which uses a combination of high-powered computers and lasers, can manipulate particles with accuracy and precision that was not previously possible. With the help of these technologies, scientists can now manipulate particles that are smaller than a millimeter in size. This new technique will be invaluable in the development of new treatments and technologies in the medical, engineering, and other fields.
Today marks the one-year anniversary of the start of operations for the Vera Rubin Observatory, the first observatory dedicated to interstellar exploration. Named after the pioneering astronomer Vera Rubin, the observatory has made a number of groundbreaking discoveries in its first year, including the discovery of a supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy. By monitoring the sky with unprecedented sensitivity and resolution, the observatory has helped astronomers to better understand the mysteries of the universe and the evolution of galaxies.

In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have discovered that 10 fly species have gained sole access to a previously unknown insect-feeding resource. This new resource, which is found in a specific type of plant, has enabled the flies to outcompete other insect species and become the dominant insect in the area. This discovery is a huge breakthrough for scientists, as it could lead to a better understanding of how species adapt to new resources to gain a competitive advantage.

Scientists have recently announced a breakthrough in superconducting technology - a successful World Wide Strip (WWS) of photon transmission. This new technology will revolutionize our ability to transfer energy, data, and information across vast distances with greater efficiency than ever before. By utilizing a new type of superconducting material, WWS can now transmit photons over distances of up to 10,000 kilometers - more than double the distance of current fiber optic cables.

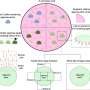
A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of California, Davis has developed a novel method for isolating extracellular vesicles (EVs) from cell cultures using agarose beads. The method uses a combination of size-exclusion chromatography and immunoaffinity chromatography to separate the EVs from other components in the cell culture, allowing for a highly specific and efficient isolation of the EVs. This agarose-based method has the potential to be used for isolating EVs from other sources, such as biofluids, with further research.