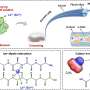
Scientists have recently discovered a way to make silk stronger and tougher than ever before. This incredible breakthrough has been made possible by introducing a rare mutation in silkworms. The mutation causes the silk they produce to be up to twice as strong and five times as tough as regular silk. This could have huge implications for the fashion industry and could lead to revolutionary new materials. Scientists are hopeful that this new silk could be used to create clothing that is comfortable, lightweight, and long-lasting, as well as fabrics that can be used for medical applications.

A recent study conducted by scientists from the University of Washington has identified a new method for studying proteins in ecologically significant moss. By utilizing a combination of genetic engineering and analytical chemistry techniques, the researchers were able to detect levels of proteins in a particular species of moss. This discovery has the potential to open new opportunities for understanding how environmental changes affects the growth and development of moss species.

A study published in Nature Communications has revealed new insight into the evolution of antibiotic resistance in a common intestinal bacterium. This research has implications for the treatment of bacterial infections in humans and could help inform strategies for limiting the spread of antibiotic resistance.
In this groundbreaking study, researchers studied the evolution of antibiotic resistance in the intestinal bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli). By sequencing the entire genome of multiple E.
Today, researchers from the University of Tokyo have made a remarkable discovery regarding the skin of sharks. By studying the structure of shark skin, researchers have found a unique design which could revolutionize medical treatments. The structure of shark skin consists of hundreds of microscopic ridges and grooves which have been found to contain antimicrobial and antifouling properties. This means that the shark’s skin is resistant to bacterial and fungal growth, as well as other organisms found in water.

Recently, scientists have made a breakthrough in graphene research, discovering that a liquid water molecule-based graphene heterogeneous photodetector can be produced. This new device has the potential to revolutionize the field of photodetection due to its ability to detect light with unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity.
The graphene-based photodetector is made up of a graphene sheet and a liquid water molecule layer. By combining these two components, the researchers were able to create a device that can detect light in a much more sensitive and accurate way than traditional photodetectors.

This summer, scientists from around the world made a momentous discovery—one that’s been a million years in the making. In a groundbreaking study, researchers uncovered the remains of a prehistoric, extinct species of dinosaur in the Utah desert. The fossilized remains, named Moros intrepidus, are estimated to be around 80 million years old. This makes the dinosaur one of the oldest species of its kind ever discovered.
The discovery of Moros intrepidus is an incredible accomplishment for the scientific community, and opens up a wealth of knowledge about Earth’s ancient past.

A recent breakthrough in medical science has researchers excited about the potential of a new antimicrobial molecule that could effectively prevent the growth of bacteria in humans. The molecule, called BactoX-3, was discovered by a team of scientists at the University of Texas at Austin and was tested in both laboratory and animal studies. The results of the study showed that BactoX-3 was able to stop the growth of bacteria in both settings, making it a promising new tool for fighting bacterial infections in humans.
A new study has revealed that the famous red supergiant star Betelgeuse is likely to consume a smaller star in the future. This finding was made when researchers used observations from the Hubble Space Telescope and other ground-based telescopes to take an in-depth look at the star. It was discovered that Betelgeuse has an unusual, distorted shape that is likely caused by the presence of a nearby companion star. This companion star is likely to be eventually engulfed by Betelgeuse in a stellar merger, leading to a dramatic increase in the star’s brightness.
Scientists have made an exciting new discovery in the realm of Alzheimer’s disease research. A team of researchers have developed a novel chemical peptide that is remarkably similar to the amyloid plaques present in the brain of Alzheimer’s patients. This peptide has the potential to be used as a drug to treat Alzheimer’s, and could even be used to diagnose the disease early on. This breakthrough could revolutionize the way we treat and diagnose Alzheimer’s, giving hope to those suffering from the disease.

Recently, a study conducted by scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has revealed a class of materials that can reach exceptionally high superconducting critical temperatures. Superconductivity is a phenomenon in which electrons can flow without any resistance, allowing electricity to be conducted with greater efficiency. This new discovery may revolutionize the way we use and store electricity, and could have a profound impact on the way we live.

Today, chemists have made a breakthrough discovery in drug discovery chemistry. This new technology, called “dynamic combinatorial chemistry” (DCC), will enable scientists to rapidly create and screen large libraries of molecules for drug discovery. By utilizing DCC, scientists can now synthesize and screen thousands of small molecules in just a few days. This new technology could revolutionize the way drug discovery is conducted, enabling researchers to create new and more effective drugs in a fraction of the time it used to take.

“Scientists have recently developed a way to create a true to life three-dimensional (3D) image of the thickness of the Earth’s crust. This breakthrough could have wide-reaching implications for geology, seismology, and other Earth sciences.
Using new technologies and data analysis techniques, scientists were able to create a highly accurate 3D image of the Earth’s crust, revealing details such as the thickness of the Earth’s crust in different areas and how it changes over time.

Scientists have just discovered a small celestial body with four legs orbiting a distant star! This is the first time a four-legged celestial body has ever been observed and is a major breakthrough in our understanding of the universe. The body, which is estimated to be only 2km in diameter, was discovered by a team of astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope. The team believes the legs may have been formed by gravitational effect, similar to the formation of rings around planets.
Recently, a team of researchers from the University of Bristol conducted an analysis of ancient fish fossils to explore the evolution of the shoulder joint. The team discovered evidence that the shoulder joint evolved more than 400 million years ago and has remained relatively unchanged since then. This finding provides insight into the evolution of vertebrates and the emergence of land-dwelling animals. The researchers believe that the shoulder joint has been the key to the success of land-dwelling animals, as it allows for greater mobility and stability.

A recent breakthrough in nanoreactor technology could revolutionize the hydrogenation process. Scientists have discovered a way to enrich reactants in nanoreactors, which could open up exciting new possibilities for the hydrogenation process. This means that the time it takes to hydrogenate a molecule could potentially be reduced from hours to mere seconds. This could have far-reaching implications for industrial processes and laboratory experiments. The team is currently working to optimize the nanoreactors to make them even more efficient.
Recent advancements in bioprinting and biofabrication have enabled the fabrication of 3D structures with single-cell resolution. This opens up a world of new possibilities for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. A team of researchers from the University of Tokyo has explored new biofabrication strategies that could make it possible to fabricate complex 3D structures with single-cell resolution. The team has developed a method in which DNA origami structures are used to create 3D scaffolds that can be used to precisely control the position and orientation of cells.

Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery: the Earth is part of a group of galaxies! This group of galaxies, known as a “Local Sheet,” is composed of the Milky Way, the Andromeda galaxy, and dozens of other smaller galaxies. This new discovery, which was recently published in the journal Nature Astronomy, sheds light on how galaxies form and evolve in the universe.
Astronomers have long known that the Milky Way and Andromeda are part of a larger group of galaxies.

In November 2023, the world’s largest and most powerful telescopes will be turned on to examine the aftermath of the Big Bang. This groundbreaking event will mark the beginning of a new era of exploration into the mysteries of the universe. The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) and the Square Kilometer Array (SKA) will bring unprecedented resolution in imaging and data analysis, enabling astronomers to uncover the secrets of the earliest moments of cosmic history.

A team of researchers from the University of Texas has recently reported on their discovery of a new strain of lactic acid bacteria, a type of bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt and cheese. The new strain, named Lactobacillus arizonensis, is the first of its kind to be discovered in a long time and could open up new avenues for food production and preservation. The researchers believe that this new strain could be used to create more flavorful and healthier foods, as well as to help extend the shelf life of certain food products.

A recent study has revealed that plastics floating in rivers can harbor potential pathogens from nearby sewage systems, posing a public health risk. According to the study, plastics in rivers can act as a surface for microorganisms to attach to, allowing them to spread among nearby populations. This could be particularly concerning in areas with poor sanitation, potentially leading to waterborne diseases. Therefore, it is important to consider the environmental impacts of plastic pollution, as it can directly affect the health of those living near the contaminated rivers.

Recently, scientists have discovered a new way to answer some of astronomy’s most pressing questions - gravitational lenses. Gravitational lenses are objects that bend the light of distant stars and galaxies, allowing us to observe them in unprecedented detail. With this new technique, we can study the light from distant stars and galaxies that would otherwise be too faint to see. This allows us to learn more about the formation of stars and galaxies, measure the expansion of the universe, and even search for evidence of dark matter.

A team of researchers have recently announced a breakthrough in simulating electrons in biological nanowires. Using advanced computer simulations, the researchers were able to recreate the behavior of electrons in nanowires and determine how they interact with the nanowire’s molecular structure. This research could lead to a better understanding of the behavior of electrons in living systems, and could potentially help develop more efficient and effective treatments for diseases. These findings could also have implications for the development of nanoscale electronics and sensors.

In a major breakthrough, scientists have discovered a new method of bioprospecting for unknown bacterial enzymes encoded in microbial genomes. By using a combination of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), the team of researchers was able to identify specific bacterial enzymes that can be used in industrial processes such as bioprocessing, biorefining and bioremediation. The new method is expected to revolutionize the bioprospecting industry, allowing researchers to quickly and accurately identify enzymes that have been previously unknown.

We are living in an exciting time for sustainable seafood. A team of researchers from the University of Bay has recently announced plans to begin farming tuna, heralding a new era of sustainability for this beloved animal. The team plans to use a combination of advanced aquaculture techniques and artificial intelligence to create a closed-loop system that will allow tuna to be farmed with minimal environmental impact. This project will be a major step towards ensuring that tuna will remain plentiful and sustainable for generations to come.

A new study has found that sperm can adjust the style of their swimming in response to a fluctuating fluid environment. This finding could have major implications for reproductive biology, as it suggests that sperm may be able to better adapt to their environment. The research, conducted by a team of scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, was recently published in Nature Physics.
Researchers discovered that sperm can adjust their swimming style in response to different levels of fluid viscosity.

