Gravitational lensing is quickly becoming one of the most important tools in astronomy. A new study by scientists at the University of Manchester has shown that gravitational lensing has a significant effect on our understanding of the cosmic structure of the universe. The research team found that gravitational lensing can reveal details of the cosmic web, which can provide insight into the formation and evolution of galaxies. The team’s findings could lead to a better understanding of the universe’s large-scale structure and evolution.

As our global population continues to rise, there’s a growing need to ensure that our food sources are sustainable. Dairy farmers are at the forefront of this effort, and new research is uncovering ways to make their operations more economically viable. The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, found that sustainable dairy farming can be an economically successful endeavor, with the potential to generate higher profits than traditional dairy farming.

The future of energy storage is here! Researchers at the University of Manitoba have developed a new electrolyte for solid-state batteries that could revolutionize the way we store energy. This new electrolyte is based on viscoelastic materials, which have properties that change depending on the temperature and the application of force. This new electrolyte is more stable and longer lasting than other electrolytes currently used in solid-state batteries, and could enable batteries to store more energy in a smaller form factor.

A new centralized pollination portal, the Global Bee Network, is being developed to help protect and monitor the world’s bee populations. The portal, backed by the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), will provide a platform for scientists, beekeepers, farmers, and government agencies to share data on bee populations and pollination services. This unprecedented, global network will create a comprehensive understanding of the state of bee populations and their role in sustaining global food systems.

A new discovery in the field of opto-physical unclonable functions (OPUFs) may revolutionize the world of authentication. Researchers from the University of Michigan have developed a way to create random wrinkles in nanoscale materials that can act as a unique identifier for a device. This could be used to authenticate devices, such as computers or phones, without the need for passwords or biometrics. The team’s findings, published in Nature Communications, demonstrate a new way to create truly random OPUFs that could be used for device authentication.
In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists at the University of Michigan have created a new type of plastic that is stronger, stretchier and self-healing. The new material, known as VPR, is a combination of two existing plastics, one with superior strength and the other with superior elasticity. When these two materials are combined, the result is a plastic that is stronger and more resilient than either of its parents. It is also capable of self-healing when exposed to heat or light, making it a potentially revolutionary material for use in a variety of industries.

NASA has announced that its Lucy spacecraft will be the first to explore a second asteroid in the Trojan family! Lucy is a robotic spacecraft that has been designed to explore 6 asteroid targets, the first of which it is currently orbiting. The second asteroid it will visit is called Eurybates, and is located in the outer asteroid belt. By visiting this second asteroid, Lucy will be able to provide insight into the formation of our Solar System, and the evolution of the environment around the asteroids.

Norway has just taken a big step forward in the world of space exploration, as the country has inaugurated its first satellite site. The new facility, located in the municipality of Andøya, is set to become a major hub for space research and operations. The satellite site will be home to a variety of activities, such as the launch of new satellites, tracking of existing satellites, and the development of new technologies.

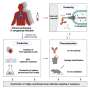
Scientists have recently developed a revolutionary new technology that could revolutionize the way we treat infections. Re-engineered pseudoviruses, which are 3D-printed viruses made from human cells, could allow doctors to target infections with much greater precision, significantly improving the effectiveness of treatments. This new technology could also be used to create personalized treatments for patients, providing them with the most tailored care possible. The potential for 3D-printed pseudoviruses to revolutionize the way we treat infections is exciting and could open up a new world of possibilities for medical treatments.
In recent years, biodiversity has become a major issue in conservation and environmentalism. Scientists are now warning that if we don’t take a radically different approach to biodiversity benefit sharing, we could be heading down a dangerous path.
In a new study, researchers argue that conservation efforts must focus on both the global and local level in order to ensure maximum benefits for the environment, communities, and businesses alike. They say that a new approach to biodiversity benefit sharing should be based on a partnership between governments, civil society organizations, and businesses, rather than relying on a top-down approach.
It’s no secret that microorganisms are immensely important to our lives and ecosystems. Recent research has uncovered a new way to understand their behavior and function: by studying the textbook knowledge that governs their behavior. A new paper published in Cell Reports has identified a set of “textbook” rules that govern the behavior of microorganisms. These rules can be used to predict the behavior of individual microorganisms, as well as their interactions with other species.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have identified a group of antibodies that can effectively combat bacteria that are resistant to traditional antibiotics. These antibodies, which are found naturally in humans, have been found to be effective against multiple bacterial species, including those that cause gonorrhea, cholera, and typhoid. This discovery has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat bacterial infections, as it provides a new, drug-free way to fight the spread of these dangerous illnesses.
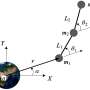
Today, scientists from the Institute of Space Systems announced the successful deployment of a three-body chain type tethered satellite system. This new satellite system was launched from the International Space Station and is the first of its kind. The three-body chain type tethered satellite system consists of three small satellites connected together by tethers. The satellites are connected in a line and rotate around each other, allowing them to survey a much larger area than a single satellite.
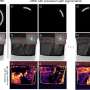
In recent years, scientists have been researching a long-standing problem in Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) – the difficulty of obtaining high resolution images. TEM is an essential tool in material science, allowing researchers to visualize the structure of materials at the atomic level. However, obtaining a high resolution image with TEM is often challenging, as the images are affected by various sources of noise and blurring. By understanding the sources of noise and blurring in TEM, scientists can develop new methods to reduce these effects and improve the resolution of TEM images.
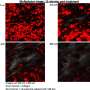
A team of researchers has made a breakthrough in regenerative medicine by developing a stem cell that is capable of growing and regenerating skeletal muscle tissue. This new stem cell, dubbed the “Pax7-expressing stem cell”, was created by introducing Pax7, a gene that is responsible for skeletal muscle growth, into a type of stem cell called a myogenic progenitor cell. The Pax7-expressing stem cell was then able to differentiate into skeletal muscle cells that are capable of generating new muscle fibers and repairing damaged muscle tissue.

A new image of a high-power electric thruster has been released, and it is an exciting glimpse into a new era of space exploration. This image shows the thruster, which is a key part of the Qualification Gateway, a testing platform that will help to ensure that high-power electric thrusters are ready for use in space missions. The Qualification Gateway is an important step towards the development of powerful electric thrusters, which will open up new possibilities for space exploration.

Scientists have made a remarkable discovery: the first ever virus found in a fossil. The fossilized virus, estimated to be around 30,000 years old, was discovered in a piece of Siberian permafrost. This is a significant breakthrough in the field of virus research, as it provides the first ever physical evidence of a virus’s existence beyond the present day. Scientists are now hopeful that this discovery could shed light on the evolution of viruses over time.

The night sky of the East Coast of the United States is about to get a whole lot brighter, thanks to a new image of the night sky. A team of researchers from the University of Maryland have created the first ever detailed image of the night sky from the East Coast, using data collected from dozens of observatories and satellites. The image reveals thousands of galaxies, stars, and other celestial objects in stunning detail, giving us an unprecedented view of our night sky.

A new breakthrough in medical science has been discovered that could revolutionize the treatment of autoimmune skin diseases. Scientists have discovered a new compound called ‘Bliss’ that, when taken orally, has been able to reduce the symptoms associated with autoimmune skin disorders such as psoriasis, eczema and alopecia. This compound works by targeting the body’s immune system and helping to regulate it, allowing it to better manage the symptoms of these disorders.
Turkish astronomers have recently made a remarkable discovery in our night sky! A new open star cluster, called Collinder 406, has been identified in the constellation of Auriga. This is only the second open star cluster to be discovered by Turkish astronomers.
Collinder 406 is a sparsely populated cluster located about 6,000 light-years away from our home planet. It contains around 50 stars, the brightest of which are yellow-white supergiants. These stars are incredibly luminous, and are estimated to be between 10 to 20 million years old.

A new way to track near-Earth cosmic explosions has been developed by a team of international researchers. The technique, known as “all-sky imaging”, is capable of detecting and tracking the origin of gamma-ray bursts, a type of powerful explosion that can be caused by the collision of two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole. The new method could help scientists better understand the nature of these explosive events and their effects on the universe.

Scientists have recently discovered a new mechanism that bacteria use to uptake vitamin B12. This is exciting news, as it could lead to a better understanding of how bacteria interact with their environment and could potentially lead to new treatments for bacterial infections. The mechanism discovered is an active-transport system, which uses energy to move molecules across a membrane. The transport system is composed of two proteins, BtuB and BtuF, which form a channel on the cell membrane.
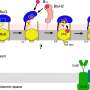
A groundbreaking discovery has been made! Scientists have found a new gene in mice which determines the sex of unborn pups. This is the first time that this gene has been identified in a mammal, and the implications for human sex determination are huge. The research team hopes that this discovery will open up a better understanding of how sex is determined in humans. With this knowledge, scientists can develop new treatments for sex-specific diseases.

A recent study has revealed a completely new way of using DNA to create materials that behave like quasicrystals. Scientists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have created a type of colloidal quasicrystal, made up of modified DNA blocks, that can be used to form novel materials with unique properties. This is a groundbreaking development in the field of materials science and provides an alternative to traditional methods of forming quasicrystals.

Researchers have recently made a breakthrough in supramolecular upconversion, a process in which light of a low frequency is converted to a higher frequency. This breakthrough involved the synthesis of a new multimer, which is a complex system composed of multiple components. This multimer contains a combination of lanthanide and organic components, which work together to increase the efficiency of the upconversion process. The results of this research could lead to applications such as solar energy conversion and biomedical imaging.