
A new approach to combatting Lyme disease is on the horizon. A team of researchers at the University of California San Diego (UCSD) have developed a novel antibiotic drug candidate that could provide a more effective treatment for the disease. The drug candidate, known as LP30, works by targeting a critical enzyme in the Lyme bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi, which helps it to survive. In laboratory studies, the drug was found to be up to 90 percent effective in killing the Lyme bacterium.

Astronomers have recently made a breakthrough in understanding how supermassive black holes impact the evolution of their host galaxies. By studying the “feedback” from active supermassive black holes, they were able to observe how the energy released from matter falling into the black hole impacts the surrounding gas, affecting the buildup of stars in the host galaxies. This research could provide the missing link between the growth of supermassive black holes and the evolution of their host galaxies.

Craft beer lovers rejoice! A new study has found that sorghum-based beers can be easier to brew than traditional gluten-containing beers, making them a great alternative for those with a gluten-intolerance. Not only are these beers gluten-free, they are also said to have a unique flavour due to the different types of sorghum and enzymes used. Researchers from the University of Pretoria in South Africa have been studying the brewing of sorghum-based beers and have found that the process can be much simpler than traditional beer brewing methods.
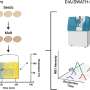
Scientists have recently made a breakthrough in imaging technology that will revolutionize our ability to observe and measure the behavior of individual atoms and molecules. Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have developed a powerful new technique that allows them to capture high-resolution images of magnesium ions in real-time. This new technique could be used to investigate a wide range of scientific applications, from medical imaging to nanoscale engineering. The technique works by using a laser to trap and cool individual magnesium ions, then using a high-resolution imaging system to image and measure their motion.

The world’s coral reefs are facing unprecedented levels of stress due to climate change, with one of the most pressing problems being hypoxia. Hypoxia is a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the water, and it can be harmful to the corals. Now, a new study has found that the coral microbiome shifts in response to hypoxia, and this could be key to helping corals survive in a changing environment.

Today, a research team has announced the creation of the world’s first curated knowledgebase of biomarkers for animals. This new online resource, which is free to the public, provides a comprehensive collection of data on animal biomarkers, making it easier for researchers, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders to identify and study the biological markers of animals. The knowledgebase includes data on the biomarkers of more than 80 species of animals, including mammals, reptiles, and fish.

The future of microchip sensors just got a lot brighter. Scientists have developed an ultra-strong material that combines the strength of graphene and the flexibility of rubber, making it ideal for use in microchip sensors. This new material, called rubber-graphene, is said to be 10 times stronger than steel and 100 times more electrically conductive than copper. With its remarkable properties, rubber-graphene could revolutionize microchip sensors and pave the way for a new era of sensor technology.

Chatbots are becoming increasingly popular as a way to interact with customers in the digital space. However, there have been some concerns that chatbots are replacing human customer service agents, leading to a decrease in customer satisfaction.
In this article, we will examine the pros and cons of chatbots in customer service, as well as why it’s important to remember that chatbots should not be blamed for any customer dissatisfaction.

One of the essential skills for engaged citizens in the 21st century is a strong foundation of mathematical knowledge. Mathematics is the language of science and technology, and it is increasingly present in everyday life. From understanding the news to participating in decisions that affect our local communities, a basic understanding of mathematics is essential for engaged citizens. According to recent studies, there are five critical mathematical skills that citizens should be familiar with in order to fully participate in civic life.

The reproductive process is a complex and delicate one, and understanding its nuances can be challenging. However, advances in imaging technology have recently made it possible to gain unprecedented insights into reproduction. Scientists have developed a new imaging technique that can observe interactions on a cellular level and generate 3D images of reproductive processes. This technology is expected to revolutionize the field of reproductive biology, providing an unprecedented level of detail and allowing researchers to gain valuable insights into how reproduction works.
In a new study, scientists from the University of California, Davis, have uncovered a chaotic behavior in the way scientists barter for resources. This behavior could have implications for the future of scientific collaboration and resource sharing. The researchers found that when scientists barter for resources, the amount of resources exchanged becomes unpredictable and highly variable. This could lead to an inefficient use of resources, as scientists could end up trading away valuable resources for items of lesser value.

Recently, scientists have uncovered a collapsed lava chamber on Mars. This remarkable discovery gives insight into the planet’s geological history and could provide clues to the formation of the Red Planet. This collapsed chamber was created when magma drained from its original chamber, leaving behind an empty void. This empty space is now filled with debris from the surface, which has been preserved for billions of years. The findings of this study provide new evidence for the volcanic activity in the Martian past and could help us to better understand the formation of the Martian landscape.

A new study has revealed major advances in the field of fungal infection research. Scientists at the University of California, Davis have developed a novel imaging tool to visualize deep-seated fungal infections in living hosts. This breakthrough could lead to a better understanding of how fungal infections cause disease, and how they can be treated more effectively.
This new imaging tool is based on a combination of two imaging technologies: optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescent confocal microscopy (FCM).
In a recent study, scientists have discussed the differences between male and female brains that have evolved over time. This study outlines the differences in the ways men and women think, and how these differences have been heavily influenced by evolution. Men and women are wired differently, and this study looked into the underlying neuroscience behind this. Dr. Jack Lewis, the lead researcher, states that “evolution has shaped the brains of men and women to think differently in order to maximize reproduction, and this has affected the way they interact with the world”.

Recently, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been making waves in the education sector. AI is now being used to enhance the learning experience in many classrooms around the world. AI is being used to provide more personalized instruction, tailor content to student needs, and even grade assignments. As AI continues to become more prevalent in classrooms, its impact on history education is becoming more evident.
AI can help history teachers to provide more personalized instruction to their students.

A new study conducted by researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder has revealed some interesting findings about the effect of cold temperatures on different genetically diverse varieties of plants. The study, which was published in the journal Nature Communications, found that different varieties of the same plant species respond differently to cold temperatures. The researchers conducted the study by exposing various varieties of Arabidopsis thaliana (a species of mustard plant) to cold temperatures.

In a recent study, scientists have discovered a new environmental hazard that can affect epigenetics in cells. Epigenetics is the study of chemical modifications to DNA that can change the way genes are expressed without changing the underlying DNA sequence. The environmental hazard in question is a by-product of the manufacturing of polymers, called polypropylenedinitrile (PPND). It’s been found that PPND can cause epigenetic changes to cells. This means that even if a person is exposed to low levels of PPND, their cells could be affected by it.
Recently, scientists have uncovered exciting new findings about the molecular mechanisms underlying lipid recycling. Lipids—molecules that include fats, oils, and waxes—are an important part of our body’s metabolism and are essential for the regulation of metabolic processes. By understanding the mechanisms of lipid recycling, scientists are hoping to gain insight into how the body regulates the metabolism of lipids and how diseases like obesity and metabolic syndrome can be better managed.

Today, scientists have unveiled a new form of matter: a two-dimensional quantum superfluid. Researchers at the University of Rochester have created a superfluid composed of electrons, dubbed a “2D quantum superfluid”. This new state of matter has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of how electrons interact in two-dimensional materials.
This 2D quantum superfluid was created by researchers at the University of Rochester, who used lasers to cool a thin layer of electrons until they reached temperatures of just a few millionths of a degree above absolute zero.

A recent study published in the journal Nature Astronomy has found that planets orbiting white dwarf stars could potentially be habitable. White dwarf stars are the remnants of Sun-like stars that have used up all of their nuclear fuel and collapsed. While these stars are much dimmer than their predecessors, the study suggests that planets orbiting white dwarf stars could still be habitable. Due to their low luminosity, these planets can exist in closer orbits than those orbiting Sun-like stars, leading to shorter orbital periods and higher chances of habitability.

For centuries, the rhinoceros has been one of the most iconic animals on the planet. Now, a recent study has revealed new information about these majestic creatures, thanks to the discovery of two fossilized skulls dating back to the Pleistocene era. The findings of this study suggest that the rhinos we know today are largely unchanged from their ancient ancestors, and that they have survived in remarkably similar form for the last two million years.

Recent research has uncovered compounds and molecules that are involved in the processes of cannabis. Scientists are now one step closer to understanding the complex plant and what it can do for human health. With the help of sophisticated new techniques, they have identified more than 400 compounds, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. These compounds work together to produce the effects associated with cannabis use, from calming and pain relief to enhanced creativity.

A recent breakthrough in science promises to revolutionize the way we measure and monitor substances in our environment. Researchers have developed a self-powered microbial fuel cell (MFC) biosensor that can detect and measure biological and chemical substances. This device is powered by the microorganisms themselves, and can be used to detect substances such as heavy metals and antibiotics in water. The MFC biosensor is a great advancement in environmental monitoring, as it is cost-effective and requires no additional power source.

Recent research has found that the use of nanoparticles in the treatment of tumors could be a breakthrough in treating one of the most deadly forms of cancer: brain tumors. In a study conducted by scientists at the University of California, Irvine, they used nanoparticles to deliver cancer-fighting drugs directly to the tumor site. The study found that the nanoparticles were able to successfully penetrate the tumor and deliver the drugs to the tumor cells, leading to a significant reduction in tumor size.
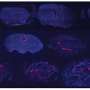
The search for patterns in Mars’ clouds has just been made easier, thanks to a team of citizen scientists. By using the Zooniverse platform, the team was able to enlist the help of over 4,000 volunteers to classify the patterns in images of Mars’ clouds. The results of their work have revealed new information about the nature of these clouds and how they may be changing over time. This research has the potential to provide valuable insight into the climate and weather patterns of Mars.

