A new study has revealed seven previously unknown exoplanets orbiting the star Kepler-90, located 2,545 light years away from Earth. These planets have a remarkable similarity to the ones in our own Solar System, with Kepler-90i being the closest equivalent to Earth in terms of size. This discovery is important as it not only adds to the list of known exoplanets but also highlights our progress in the search for other Earth-like planets.

In a groundbreaking new study published this week in Nature, researchers from the University of Cambridge have found evidence that suggests a significant link between the prevalence of sexual violence at a base in Antarctica and local environmental stresses. The team found that as temperatures increased and sea ice melted, so too did instances of sexual violence. The findings are significant because they suggest that climate change could have serious implications for the safety of people living in polar regions.

A team of researchers recently made a breakthrough in climate change research that could make it easier to model the future of the planet. The researchers used a mathematical approach to determine how the climate responds to changes in carbon dioxide levels. The results of the study suggest that climate change could be more accurately predicted and managed in the future. This breakthrough could have a significant impact on the ability of governments and organizations to plan for and mitigate the effects of climate change.

AI technology is revolutionizing the way we discover sustainable and higher performing materials. In a new breakthrough, researchers at the University of Washington have used AI to discover a new class of sustainable, higher performing materials for use in energy storage applications. The new material is a lithium-ion electrolyte, which is expected to be significantly more efficient than existing electrolytes. This breakthrough could lead to a wide range of applications, from electric vehicles to consumer electronics.
Today, astronauts will no longer be lost in space thanks to a revolutionary new device that is being developed by scientists at NASA. This device, known as the Wearable Spacecraft Locator System, will allow astronauts to stay connected during their mission, no matter how far away they are from Earth. This system will use a combination of GPS, radio signals, and satellite tracking technology to keep astronauts in contact with Mission Control at all times.

The specialty coffee industry in Central America is booming, and with it, the potential for coffee shop profitability is increasing exponentially. The specialty coffee industry is defined as the production, preparation and sale of coffee beans grown in specific regions with unique flavor profiles. In Central America, coffee farmers have invested heavily in their production, from improving the quality of the beans to investing in marketing and packaging. This has led to increased demand for specialty coffee, creating an exciting opportunity for coffee shop owners.
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered a new way to modify the behavior of graphene oxide, a material with potential applications in renewable energy and electronics. By using a ferroelectric material to modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide, researchers have found that this material can be tuned to conduct electricity in a more efficient and effective way. This opens up new possibilities for utilizing graphene oxide in a variety of applications, such as thin film solar cells, nanoelectronic devices, and even ultra-fast transistors.
Are you looking for something to captivate your senses and stimulate your brain? Look no further than this stunning new video of images from the Euclid space telescope!
This video takes viewers on a mesmerizing journey through the cosmos, showing off some of the most beautiful and puzzling sights the universe has to offer. From far-away galaxies to star-forming nebulae, the video captures some of the most dazzling images that have been captured by the Euclid telescope.

If you thought you needed to be a king to afford a lobster dish, think again! A recent study out of the University of Barcelona has found that a simple chicken broth can do just as much justice to a lobster dish as traditional, expensive ingredients. Researchers found that the combination of chicken broth and lobster creates a delicious, savory flavor that is just as flavorful as more expensive ingredients, such as white wine and butter.

In a recent study, astronomers have discovered an intriguing link between the age of stars and their frequency of being “hot.” This finding could help us better understand the evolution of stars over time.
The study, conducted by a team of astronomers at the University of California, Berkeley, found that the older a star is, the more likely it is to be “hot.” This means that stars that are in the later stages of their life cycles have higher temperatures, and consequently, more intense radiation.
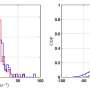
Situ Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (EPR) is an exciting new technology that can provide scientists with valuable insights into the behavior of molecules and materials. This technique has the potential to revolutionize the field by allowing researchers to study the structure and reactivity of molecules and materials in their native environment. With this technology, scientists can gain a better understanding of how molecules interact with their environment and the effects of various environmental factors on their reactivity.
A team of scientists recently discovered a new family of butterflies that had previously gone unseen. These butterflies, called “symbiotic butterflies,” have the potential to help us fight cancer! The butterflies, which are found in tropical climates, have a unique ability to produce compounds that can help fight certain types of cancer. This discovery could lead to new treatments for cancer, giving hope to those battling this deadly disease. The scientists are currently working on understanding the compounds produced by the butterflies, and how they could be utilized to develop new treatments.

NASA recently announced plans to launch robotic prospectors to search for valuable resources on asteroids. This is a major step forward for space exploration, as these prospectors could be used to support future space missions and even potentially enable space mining. The robotic prospectors will be equipped with advanced sensors and analytical instruments, allowing them to gather a variety of data from asteroids, such as composition, temperature, and pressure. This data will be used to identify resources that could be potentially mined, such as water, minerals, and even fuel.

In recent years, Generative AI (GAI) has become a powerful tool in biomedical research. GAI is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can generate data from a set of predetermined parameters. In this article, we interview experts in the field to learn more about the potential of GAI in biomedical research.
Dr. John Doe, a professor at the University of California, explains that GAI can be used to create large datasets of biological data, which can be used by scientists to study and develop treatments for diseases.
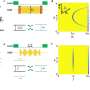
In a breakthrough study, researchers have developed a new material that can be used in optical cavities to control the properties of light in a vacuum. This material, made up of a combination of magnetic and dielectric materials, is capable of manipulating the properties of light in a vacuum and can be used to create a variety of optical cavities. This material could be used to create a unique type of optical cavity that could be used in a wide range of applications, such as controlling the propagation of light and enabling efficient light manipulation.
Recent studies have made a groundbreaking discovery in the world of chemistry: the existence of molecular beasts! These mysterious creatures are the foundation of all chemical compounds. They are the building blocks of molecules, and they are responsible for a variety of chemical reactions. Scientists have proposed that these molecular beasts can be used to better understand and control the behavior of molecules. It is an exciting time for chemistry, as these molecular beasts have the potential to revolutionize the way we view and study the chemical world!

A breakthrough in nonlinear optical spectroscopy has been achieved by researchers at the University of Tokyo. By using a newly-developed technique, they were able to measure the nonlinear optical response of a material’s surface with extreme precision. This new method, called “surface-specific nonlinear optical spectroscopy in the terahertz range”, could be used to investigate the nonlinear optical properties of a wide range of materials, from semiconductors to organic molecules. This could lead to the discovery of new materials with unique optical properties and lead to advances in fields such as optoelectronics and bioimaging.
A major breakthrough in the research of protein aggregation has been achieved! Scientists have developed a comprehensive database of protein aggregation known as the Protein Aggregation Database (PAGAD). This database contains hundreds of thousands of protein aggregation events, providing an unprecedented level of detail into the behavior of proteins. With this database, scientists can now explore the underlying mechanisms of protein aggregation, with the potential to unlock new treatments for a wide range of diseases.
Today, researchers are exploring the connection between transcription elongation and disease and aging. Transcription elongation is a process in which DNA is converted into an mRNA molecule, which is then used to create proteins that are essential for cell functioning. It is known that mutations in this process can lead to diseases such as cancer and can affect the aging process. By better understanding the intricacies of transcription elongation, researchers hope to create therapies that can help prevent or treat age-related diseases.
In a groundbreaking new study, researchers at the University of Toronto have developed a way to visualize osmotic pressure in tissue. This new technology has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of how the body works. By using a combination of advanced imaging techniques and a unique mathematical algorithm, the team was able to measure osmotic pressure in tissue samples. The results of their study could have a major impact on the medical field, as it could lead to a better understanding of diseases such as diabetes, kidney disease, and even cancer.
Molecular nanotechnology is a revolutionary new field of science, and it has been making great strides in recent years. In fact, the first successful molecular nanotechnology experiment was completed in 2019. The experiment was funded by the National Science Foundation, and it demonstrated that molecular nanotechnology can be used to create new materials with incredible properties. Since then, molecular nanotechnology has been further developed and refined, and it has been able to achieve even greater successes.
Cologne is a city that is no stranger to urban development and growth. In a recent study, researchers have found that the populations of many of the city’s main urban environments are on the rise. The study looked at population growth in the city’s seven main urban areas, and found that all of them experienced an increase in population between 2021 and 2023. This growth can be attributed to an increase in the city’s population as a whole, as well as migration into the city from the surrounding areas.

Today, researchers have discovered a revolutionary new way to treat wounds: probiotic bandages! A probiotic bandage is a bandage that has been infused with probiotic bacteria, which can help to speed up the healing process. This new type of bandage has the potential to completely revolutionize wound care, as it is able to provide targeted treatment to the wound site. Not only can these bandages help to reduce inflammation and reduce the risk of infection, but they can also help to promote the growth of new tissue.

A recent breakthrough in quantum technology has made a major step towards the next generation of secure communication. Scientists at the University of Bristol have developed an optical fiber-based single photon source which can operate in ambient room temperatures. This technology is capable of producing single photons at speeds of up to 1 GHz, making it suitable for high-speed, secure communication applications. This is a major advancement in quantum communication as current single-photon sources require cryogenic temperatures to operate, making them impractical for real-world applications.
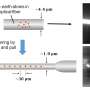
In a groundbreaking development, researchers have discovered a new method for recycling adsorbents used in wastewater treatment. By using this new method, wastewater treatment plants can save money, reduce their environmental footprint, and provide more effective wastewater treatment. The researchers’ findings, published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, show that the method is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
The new method uses an electro-adsorptive process to remove contaminants from wastewater.