
Scientists have recently revealed the existence of a new type of wireless organism, dubbed the “Wireless Worm.” This remarkable creature is essentially a living being that is capable of communicating without the need for traditional wires, cables, or other forms of wired connection. The Wireless Worm has a unique nervous system that is capable of sending and receiving signals over long-distance wireless networks. This allows them to communicate with other organisms and to respond to their environment.

Today, scientists have announced a major breakthrough in the fight against bird flu. For years, poultry have been at risk of contracting the highly contagious H5N1 virus, but now researchers have identified a gene in chickens that makes them immune to bird flu. This discovery could pave the way for a future where bird flu is eradicated altogether. Scientists have developed a gene-editing technique that can be used to insert the immunity gene into chickens, creating a population of birds that are 100% resistant to the virus.

The search for exoplanets in our universe has been a long and arduous journey, but a recent breakthrough has opened up a whole new realm of possibilities. Scientists have recently discovered that the Kepler Space Telescope, which has been in operation since 2009, has identified over 3,000 planets orbiting distant stars. This is a dramatic increase from the previously known tally of 1,337.
This discovery is monumental as it marks the first time a single telescope has been able to detect so many planets in one go.

NASA has announced a groundbreaking mission to send a spacecraft to a tiny moon orbiting a distant asteroid. The mission, dubbed “Lucy,” will explore a unique region of our Solar System that has never before been visited. The mission is set to launch in October of 2023 and will arrive at its destination in May of 2025.
NASA’s Lucy mission is set to be a historic exploration of our solar system.

NASA’s ambitious plans to build a new space center, named “Endeavour,” have recently been announced. Endeavour is set to be built on the surface of the moon and will serve as a science and research center. It is estimated that over the next ten years, the center will be equipped with more than a ton of rockets, robots, and other tools that will help astronauts explore the moon’s surface. Scientists will be able to conduct experiments and research on the moon, such as looking for signs of life and studying the geological features of the lunar surface.

In a stunning discovery, scientists have recently found evidence of a possible human presence on the asteroid 16 Psyche. By analyzing images taken by the spacecraft Dawn, researchers noticed what appears to be a large structure shaped like a human face. The discovery has left scientists wondering if this could be evidence of an artificial structure, hinting at a potential alien species or even a long-lost human civilization. The structure, dubbed “The Capital Selfie”, is estimated to be around one mile across and appears to have been carved into the surface of the asteroid – an astonishing feat.

Recently, scientists have made a shocking discovery that could change our understanding of the Earth. They’ve discovered huge blobs of material deep in the Earth’s mantle, about 660 miles below the surface, that are completely different from the surrounding rocks. This material, which has been named “ultra-low velocity zones,” could be up to 10 times more viscous than the surrounding rocks and may even contain unknown elements. This discovery could shed light on the Earth’s formation and evolution, as well as potentially provide new insights into the planet’s composition and behavior.

It’s been almost a century since the first humans landed on the moon, but the scientific community is still abuzz with excitement. Recently, the American Astronomical Society made headlines when they announced the Saturday Citations for Moon Rat Whimsy, an award recognizing scientists who have made significant contributions to the study of moon rats.
The Saturday Citations for Moon Rat Whimsy are awarded each year to five scientists who have conducted groundbreaking research on the behavior and biology of moon rats.

A recent study has revealed that sea urchins are becoming increasingly more of a problem in coastal waters around the world. The study, conducted by a team of researchers from the University of California, Santa Barbara, found that sea urchin populations are rapidly growing and negatively impacting corals and other sea life. The research suggests that the increase of sea urchin populations is due to warming ocean temperatures, overfishing, and harmful algal blooms.

Scientists have recently discovered a new type of material that could revolutionize the way we create energy. The material, called a perovskite nanocomposite, is a plate-based material made out of nanoscale particles. Scientists believe this material could be used to create solar cells, wind turbines, and other forms of renewable energy. The material is composed of multiple layers of different materials, which allows it to capture and store energy more efficiently than traditional materials.
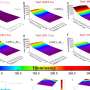
A new research has found that strong noise can be beneficial to the performance of silicon-based quantum computers. The team of researchers from the University of Cambridge and the University of Bristol have discovered that, despite the fact that noise is usually seen as an enemy to quantum computing, it can actually be used to improve the performance of qubits. The team found that, by introducing strong noise to silicon-based qubits, the qubits could perform better than normal.
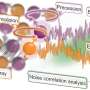
Today, a research team from the University of Toronto has revealed a new approach to electrolysis, a process used to produce green hydrogen. The new method uses a combination of a nickel-iron alloy and a special electrolyte to create a more efficient and cost-effective way to generate hydrogen. This breakthrough could be a game-changer for the renewable energy industry, as it could provide a cleaner, cheaper, and more efficient way to generate energy.
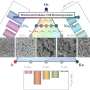
The European Space Agency (ESA) is getting ready to launch one of its most ambitious missions yet: the Hera mission. This mission will use two CubeSats to explore the interior of a near-Earth asteroid, and to demonstrate the feasibility of asteroid deflection. This mission is not only exciting for scientists, but for space enthusiasts as well - it will be the first time a CubeSat has been used to explore a space object!

The Hubble Space Telescope has recently provided us with a unique look at our solar system’s largest planet, Jupiter. Using its ultraviolet capabilities, Hubble was able to capture stunning images of the planet’s colorful clouds, revealing subtle details that can’t be seen in visible light. The images show a variety of bands of clouds swirling in Jupiter’s turbulent atmosphere, and the bright and dark clouds of the Great Red Spot. Hubble also provided scientists with a close-up view of the auroras near Jupiter’s poles, showing the intricate structure of the planet’s magnetic field.

Recent developments in machine learning have led to the creation of a new tool, the Deep Variational Autoencoder (DVAE), which could revolutionize the field of proteomics. The DVAE is a deep learning algorithm that uses a type of artificial neural network to analyze mass spectrometry data. This data is used to identify and quantify proteins in biological samples, and the DVAE can do this faster and more accurately than ever before.
In this article, we speak with Professor Rani Saxena, a renowned expert in cell and developmental biology to discuss the future of this field.
Professor Saxena states that, “Cell and developmental biology is an incredibly dynamic field, with new discoveries and applications coming out every day. We are on the cusp of a revolution in this area, and I am excited to see where it will take us in the future.

The future of space exploration is looking brighter than ever. In November 2023, a major milestone will be achieved in the world of space science as robotic helpers will be sent into space to assist astronauts and scientists alike. These robots will be able to perform a variety of tasks, such as data collection, repair work, and assisting with various experiments. Not only will this allow astronauts to focus on more complex tasks, but it will also open up a world of possibilities for scientists in the field of space exploration.

Astronomers have recently made a remarkable discovery in the depths of space: a supernova remnant with an incredibly rare set of properties. Named 1E 0102.2-7219, this supernova remnant is located in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. What makes this supernova remnant so unique is that it consists of two distinct components: a central core, and an outer shell. The outer shell is made up of a mixture of oxygen, neon, magnesium, and silicon, while the core is composed of almost entirely oxygen, with a few traces of magnesium and silicon.
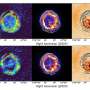
We are entering a new era of scientific exploration with the introduction of the High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program, or HAARP. This innovative project is set to use radio waves to create artificial airglow in the sky, and could be visible across the entire planet. This will allow scientists to study the effects of the atmosphere on radio waves, as well as the effects of radio waves on the atmosphere.

Farmers in Ohio are ushering in a new era of cattle farming with the introduction of an exotic breed of cattle! The breed, called “American Wagyu,” is a hybrid of Japanese Wagyu and American Angus cattle. While the Japanese Wagyu cattle are renowned for their marbled beef, the American Wagyu hybrid combines this marbling with the hardiness of Angus cattle. Farmers are hoping that this new breed will produce a high-quality beef that is both flavorful and economical.

Recent technological advances have enabled the creation of a new type of device that has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with our environment - liquid crystal spatial modulators! These devices are able to manipulate light in a way that has never been seen before, allowing us to control the direction and intensity of light. This can be used for a variety of purposes, including medical imaging, projection mapping, and holographic displays.

NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center has developed a revolutionary new antenna chamber that allows them to test antennas in a much more efficient and accurate way than before. This spiky antenna chamber, as it’s been dubbed, is something of a game changer in the world of antenna testing. Instead of having to use a traditional anechoic chamber, something that blocks out all external noise, the spiky antenna chamber actually amplifies signals coming in from the outside.

Chemists have developed a new sensor that is capable of measuring pH in a microvolume of liquid with unprecedented accuracy. The new sensor is a solid-state device that works at the nanoscale and can measure pH in a liquid sample as small as 10 picoliters with an accuracy of +/- 0.01 pH units. This is a major advancement for researchers who study samples that are too small for traditional pH sensors.
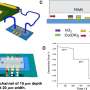
Recently, physicists have developed a new particle collider that promises to make the process of gathering data from particle collisions more energy efficient. This new particle collider uses a combination of magnets and electric fields to accelerate particles to higher speeds faster than ever before. This means that scientists are able to gather more data in less time and with less energy than ever before. This new technology is an important step forward in the world of particle physics and could lead to major breakthroughs in the field.

It is with great sadness that we report the passing of Apollo Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II. Mattingly was a pioneer in the field of space exploration, having served as the Command Module Pilot on the Apollo 16 mission in 1972. During the mission, Mattingly and fellow astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke, Jr. explored the lunar surface, conducted various scientific experiments, and achieved many firsts in space exploration.

