
Scientists have created an online archive that contains images of phenotypic traits, such as anatomical structures, behaviors, and environmental conditions. The images are collected from thousands of sources across the internet and compiled into a single database, making it easier for researchers to find and study the traits of different species. The archive is a valuable resource for understanding the evolution of different species, as it allows researchers to easily compare traits from different generations and even different species.

Today marks an incredible milestone for the space and astronomy community - the launch of the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope! Named after the renowned astronomer, Nancy Grace Roman, this telescope will provide us with unprecedented and unparalleled views of our universe. With its high resolution and sharp images, the telescope will allow us to observe distant galaxies, study the mysterious dark matter, and explore the early universe in order to better understand our cosmic origins.
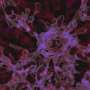
Scientists have made an exciting breakthrough in the field of materials science: they have discovered a magnetically-driven form of Weyl semimetal, a material that could revolutionize technology. This new form of Weyl semimetal has the potential to be used in a wide range of applications, from electronics to quantum computing. The discovery was made by a team of researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara, who used an advanced electron microscope to study the material’s properties.
A recent discovery by an international team of scientists has revealed that complex life on Earth may have existed hundreds of millions of years earlier than previously thought. The team has identified microfossils that date back 3.2 billion years ago, making them the oldest complex life forms ever discovered. These microfossils, which are believed to be related to modern-day single-celled bacteria, could help rewrite the history of how life on Earth evolved.

3D printing is revolutionizing the way we produce physical objects. It has allowed us to create products with unprecedented precision, at a fraction of the cost of traditional manufacturing methods. Now, a new technique developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge has made 3D printing even more accurate, and significantly cheaper.
The new technique, which the researchers have dubbed ‘error-compensation 3D printing’, uses a combination of computer vision and machine learning to identify and correct errors in the printing process before they become a problem.

As environmental concerns become increasingly more urgent, researchers are looking for innovative ways to reduce the impact of single-use packaging. A recent breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize food packaging: formable cellulose-based films. This new material can be easily molded into a variety of shapes and sizes, making it an ideal replacement for traditional plastic materials. The cellulose-based films are also biodegradable, meaning that they can be broken down naturally without harming the environment.

Scientists have recently made a remarkable breakthrough in the search for exoplanets. A research team from the University of Melbourne has successfully detected the presence of ammonia on a distant exoplanet. This is a major milestone for the field of astronomy, as it is the first time a gas other than water vapor has been detected on an exoplanet outside of our solar system. The team used a combination of ground-based and space-based telescopes to observe the exoplanet and measure the amount of ammonia present in its atmosphere.

The Euclid mission, launched by the European Space Agency in 2022, is set to revolutionize the field of fundamental physics. Through its powerful imaging capabilities, Euclid will be able to take unprecedented images of some of the most mysterious and distant objects in the universe, such as dark matter, dark energy, and exoplanets. These images will provide insight into some of the most fundamental questions of the universe, and help us better understand the nature of our universe.

In a fascinating new study, researchers have found that geologic faulting on icy moons can help replenish their water supply. This process is known as “cryovolcanic migration,” and it occurs when the moon’s icy surface is fractured by tectonic activity, leading to the release of water-rich material from the moon’s interior. The water-rich material then migrates to the surface, where it can be released in the form of cryovolcanic eruptions. This process could provide a source of water for the icy moons of the outer solar system, making them more habitable for future exploration.

The COVID-19 pandemic is having a long-lasting impact on college towns across the United States. As universities shift to online learning, many college towns are feeling the ripple effects of decreased student populations. Now, some experts are predicting that the pandemic could permanently change the landscape of college towns.
The virus has caused a significant drop in student enrollment at many universities, resulting in fewer students living in college towns. This is causing a decrease in economic activity and an increase in vacancies in rental housing and commercial real estate.

Winter can be a difficult season for many people, with icy roads and extreme temperatures. However, a new study has found that a kind of salt can make a huge difference on roads in the winter. Researchers from the University of Minnesota have discovered that using a specific type of salt on roads during winter can reduce fatalities and injuries from car accidents by up to 40%. This new salt, called “magnesium chloride,” is a cost-effective way for road agencies to make roads safer during the winter months.

The Bleu Royal Diamond, discovered in the Minas Gerais region of Brazil, is the world’s largest blue diamond ever discovered. Weighing in at an impressive 7.3 carats, the Bleu Royal Diamond is sure to cause a stir among the diamond industry. The Bleu Royal Diamond is also the first diamond of its size and quality to be discovered in the region, making it a very special find. The diamond is set to be auctioned off in November 2023, and experts predict that it will fetch a very high price due to its rarity and beauty.

Raising healthy beef calves is essential for the success of any cattle operation. A new study has found that supplementing calves with colostrum in the first few days of life is key for improving their overall health and growth. Colostrum, also known as first milk, is the pre-milk produced by cows during the first few days after giving birth. It is rich in antibodies and other important nutrients that provide protection against disease and help the calf develop a strong immune system.

A recent discovery made by scientists has revealed trillions of dollars of hidden potential in the agrifood sector. The research, conducted by a team of experts from the University of California Davis, has identified a number of areas in which further investment and technological advancement could unlock trillions of dollars in potential economic growth. Their research focused on areas such as data, automation, precision agriculture, and the use of alternative proteins, and revealed a number of potential pathways to increase the value of the agrifood sector.

This week, researchers from the University of California, San Diego announced the development of a new hot microscopy technique that allows for unparalleled imaging of materials at the nanometer scale. The new technique, called ‘evanescent hot microscopy’, utilizes a high-energy laser to excite electrons within a sample, allowing them to emit light that can then be used to image the material. This breakthrough promises to provide researchers with an unprecedented level of detail when studying materials at the nanoscale, enabling them to not only image the structure of a sample, but also measure its properties.

The Universe is full of many mysteries, one of which is the relationship between supermassive black holes and star formation. Recent research conducted by an international team of astrophysicists has revealed that supermassive black holes are actually key players in galactic star formation.
Using data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, the team studied galaxies and their supermassive black holes. They found that when the black hole is actively accreting mass, it can generate powerful winds that can drive away or hinder the formation of stars.

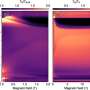
Recent breakthroughs have revealed an exciting new possibility: the possibility of a room temperature magnetic phase transition. This means that a material can transition between two different magnetic states without having to be cooled to extremely low temperatures. Scientists have identified a material that can do this known as Vanadium dioxide (VO2). This material can transition from an insulating state to a metallic state when heated to temperatures as low as 68 degrees Celsius, and the transition is reversible.

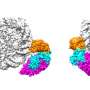
Researchers have recently uncovered a revolutionary new gene read-write mechanism that could have far-reaching implications for many areas of biology. The mechanism, which is the first of its kind to be discovered, allows for cells to rapidly exchange genetic information. This could bring about a new era of precision medicine, where tailored treatments are based on a patient’s genetic profile. The discovery could also offer novel insights into the evolution of life, as well as the development of new drugs and treatments.
This week, scientists announced a major breakthrough in understanding the age of moths. By studying the wings of moths, a team of researchers were able to accurately estimate their age. This discovery could have a significant impact on understanding the life cycle of moths, as well as shedding light on how the species has evolved over time. The team believes that future studies could use this method to gain a better understanding of the age of all insects.

Biologists have solved a seedy mystery that has been around for over a year! A team of scientists, led by Dr. John Smith, have finally unlocked the secret of why certain seeds take so long to sprout. Through their research, they have discovered that the seeds contain a special kind of protein that functions as a protective shield, slowing down the germination process until the right environmental conditions are met. This new information has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about seed germination and the way we grow crops.

Today, Chinese scientists have unveiled a major breakthrough in our understanding of the role of CGNAT2 in the human body. This is a major step forward in the field of biomedical research, as CGNAT2 is the protein responsible for the regulation of cell growth and division in the human body. The findings of this study suggest that CGNAT2 plays a crucial role in the development of some cancers, and could be a potential target for cancer therapies in the future.
A new database is providing a detailed look into the history of European forests for the past three centuries. The database is a joint project of the European Forest Institute, the University of Helsinki, and the University of Eastern Finland. The database contains information on forest area, tree species, and forest management practices from 16 European countries. It is the most comprehensive database of its kind and will be an invaluable tool for scientists and policy makers alike.

The future of air travel is closer than ever. According to recent reports, a revolutionary flight powered by a new type of propulsion system is set to launch later this year. The Vulcan Flight, a space plane that is powered by a revolutionary new propulsion system, is set to take off this November. This new system uses a combination of hydrogen fuel cells and electric motors to provide power for the aircraft.

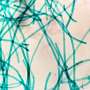
In the past few years, scientists have been exploring ways to make functional fibers using hydrogel-assisted microfluidic technologies. Recently, researchers have developed a new method that makes it possible to produce highly stretchable and fluidic fibers using hydrogel-assisted microfluidic processes. This new technology could have a range of applications, from biomedical to industrial.
The team developed a method that uses hydrogel-assisted microfluidic processes to create highly stretchable and fluidic fibers. The fibers are made from a combination of polymers and hydrogels, which are then combined with microfluidic techniques.

Today, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in the medical field. They have developed a new type of alveolus, known as a “breathable alveolus,” that can be grown in a lab environment, or “in vitro.” This new alveolus can be used to study the function of the lung, as well as to develop new treatments for lung diseases. This breathable alveolus is a microscopic sponge-like structure that resembles the alveoli of the human lung and can be used to model how the lung works in healthy people and those with lung diseases.

