
The ability to control light waves is a key component of optical communication technology. It is also a crucial element of many other fields, such as spectroscopy, imaging, and medical diagnostics. Now, a research team from the University of California, Berkeley, has discovered a new method for controlling light waves that could revolutionize these fields. The method, known as Brillouin-Mandelstam, relies on a special type of vibration called a phonon. Phonons are tiny vibrations that occur in materials, and they can be used to precisely control the properties of light waves.

Today, scientists have discovered something remarkable – a new chromosome! This newly discovered chromosome, known as Chromosome XI, is the first of its kind to be identified in over a century. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about the human genome. Chromosome XI is composed of two distinct parts, an active and a dormant one. The active part of this chromosome contains genes which are responsible for many traits and characteristics such as height, eye color, and various other physical and behavioral traits.

Today, physicists have made a major breakthrough in understanding electrons in 3D crystals. In a recent study, the team of physicists demonstrated that electrons in a three-dimensional crystal can be controlled and manipulated in a previously unseen way. The findings of the study open up exciting possibilities for new materials and technologies.
The team of physicists used a combination of sophisticated computer simulations and theoretical models to study the behavior of electrons in 3D crystals.

Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have made a startling discovery about the behavior of glassy materials. By crumpling sheets of glassy material, they were able to gain insight into the internal mechanism of glassy materials. This discovery could have implications for the design and optimization of materials for a range of applications.
Have you ever wondered what happens when you crumple a sheet of paper or plastic? It may seem like an odd thing to do, but researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have found that crumpling sheets of glassy material can reveal a surprising mechanism at work within the material.

Scientists have made a remarkable discovery about supermassive black holes: they possess incredibly strong magnetic fields. By studying the light from the quasar 3C 279, researchers from The Ohio State University (OSU) were able to measure the magnetic field of a supermassive black hole at the center of a distant galaxy. The researchers found that the magnetic field was 10 million times stronger than the strongest magnetic field ever generated on Earth.

In a groundbreaking new study, scientists have successfully created a synthetic yeast genome in a laboratory. This could have implications for the future of biotechnology and human health. By removing the natural genetic constraints of the yeast, scientists can now manipulate the genome to create new strains of yeast that are more resilient and productive. This could lead to more efficient production of chemicals, proteins, and other useful materials. In addition, the new yeast strains could help scientists better understand the genetic basis of disease and develop new treatments and cures.

In a recent breakthrough, scientists have made progress in the field of quantum biology, bringing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to sharpen the accuracy of quantum models. This new development could have wide-ranging implications for the development of new technologies, such as quantum computing, and could even lead to a better understanding of the fundamental laws of nature. The research team, which included scientists from the University of Minnesota, utilized machine learning algorithms to analyze quantum models and refine their accuracy.
A new study from the University of South Carolina has found that wild harvesting of native plants may be a long-term sustainable solution for managing areas of land. Wild harvesting is a method of collecting plants in their natural state from their native environment, instead of growing them in a managed setting like a farm or garden. The study found that this method may be more beneficial for both the environment and its inhabitants in the long run.

Astronomers have discovered a new globular cluster, NGC 2419, located in the outer fringes of the Milky Way. This cluster is located approximately 300,000 light-years from Earth and is one of the most distant globular clusters known. It is the brightest and most massive globular cluster in the outer halo of the Milky Way, making it an important discovery for astronomers.
Astronomers have made an exciting discovery in the outer fringes of the Milky Way!

Recent research has uncovered a potential new treatment for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Scientists at the University of Birmingham in the UK have discovered that a combination of lipid nanoparticles and antibiotics can be more effective in treating these infections than antibiotics alone. The combination of the two treatments is thought to increase the effectiveness of the antibiotics by increasing the permeability of the bacteria’s cell membrane, allowing the antibiotics to penetrate more effectively.
Astronomers have recently discovered a remarkable new exoplanet - one that orbits two stars instead of one. This exoplanet, located in a polar circumbinary disk, is the first of its kind to be discovered and is an exciting step forward in the exploration of our universe. The researchers believe that this new exoplanet could provide valuable insight into how planets form in binary star systems. Additionally, the planet is thought to be a gas giant, like Jupiter, and is believed to be the first of its kind to be discovered in such a configuration.

Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of medicine, and a recent breakthrough has taken this even further. Researchers have developed an AI system that can mimic intuition, allowing it to make better and faster decisions than human doctors. This AI system can quickly and accurately diagnose conditions and recommend treatments with accuracy levels only seen in experienced medical professionals. This technology has the potential to revolutionize medical care, making access to quality healthcare more equitable and efficient.
Exciting news from the world of astrophysics! NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has successfully detected carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a distant object known as a Centaur! A Centaur is a small, icy body that orbits in the outer reaches of the Solar System. This marks the first time that carbon dioxide has been detected in the atmosphere of a Centaur, and its implications for our understanding of the Solar System are immense.

NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center has recently announced the development of a revolutionary new seismometer array to be placed on the lunar surface. This array, the Gravitational Interferometric Seismometer Array (GISAR), is the first of its kind and will be able to detect faint seismic signals with unprecedented accuracy. GISAR will be deployed on the lunar surface in 2024 and will be able to detect minuscule seismic signals such as those caused by moonquakes, meteorite impacts, and even the faint rumblings of the moon’s core.
Today, scientists are developing a new way to make use of space exploration for the benefit of humanity: space bioprocessing! This new technology will enable the production of recombinant proteins in space, with the potential to drastically reduce the cost and time associated with producing such proteins on Earth. This new method of producing recombinant proteins could have a huge impact on medical research, as it could enable scientists to create proteins that are much more effective and efficient in treating diseases.
Recent advancements in technology have allowed scientists to create metal-enhanced fluorescence probes, which can be used to detect the presence of the influenza virus. These probes are incredibly sensitive and can detect even virus particles present in parts per trillion. This is a remarkable breakthrough, as it allows for earlier detection of the virus, giving people a better chance of preventing its spread. Furthermore, the probes are environmentally friendly and can be used multiple times without losing sensitivity.

In a new study, researchers have created a machine learning algorithm that can provide unique insights into the magnitude of biodiversity loss over the past century. The algorithm, developed by a team of scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, can analyze vast amounts of data to accurately predict changes in biodiversity over time. The team’s findings, recently published in the journal Nature, suggest that global biodiversity has declined by an average of 3.

Have you ever wanted a sneak peek into the depths of the universe? Now, with the help of the Euclid space telescope, we’re getting our first glimpses of the “Galactic Zoo.” Euclid has recently released its first images of distant galaxies, providing us with a tantalizing look into the unknown. These images show us the beauty and complexity of the universe, and will help scientists gain a better understanding of the evolution of galaxies.

Climate change is a serious problem, and researchers are looking for new ways to combat its effects. Recently, scientists have discovered a new type of fungus hybrid that may be able to help fight the climate crisis. These hybrid fungi are able to take up and store large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This could have a significant impact on reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the environment and mitigating the effects of climate change.

A recent study published in the journal Nature Communications has revealed a new strategy for conservation of bird populations in the face of global climate change: the establishment of local buffers. The study found that if local habitats are managed to promote the stability of bird populations, this “buffer” can help protect them from the effects of climate change. This strategy could be especially effective in regions where birds are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, such as mountain regions or areas with seasonal weather fluctuations.

A recent study has revealed that photorespiration, a process in plants that reduces their photosynthetic efficiency and can lead to low crop yields, is more sensitive to environmental fluctuations than previously thought. The research, published in Nature Communications, provides an explanation for why photorespiration can be a greater threat to plant productivity in changing climatic conditions.
Climate change is threatening the productivity of crops around the world, making it increasingly important to understand the effects of fluctuating environmental conditions on plants.

In exciting news, scientists have developed a new type of lab-made catalyst that could drastically reduce the amount of difficult-to-remove greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. This new catalyst is made up of a combination of copper, iron, and nitrogen, and is capable of breaking down greenhouse gases like methane and ethylene into carbon dioxide and water. This could be an invaluable tool in the fight against climate change, as it could potentially reduce the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere by up to 50%.
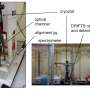
Recently, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley have made a breakthrough in the study of single molecule Raman spectroscopy. They have created an optical-electrically driven single molecule Raman spectroscopy device that is able to detect extremely small amounts of molecules. This device is a major advancement in the field, as it is able to perform single molecule Raman spectroscopy with unprecedented resolution and sensitivity. This new device could be used to study the properties of molecules and their interactions with other molecules on a level never before seen.
Today, scientists have developed a new method to inhibit cholera infection, an intestinal infection caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Cholera is a major cause of death and disease in many parts of the world, especially in developing countries. Researchers at the University of Queensland in Australia have identified a compound that can reduce the amount of cholera bacteria in infected cells. This compound, which is derived from natural products, has the potential to be used as a therapeutic drug to treat cholera and other infections caused by Vibrio cholerae.

A groundbreaking new method has been developed to produce nanosized vaterite particles without the use of organic solvents. This method, developed by a team of researchers from the University of L’Aquila in Italy, is a major step forward in the production of nanomaterials, and could have far-reaching implications for the development of more efficient and environmentally-friendly manufacturing processes. The team was able to successfully create nanosized vaterite particles without the use of organic solvents by using a novel combination of techniques, including sonication, temperature control and pH adjustment.

