In a new breakthrough in crop science, researchers have developed a way to genetically modify rice to produce silicon instead of grain. This could have a major impact on global food production and sustainability. The silicon-producing rice is the result of years of research and engineering, and could have a significant impact on nutrition and poverty reduction. This new technology offers the potential to increase rice production and reduce the impact of global warming.
We’ve all heard the horror stories of asteroids hitting Earth and the devastating destruction they can cause. But thanks to a new breakthrough, we now have a better chance of keeping our planet safe from these space rocks. According to a recent study published in the journal Nature Astronomy, scientists have discovered a way to identify and track asteroids that have an especially high risk of impacting Earth. This is a major development that could help us avert potential disasters in the future.

Today marks an exciting breakthrough in the field of particle physics! Scientists have successfully created an electron-optimized MoS2 monolayer that has the potential to revolutionize the way we look at nanoelectronics and computing. This new MoS2 monolayer is composed of a single layer of molybdenum and sulfur, and is only 3 atoms thick. This is incredibly thin for a material, allowing for unprecedented control over its physical and electronic properties. The potential applications of this new material range from the development of ultra-tiny transistors to enhanced energy transfer in photovoltaics.
A team of researchers have developed a proof-of-concept device that can separate seawater molecules, potentially opening up a new way to improve the efficiency of desalination. The device, which is based on a nanostructured membrane, was tested in lab settings and showed promising results. In the experiment, seawater was introduced to the membrane, where it was then separated into ions and molecules. The ions could be easily collected, while the molecules were left on the other side of the membrane.

A team of researchers from the University of California San Diego have developed a new method that reveals how bacteria interact with their hosts during metabolism. This new method, called Metabolism-Bacteria Interaction (MBI), uses mass spectrometry to measure the metabolites of bacterial organisms in the presence of their hosts. This provides insights into the metabolic functions of bacteria, which can help researchers understand how these organisms interact with their hosts and how they affect their hosts’ health.
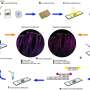
Recent medical advances have made it possible to detect uric acid levels in a patient’s body without the need for invasive methods. A team of researchers has developed a new set of sensors that are capable of accurately measuring the uric acid levels of a patient, simply by analyzing the sweat on their skin. This noninvasive method of monitoring uric acid levels could revolutionize the way doctors diagnose and treat disorders such as gout, kidney stones, and metabolic syndromes.

In a new study, researchers have identified a new type of superbug: hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. This strain of bacteria is resistant to the widely used carbapenem antibiotic, which is used to treat a wide range of infections. Klebsiella pneumoniae is a gram-negative bacteria, which is increasingly becoming resistant to antibiotics. In the past few years, this superbug has caused severe infections in healthcare settings, leading to increased rates of hospital readmissions and mortality due to its hypervirulence.
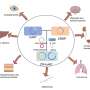
A new discovery by researchers at the University of New South Wales could revolutionize the way drugs are delivered to treat brain disorders. The team has created a new thyroxine derivative which can act as a “carrier molecule” to deliver drugs to the brain more efficiently. This new derivative is a modified form of the naturally occurring hormone thyroxine, and it has the potential to transport drugs directly into the brain without crossing the blood-brain barrier.
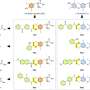
Quantum sensors are being developed to revolutionize the way we measure the world around us. Recently, researchers have identified a major obstacle to the successful development of quantum sensors: the presence of an unavoidable type of noise known as “1/f noise.” This noise can impact the accuracy of measurements and limit the range of applications where quantum sensing is possible. In order to overcome this obstacle, researchers are focusing on ways to reduce or eliminate 1/f noise from quantum sensors.
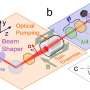
A scientific paper that suggested a room temperature superconductor has been retracted from the journal Nature. The paper, published in 2019, described a material based on hydrogen, sulfur, and carbon that could operate as a superconductor at temperatures as high as 58°F (15°C).
Recently, the authors of the paper retracted it, after the results could not be reproduced. This is a major setback for research into room temperature superconductors, as scientists had hoped that this paper would bring them closer to achieving this goal.

Today, scientists have made a major breakthrough in the field of sustainable wood production. By using extracellular vesicles (EVs) to capture and store wood, scientists have developed a way to make wood production more sustainable. EVs are tiny bubbles that are naturally produced by cells and can be used to capture and store wood, meaning that wood harvested from forests can be replaced with a more sustainable source. This method of capturing and storing wood could help reduce deforestation and the degradation of forest habitats.
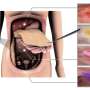
Recently, researchers have made strides in creating self-assembling nanosheets that can be used to create sustainable nanotechnology. These nanosheets, made of two-dimensional materials, are capable of forming into any shape and size desired. This new technology could revolutionize the way we create, use, and reuse materials, allowing us to create sustainable products with less waste. The technology also promises to make nanotechnology more accessible than ever before, with its ability to scale down to nano-level sizes.

SpaceX is gearing up for a historic launch from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at Cape Canaveral this Thursday! The Falcon 9 rocket will be carrying a Crew Dragon capsule, with four astronauts on board, to the International Space Station, marking the first time SpaceX has done a human mission to space from the iconic launchpad. This will be the first launch of a crewed mission from the US in almost a decade, and is a huge milestone for SpaceX, as well as for the space exploration industry as a whole.

Researchers from the University of Toronto have recently developed a revolutionary new method of drug delivery using nanoparticles. These nanoparticles, when triggered by the drug naloxone, can deliver a drug payload in a blue light-triggered system. This new system could revolutionize drug delivery, eliminating the need for injections or oral medications. The team believes that this new system could improve drug efficacy and reduce the side effects associated with traditional drug delivery methods.
An exciting new study has just been released that sheds light on the evolution of lice, and the findings are remarkable. Researchers have used advanced genetic analysis to determine that the evolution of lice has mirrored the evolution of their hosts - humans. The study, which was published in Science Advances, found that the lice have evolved in almost perfect tandem with humans, with the same genetic changes and mutations in both species.

In a groundbreaking study, researchers at the University of Cambridge have developed a new form of broadband communication based on water and air. This technology, known as ‘Acoustic Broadband’, is capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 100 times faster than currently available wireless systems, and could revolutionise the way we communicate with each other.
The team behind the project believe that Acoustic Broadband offers a viable alternative to traditional wireless communication systems, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, as it is capable of transferring large amounts of data over very long distances without any interference.
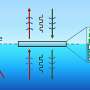
Scientists have developed a new type of magnetic shielding for particle detectors, which is capable of protecting them from powerful magnetic fields and allowing them to detect even the tiniest particles. This new type of shielding, developed by researchers at the University of Tokyo, uses a combination of ferromagnetic and non-magnetic materials to create a “scalable, force-free magnetic shield.” The shield is designed to keep out harmful magnetic fields, while still allowing the detector to detect the smallest of particles.
A new study published in the journal Science has revealed an incredible discovery: animals with stripes may have evolved this feature to help them survive in their environment. The research, conducted by scientists from the University of Cambridge, suggests that the presence of stripes can give animals an advantage, particularly in avoiding predation. The stripes may act as a form of camouflage, making the animals less visible to predators, or they may be used to make the animals more visible to other animals in the same species.

Recent research has revealed that school-based law enforcement officers may not be as effective as previously thought in making schools safer. In a study published in the journal Criminology & Public Policy, researchers from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte found that the presence of school-based law enforcement officers had no effect on the number of school-related violent incidents.
This study challenges the assumption that school-based law enforcement officers are essential to keeping schools safe.

In a recent breakthrough discovery, researchers have found that willow bark has a broad-spectrum antiviral effect. This discovery is especially important due to the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The antiviral properties of willow bark have long been known, but this new research has shown that it has the potential to fight a wide range of viruses, including the common cold, influenza, and even the human papillomavirus. This new research gives hope for a natural alternative to treating viral infections, which could help reduce the use of antibiotics and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.

Scientists from the University of Groningen have just revealed a new method of eavesdropping on electrons! By using a type of microscope called an atomic force microscope, scientists can now detect the magnetic fields around individual electrons, allowing them to measure the noise emitted by the electrons as they interact with their environment. This is an exciting breakthrough, as it could potentially provide new insights into the behavior of electrons, allowing us to better understand how they interact with their surroundings.

Recent research has revealed that there are many genetic links between crops and livestock that have been hard-to-spot until now. Scientists at the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) have discovered that some plants have evolved to be able to detect the presence of livestock, and respond accordingly. They have found that certain plants have developed traits that make them more attractive to livestock, such as sweet foliage or a strong aroma.
In a groundbreaking research project, Professor of Philosophy and Physics at the University of Cambridge, Dr. Ian Wilson has uncovered the hidden links between philosophy and physics. By combining the two disciplines, Dr. Wilson has opened a fascinating new area of exploration. In an exclusive Q&A with Phys.org, Dr. Wilson explains his innovative approach to understanding the universe and how his research could change the way we think about physics.

In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Astronomy, an international team of astrophysicists have discovered a link between the formation of dwarf galaxies and the formation of stars. The team used powerful telescopes to identify the faintest stars in the sky and trace their origins. They found that some of the stars were formed in dwarf galaxies before they were pulled away by the gravitational pull of larger galaxies. This finding could provide a greater understanding of how galaxies form and evolve over time.

A team of scientists from Texas A&M University recently announced the development of a groundbreaking new technology that will help to document the diversity of bird species. The 3D scanning technology will allow researchers to capture the size, shape, and color of different bird species with unprecedented accuracy. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of ornithology and provide a comprehensive view of bird diversity across the world. With this new tool, researchers will be able to gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary relationships among different bird species and how they have changed over time.

