
A recent breakthrough in plant genetics research could have far-reaching effects on the agricultural industry. Scientists at the University of Göttingen in Germany have successfully demonstrated pollen-mediated gene transfer in the plant species camelina. This method of gene transfer uses pollen from one plant to transfer genetic material to another, allowing researchers to introduce new traits to plants without the need for genetic engineering. The research team, led by Professor Georg Jander, used the technique to introduce a gene for cleistogamy—the ability of a plant to self-pollinate—to camelina plants.

A new virus has been discovered that could be a powerful tool in the fight against germs. Scientists have identified a new virus, called virophage, that is capable of infecting and killing germs. This discovery could provide a much-needed source of ammunition in the battle against germs that are becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics. The virus, which was discovered in a water sample taken from the Caribbean Sea, is able to infect and kill bacteria without harming other organisms in the sample.

Today, a breakthrough in laser pulse compression technology has been announced by researchers at the University of Oxford. By combining a density gradient with laser pulse compression, they have developed a way to compress high-intensity laser pulses to much shorter duration while maintaining their peak power. This new technique could have far-reaching implications for lasers used in applications such as ultrafast spectroscopy and strong-field physics. The team has demonstrated that the peak power of a laser pulse can be increased by a factor of 5 compared to conventional laser pulse compression techniques.

The microbial world that exists within and around us is a largely unexplored, yet incredibly important, aspect of our lives. Recent advancements in research have shown that the microbiomes of humans, animals, and the environment impact our overall health and sustainability. In a new study, researchers have outlined the ways that microbiomes can be used to improve our health and ensure sustainable development.
The findings, published in the journal Nature, suggest that harnessing the power of microbiomes could be a key factor in achieving a more sustainable future.
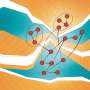
A recent study conducted at the University of Florida has uncovered a new and exciting way to decode the genetics of ascorbic acid. The research team, led by Dr. Ankur Sharma, used a combination of techniques to examine the genetic processes that control the production of ascorbic acid in plants. The results of the study revealed that the production of ascorbic acid in plants is regulated by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
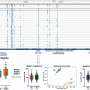
Scientists have just made a fascinating discovery about how certain fungi are able to survive in extreme hypersaline environments. By studying the structure of certain species of filamentous fungi, scientists have uncovered the secret to their survival in environments with extremely high salt concentrations. The research has implications for understanding the limits of life in extreme environments, and could potentially be applied to biotechnology.
The study, published in Nature Communications, focuses on two species of filamentous fungi, Acremonium halotolerans and Acremonium strictum, that can survive in environments with salt concentrations up to ten times higher than that of seawater.
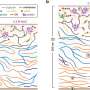
In a recent breakthrough, scientists have discovered an unexpected way to create a new type of polymer-based semiconductor. This new material could revolutionize the way we think about electronics, potentially leading to faster, cheaper, and more energy-efficient devices. The new material is created by combining two different types of polymers in a specific way, resulting in a semiconductor that has properties similar to traditional silicon-based semiconductors. By combining these two polymers, scientists have been able to create a semiconductor with higher levels of conductivity, which could lead to improved performance of devices such as transistors, LEDs, and solar cells.

Have you ever wondered how sugar affects cell biology? Well, researchers have recently discovered a new type of sugar that could have a dark side when it comes to cellular health. This sugar, known as galactosylceramide, is found in the membranes of many cells throughout the body, and it could be linked to some serious health problems. To better understand how this sugar works, researchers are studying the effects of galactosylceramide on cell growth, death, and metabolism.

In a new study, scientists have unveiled the tale of proteins that govern the clockwork of fundamental crops. Led by the Institute of Plant Sciences at ETH Zurich, the researchers developed a comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanism that controls the flowering time of plants. By unlocking this insight, they have created the potential to improve the yield and quality of a variety of crops.
The research team discovered that the flowering time of plants is regulated by a complex network of proteins, which interact with each other to determine when a plant will flower.

We are on the cusp of a revolution in microscopy, with the power to make the invisible visible. Scientists have developed a new kind of microscope that is capable of imaging the nanoscale world with unprecedented clarity and resolution. This microscope, known as a super-resolution microscope, combines several techniques to break through the diffraction limit of traditional optical microscopes and reveal details that were previously invisible. The new technology promises to revolutionize the field of microscopy and open up exciting new possibilities in science, medicine, and industry.

A new tool developed by researchers at the University of Oxford could revolutionize how scientists track animal populations. The tool, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) and computer vision algorithms, can quickly and accurately detect and identify animals in images and videos with minimal human input. The tool has the potential to vastly improve the speed and accuracy of tracking animal populations, helping scientists better understand animal behavior and ecology. With this tool, researchers can now more effectively monitor and analyze animal populations, resulting in improved conservation and management strategies.
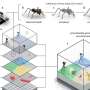
Recently, a new piece of evidence has been revealed that suggests GM crops could be an effective way of tackling climate change and food insecurity in the UK. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, found that introducing GM crops to the UK would lead to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and increased food production. The study also showed that GM crops could use fewer resources, such as water and fertilisers, while still producing the same amount of food.

Recently, a groundbreaking study conducted by researchers at the University of California, Irvine has revealed a new way of inducing cell death through a process known as ferroptosis. By using nanoparticles made of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to stabilize the drug Lipiodol, the scientists were able to induce cell death in a more targeted and efficient way than ever before. This method of inducing ferroptosis has the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment, as it allows for more targeted and effective therapy with fewer side effects.
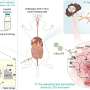
In a new study, scientists have discovered a protein in ice that could be used to create new treatments for fungal infections. The protein, called ATX-1, was found to be effective in killing various species of fungi, including some responsible for causing infections in humans. The team hopes that this discovery could lead to the development of novel antifungal treatments that are more effective than current therapies. Furthermore, the protein could be used to create new vaccines, allowing us to better protect ourselves against fungal infections.

On November 16, 2023, the space shuttle Endeavour launched successfully from Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida. This historic mission marks the first time a space shuttle has successfully launched in more than a decade. The mission is a collaboration between the United States, Russia, and China, three of the leading countries in space exploration. This will be a major milestone in space exploration, and a huge step forward for international cooperation.

AI is revolutionizing the way we produce oxygen. In a recent breakthrough, scientists have used AI to create a new catalyst that can produce oxygen more efficiently and cost-effectively than ever before. This new catalyst is made of a combination of elements, and its design was created with the help of AI algorithms. The catalyst is capable of producing oxygen from carbon dioxide, water, and energy. This breakthrough could have a significant impact on our ability to produce oxygen on a large scale, which could have positive implications for many industries, including energy, healthcare, and food production.

AI-based intervention is the new wave of the future for helping undergraduate students succeed in the STEM fields. A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Notre Dame found that an AI-based intervention program was able to reduce the dropout rate for undergrads in STEM courses by an impressive 20%. The AI-based intervention works by leveraging machine learning algorithms to track student progress and provide personalized feedback. This feedback is tailored to the individual student and helps them to identify areas of improvement and develop a personalized learning plan.

Tiny but mighty, the Big ALICE accelerator at CERN recently restarted operations, sending beams of ions around its 17-kilometer circumference. Big ALICE is a proton-proton collider that accelerates and collides heavy ions, producing temperatures more than 100,000 times hotter than the center of the Sun. The collider has been dormant in recent years, but researchers are now using it to investigate the properties of the quark-gluon plasma, a primordial state of matter that existed in the early Universe.

Recently, a team of paleontologists made an exciting discovery in the Gobi desert in Mongolia - a fossilized dinosaur egg with a leathery shell! This is the first time a fossilized egg with a leathery shell has been found, and it is believed to be between 70 and 90 million years old. This discovery sheds new light on the evolution of egg-laying in dinosaurs, and offers insight into the behavior of some of the earliest animals to walk the earth.

For years, scientists have been searching for a way to overcome the limitations of traditional cooling strategies for high temperature electronics. Now, an international team of researchers has made a breakthrough that could revolutionize the field. By using a new thermal control approach, they have demonstrated a way to enable cooling strategies that were previously impossible. This breakthrough could lead to an array of new possibilities for cooling high temperature electronics and could even be used in the deployment of electronic systems in harsh environmental conditions.
Today, China announced that it had successfully launched a spacecraft to Mars which will collect surface samples from the Red Planet and bring them back to Earth for further study. This is an exciting project for the Chinese space program and the first of its kind in the world. Scientists hope to gain valuable insight into the origin and evolution of Mars, as well as to learn more about the possibility of life on the planet.

Today, an international research team has developed a modular customization strategy that allows them to create defect-free metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with superior properties for use in a range of applications. MOFs are a type of crystalline material composed of metal ions and organic linkers, and they are prized for their large surface areas and potential applications in gas storage, separations, and catalysis. However, creating defect-free MOFs has been a challenge due to the complexity of the syntheses.

Scientists have just made a groundbreaking discovery: a secondary black hole embedded in an emission nebula! Using data from the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers were able to detect the black hole, which is part of a binary system located in the constellation Cygnus. This is an exciting development in the study of binary black hole systems, and could lead to more discoveries about the formation and evolution of these enigmatic objects.

The European Space Agency (ESA) has revealed plans for a revolutionary new modular rover that will be capable of carrying out a range of scientific experiments on the Moon and other planetary surfaces. The rover, dubbed “MULTIPURPOSE”, will be designed to be flexible, allowing it to be adapted and configured for a variety of tasks and payloads. It will be able to traverse a range of terrain, including rocky surfaces, sand dunes, and ice, and will be equipped with a suite of instruments to enable it to carry out a range of science experiments.

The evolution of taste is an ongoing process, and a recent study has revealed new insight into the evolution of one particular type of taste receptor. Researchers from the University of Massachusetts Medical School and the University of Hawaii have discovered that a bitter taste receptor in sharks evolved from a receptor that was previously used to detect changes in water pressure. This adaptation is believed to be an evolutionary response to the changing ocean environment and an important factor in the survival of sharks.

